1、数据
# 导入pyplot模块 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 初始化figure fig = plt.figure() # 创建数据 x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] y = [1, 3, 4, 2, 5, 8, 6]
2、大图
接着,绘制大图。首先确定大图左下角的位置以及宽高:
left, bottom, width, height = 0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8
注意,4个值都是占整个figure坐标系的百分比。在这里,假设figure的大小是10x10,那么大图就被包含在由(1, 1)开始,宽8,高8的坐标系内。
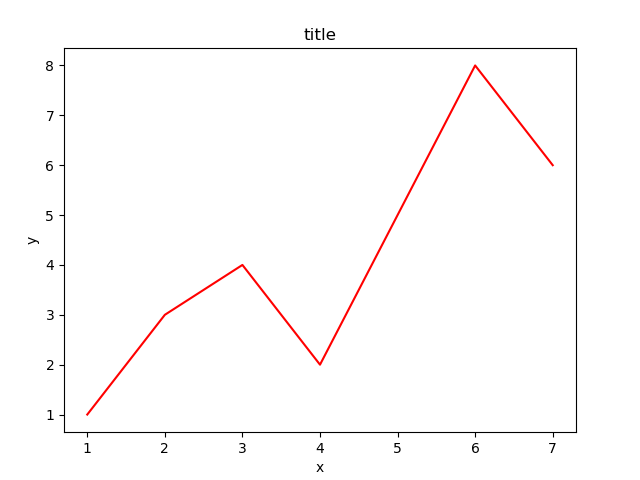
将大图坐标系添加到figure中,颜色为r(red),取名为title:
ax1 = fig.add_axes([left, bottom, width, height]) ax1.plot(x, y, 'r') ax1.set_xlabel('x') ax1.set_ylabel('y') ax1.set_title('title')
3、小图
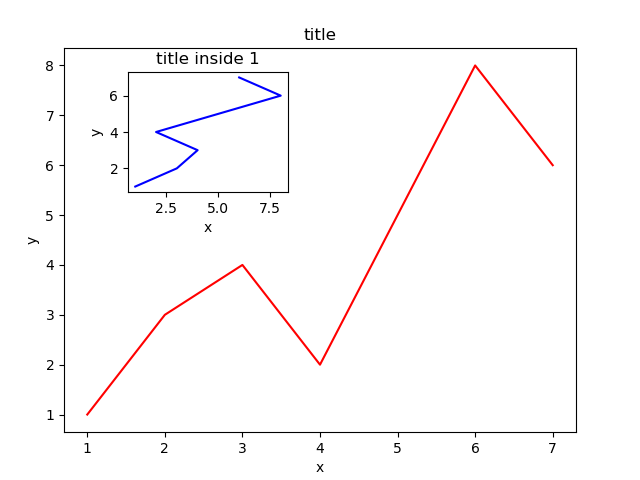
接着,绘制左上角的小图,步骤和绘制大图一样,注意坐标系位置和大小的改变:
left, bottom, width, height = 0.2, 0.6, 0.25, 0.25 ax2 = fig.add_axes([left, bottom, width, height]) ax2.plot(y, x, 'b') ax2.set_xlabel('x') ax2.set_ylabel('y') ax2.set_title('title inside 1')
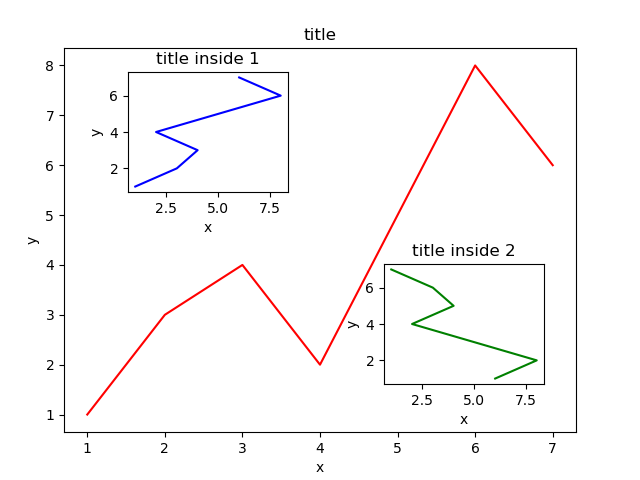
最后,我们来绘制右下角的小图。这里我们采用一种更简单方法,即直接往plt里添加新的坐标系:
plt.axes([0.6, 0.2, 0.25, 0.25]) plt.plot(y[::-1], x, 'g') # 注意对y进行了逆序处理 plt.xlabel('x') plt.ylabel('y') plt.title('title inside 2')