No1:模块
var greet = require('./hello');
var s = 'Michael';
greet(s);
var s = 'Hello';
function greet(name){
console.log(s+','+name+'!')
}
module.exports = greet;
一个模块想要对外暴露变量(函数也是变量),可以用module.exports = variable;,一个模块要引用其他模块暴露的变量,用var ref = require('module_name');就拿到了引用模块的变量。
Node利用JavaScript的函数式编程的特性,轻而易举地实现了模块的隔离
No2:
JavaScript程序是由事件驱动执行的单线程模型,Node.js也不例外
process.nextTick(function(){
console.log('nextTick callback');
});
process.on('exit',function(code){
console.log('about to exit with code: ' + code);
});
console.log('nextTick was set');
结果
nextTick was set
nextTick callback
about to exit with code: 0
process也是Node.js提供的一个对象,它代表当前Node.js进程
No3:
fs--文件系统模块,负责读写文件
异步读取文件中的字符串
var fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('sample.txt','utf-8',function(err,data){
if(err) {
console.log(err);
}else{
console.log(data)
}
});
同步读取文件
var fs = require('fs');
var data = fs.readFileSync('sample.txt','utf-8');
console.log(data)
异步写入文件
var fs = require('fs')
var data = 'Hello,Node.js';
fs.writeFile('output.txt',data,function(err){
if(err){
console.log(err);
}else{
console.log('ok.');
}
});
同步写入文件
var fs = require('fs');
var data = 'Hello,Node.js';
fs.writeFileSync('output.txt',data);
获取文件的详细信息
var fs = require('fs');
fs.stat('sample.txt',function(err,stat){
if(err){
console.log(err);
}else{
//是否是文件
console.log('isFile:'+stat.isFile());
//是否是目录
console.log('isDirectory:'+stat.isDirectory());
if(stat.isFile()){
//文件大小
console.log('size:'+stat.size);
//创建时间,Data对象
console.log('birth time:'+stat.birthtime);
//修改时间,Data对象
console.log('modified time:'+stat.mtime);
}
}
});
No4:
stream--流
读取文件
var fs = require('fs')
var rs = fs.createReadStream('sample.txt','utf-8')
rs.on('data',function(chunk){
console.log('DATA:')
console.log(chunk);
});
rs.on('end',function(){
console.log('END');
});
rs.on('error',function(err){
console.log('ERROR:'+err);
});
写入文件
var fs = require('fs')
var ws1 = fs.createWriteStream('output1.txt','utf-8');
ws1.write('使用Stream写入文本数据...
');
ws1.write('END');
ws1.end();
var ws2 = fs.createWriteStream('output2.txt');
ws2.write(new Buffer('使用Stream写入二进制...
','utf-8'));
ws2.write(new Buffer('END.','utf-8'));
ws2.end();
复制文件
var fs = require('fs');
var rs = fs.createReadStream('sample.txt');
var ws = fs.createWriteStream('copied.txt');
rs.pipe(ws);
No5:
http
服务器:
var http = require('http');
var server = http.createServer(function(request,response){
console.log(request.method+':'+request.url);
response.writeHead(200,{'Content-Type':'text/html'});
response.end('<h1>Hello world!</h1>');
});
server.listen(8080);
console.log('Server is running at http://127.0.0.1:8080/');
效果
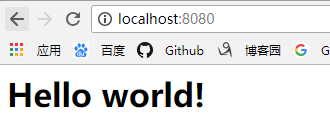
文件服务器
var
fs = require('fs'),
url = require('url'),
path = require('path'),
http = require('http');
var root = path.resolve(process.argv[2] || '.');
console.log('Static root dir: '+root);
var server = http.createServer(function(request,response){
var pathname = url.parse(request.url).pathname;
var filepath = path.join(root,pathname);
fs.stat(filepath,function(err,stats){
if(!err && stats.isFile()){
console.log('200'+request.url);
response.writeHead(200);
fs.createReadStream(filepath).pipe(response);
}else{
console.log('404',request.url);
response.writeHead(404);
response.end('404 Not Found');
}
});
});
server.listen(8080);
console.log('Server is running at http://127.0.0.1:8080/');


效果
No6:
加密
const crypto = require('crypto');
