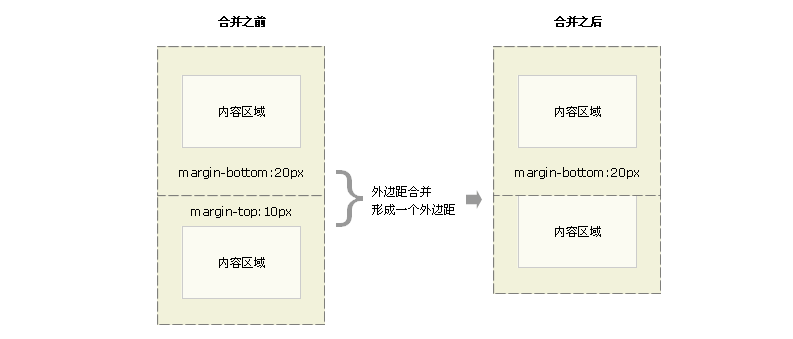
1. 外边距合并
当上下相邻的两个块元素相遇时,如果上面的元素有下外边距margin-bottom,下面的元素有上外边距margin-top,则他们之间的垂直间距不是margin-bottom与margin-top之和,而是两者中的较大者。这种现象被称为相邻块元素垂直外边距的合并(也称外边距塌陷)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
300px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
}
.xiongda {
margin-bottom: 100px;
}
.xionger {
background-color: pink;
margin-top: 150px; /*最终两个盒子的距离是 最大的那个为准 150*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="xiongda">1</div>
<div class="xionger">2</div>
</body>
</html>
解决方案:避免。
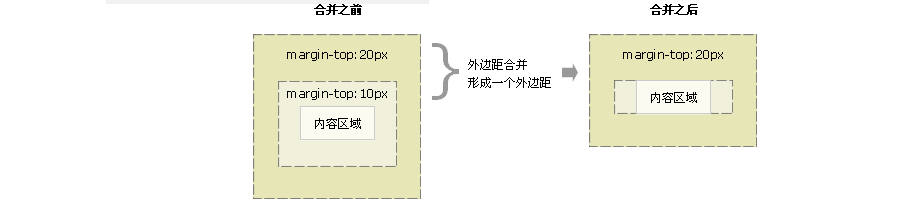
2. 嵌套块元素垂直外边距的合并(只出现在垂直和嵌套)
对于两个嵌套关系的块元素,如果父元素没有上内边距及边框,则父元素的上外边距会与子元素的上外边距发生合并,合并后的外边距为两者中的较大者,即使父元素的上外边距为0,也会发生合并。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father {
500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: pink;
/*padding-top: 50px;*/
/*border-top: 1px solid pink; 1. 用border*/
/*padding-top: 1px; 2 用padding */
overflow: hidden; 3. 用这个单词可以解决
}
.son {
200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: purple;
margin-top: 50px;
margin-left: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
解决方案:
- 可以为父元素定义1像素的上边框或上内边距。
- 可以为父元素添加overflow:hidden。