一、ThreadLocal基本使用
1.1使用场景
不同的线程对全局变量进行修改,使用ThreadLocal后会为每个线程创建一个副本,而不会影响其他线程的副本,确保了线程的安全
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> localvariable=ThreadLocal.withInitial(()->1); public static void main(String[] args) { Thread threadOne=new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Integer integer = localvariable.get(); localvariable.set(++integer); System.out.println("线程1: "+localvariable.get()); } }); Thread threadTwo=new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("线程2: "+localvariable.get()); } }); System.out.println("主线程: "+localvariable.get()); threadOne.start(); threadTwo.start(); }
运行结果:
主线程: 1
线程1: 2
线程2: 1
线程1的修改没有影响到线程2的读取,保证了线程的安全
场景二
类似于全局变量,但是不想被多个线程进行共享
private static Integer count=0; private static ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(count); } }; fixedThreadPool.execute(runnable); } count++; }
像如上代码,本来是想所有线程都输出初始的count,当主线程累加后,剩下的线程输出的值就变成了1
以上代码执行的结果:
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
那么我们可以用ThreadLocal将原始的全局变量进行保存然后传参给其他的线程,这样就获取的是原始的全局变量
private static Integer count=0; private static ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); private static ThreadLocal<Integer> local=new ThreadLocal(); public static void main(String[] args) { local.set(count); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Integer localCount = local.get(); Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(localCount); } }; fixedThreadPool.execute(runnable); } count++; }
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1.2 原理分析
threadLocals = null; inheritableThreadLocals = null;
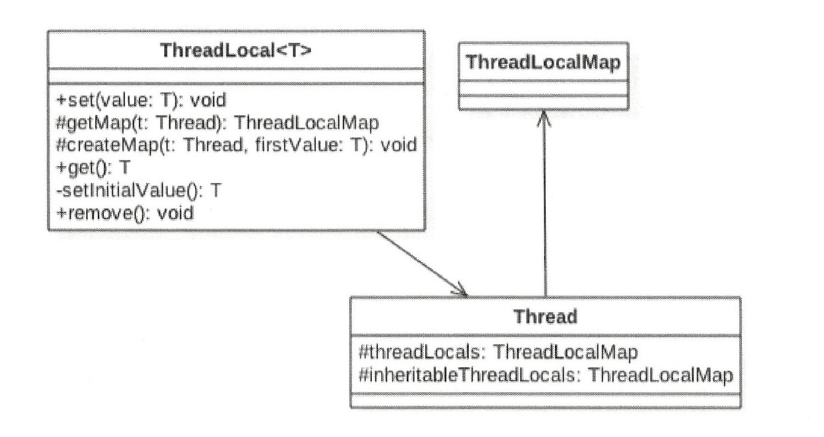
Thread类中有一个threadLocals和一个inheritableThreadLocals,他们都是ThreadLocalMap 类型的变量,默认都为null
当第一次调用set方法的时候创建
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); }
将每个线程的本地变量存放在threadLocals变量中,如果调用线程一直不终止,那么这个本地变量会一直存放在调用线程的ThreadLocals变量里面,所以当不使用本地变量是可以通过调用ThreadLocal变量的remove方法,从当前线程的threadLocals
里面删除该本地变量。
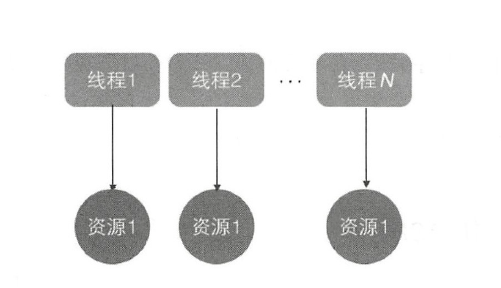
ThreadLocal 是JDK 包提供的,它提供了线程本地变量,也就是如果你创建了一个
ThreadLocal 变量,那么访问这个变量的每个线程都会有这个变量的一个本地副本。当多
个线程操作这个变量时,实际操作的是自己本地内存里面的变量,从而避免了线程安全问
题