const hash = crypto.createHash('md5');
// const hash = crypto.createHash('sha1');
hash.update('Hello,world!');
hash.update('Hello,nodejs!');
console.log(hash.digest('hex'));
const crypto = require('crypto');
const hmac = crypto.createHmac('sha256','secret-key');
hmac.update('Hello,world!');
hmac.update('Hello,nodejs!');
console.log(hmac.digest('hex'));
对称加密
const crypto = require('crypto');
function aesEncrypt(data,key){
const cipher = crypto.createCipher('aes192',key);
var crypted = cipher.update(data,'utf8','hex');
crypted += cipher.final('hex');
return crypted;
}
function aesDecrypt(encrypted,key){
const decipher = crypto.createDecipher('aes192',key);
var decrypted = decipher.update(encrypted,'hex','utf8');
decrypted += decipher.final('utf8');
return decrypted;
}
var data = 'Hello,this is a secret message!';
var key = 'Password!';
var encrypted = aesEncrypt(data,key);
var decrypted = aesDecrypt(encrypted,key);
console.log('Plain text: '+data);
console.log('Encrypted text: '+encrypted);
console.log('Decrypted text:'+decrypted);
No7:
Koa
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async(ctx,next)=>{
await next();
ctx.response.type = 'text/html';
ctx.response.body = '<h1>Hello,koa2!</h1>';
});
app.listen(3000);
console.log('app started at port 3000...');
koa把很多async函数组成一个处理链,每个async函数都可以做一些自己的事情,然后用await next()来调用下一个async函数。我们把每个async函数称为middleware,这些middleware可以组合起来,完成很多有用的功能。
app.use(async(ctx,next)=>{
console.log('${ctx.request.method} ${ctx.request.url}');
await next();
});
app.use(async(ctx,next)=>{
const start = new Date().getTime();
await next();
const ms = new Date().getTime() - start;
console.log('Time:${ms}ms');
});
app.use(async(ctx,next)=>{
await next();
ctx.response.type='text/html';
ctx.response.body='<h1>Hello,koa2!</h1>';
});
No8:
koa-router
get请求
const Koa = require('koa');
const router = require('koa-router')();
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async(ctx,next)=>{
console.log(`Process ${ctx.request.method} ${ctx.request.url}...`);
await next();
});
router.get('/hello/:name',async(ctx,next)=>{
var name = ctx.params.name;
ctx.response.body = `<h1>Hello, ${name}!</h1>`;
});
router.get('/',async(ctx,next)=>{
ctx.response.body = '<h1>Index</h1>';
});
app.use(router.routes());
app.listen(3000);
console.log('app started at port 3000...');
post请求
const Koa = require('koa');
const router = require('koa-router')();
const bodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async(ctx,next)=>{
console.log(`Process ${ctx.request.method} ${ctx.request.url}...`);
await next();
});
app.use(bodyParser());
router.get('/',async(ctx,next)=>{
ctx.response.body = `<h1>Index</h1>
<form action="/signin" method="post">
<p>Name:<input name="name" value="koa"</p>
<p>Password:<input name="password" type="password"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="Submit"></p>
</form>`;
});
router.post('/signin',async(ctx,next)=>{
var name = ctx.request.body.name || '',
password = ctx.request.body.password || '';
console.log(`signin with name:${name},password:${password}`);
if(name==='koa' && password==='12345'){
ctx.response.body=`<h1>Welcome,${name}!</h1>`;
}else{
ctx.response.body=`<h1>Loginfailed!</h1>
<p><a href="/">Try again</a></p>`;
}
});
app.use(router.routes());
app.listen(3000);
console.log('app started at port 3000...');
效果图
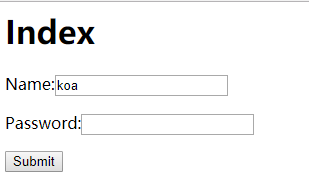


No9:
koa-router
小型工程https://github.com/michaelliao/learn-javascript/tree/master/samples/node/web/koa/url2-koa
No10:
Nunjucks:模板引擎
小型工程https://github.com/michaelliao/learn-javascript/tree/master/samples/node/web/koa/use-nunjucks
No11:
单元测试
module.exports=function(...rest){
var sum = 0;
for(let n of rest){
sum+=n;
}
return sum;
}
const assert = require('assert');
const sum = require('./hello');
assert.strictEqual(sum(),0);
assert.strictEqual(sum(1),0);
assert.strictEqual(sum(1,2),3);
assert.strictEqual(sum(1,2,3),6);
const assert = require('assert');
const sum = require('../hello');
describe('#hello.js', () => {
describe('#sum()', () => {
before(function () {
console.log('before:');
});
after(function () {
console.log('after.');
});
beforeEach(function () {
console.log(' beforeEach:');
});
afterEach(function () {
console.log(' afterEach.');
});
it('sum() should return 0', () => {
assert.strictEqual(sum(), 0);
});
it('sum(1) should return 1', () => {
assert.strictEqual(sum(1), 1);
});
it('sum(1, 2) should return 3', () => {
assert.strictEqual(sum(1, 2), 3);
});
it('sum(1, 2, 3) should return 6', () => {
assert.strictEqual(sum(1, 2, 3), 6);
});
});
});
异步测试
const fs = require('mz/fs');
// a simple async function:
module.exports = async () => {
let expression = await fs.readFile('./data.txt', 'utf-8');
let fn = new Function('return ' + expression);
let r = fn();
console.log(`Calculate: ${expression} = ${r}`);
return r;
};
const assert = require('assert');
const hello=require('../hello');
describe('#async hello',()=>{
describe('#asyncCalculate()',()=>{
it('#async with done',(done)=>{
(async function(){
try {
let r = await hello();
assert.strictEqual(r,15);
done();
} catch (err) {
done(err);
}
})();
});
it('#async function',async()=>{
let r = await hello();
assert.strictEqual(r,15);
});
it('#sync function',()=>{
assert(true);
});
});
});
No12:
为什么WebSocket连接可以实现全双工通信而HTTP连接不行呢?实际上HTTP协议是建立在TCP协议之上的,TCP协议本身就实现了全双工通信,但是HTTP协议的请求-应答机制限制了全双工通信。WebSocket连接建立以后,其实只是简单规定了一下:接下来,咱们通信就不使用HTTP协议了,直接互相发数据吧。
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const WebSocketServer = WebSocket.Server;
const wss = new WebSocketServer({
port: 3000
});
wss.on('connection',function(ws){
console.log(`[SERVER] connection`);
ws.on('message',function(message){
console.log(`[SERVER] Received: ${message}`);
setTimeout(()=>{
ws.send(`What's your name?`,(err)=>{
if(err){
console.log(`[SERVER] error:${err}`);
}
});
});
})
});
console.log('ws server started at port 3000...');
let count = 0;
let ws = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:3000/ws/chat');
ws.on('open',function(){
console.log(`[CLIENT] open()`);
ws.send('Hello!');
});
ws.on('message',function(message){
console.log(`[CLIENT] Received: ${message}`);
count++;
if(count>3){
ws.send('Goodbye!');
ws.close();
}else{
setTimeout(()=>{
ws.send(`Hello,I'm Mr No.${count}!`);
});
}
});
效果
ws server started at port 3000...
app.js:23
[SERVER] connection
app.js:10
[CLIENT] open()
app.js:30
[SERVER] Received: Hello!
app.js:12
[CLIENT] Received: What's your name?
app.js:35
[SERVER] Received: Hello,I'm Mr No.1!
app.js:12
[CLIENT] Received: What's your name?
app.js:35
[SERVER] Received: Hello,I'm Mr No.2!
app.js:12
[CLIENT] Received: What's your name?
app.js:35
[SERVER] Received: Hello,I'm Mr No.3!
app.js:12
[CLIENT] Received: What's your name?
app.js:35
[SERVER] Received: Goodbye!
app.js:12
[SERVER] error:Error: not opened
欢迎关注我的微信公众号:安卓圈
