1、String类型的数字转换成int类型
public static void main(String[] args) { String snum = "123"; int inum = Integer.valueOf(snum); System.out.println(inum); // 输出123 int inum2 = Integer.parseInt(snum); System.out.println(inum); // 输出123 System.out.println(inum==inum2); // 输出true }
源码中对valueOf的注释中有:
In other words, this method returns an {@code Integer}
object equal to the value of:
{@code new Integer(Integer.parseInt(s))}
即valueOf与parseInt作用是相同的。
2、String类的几种方法
①字符串1.concat(字符串2);
字符串2被连接到字符串1的后面。
②字符串的提取和查询
| 方法 | 说明 |
| public int indexOf(int ch) | 搜索第一个出现的字符ch(或者字符串value) |
| public int indexOf(String value) | |
| public int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 搜索最后一个出现的字符ch(或者字符串value) |
| public int lastIndexOf(String value) | |
| public String substring(int index) | 提取从位置索引开始的字符串部分 |
| public String substring(int beginindex,int endindex) | 提取beginindex和endindex之间的字符串部分 |
| public String trim() | 返回一个前后不含任何空格的调用字符串的副本 |
③字符串的拆分
字符串.split(separator,limit);
public static void main(String[] args) { String words = "枯藤老树昏鸦,小桥流水人家,古道西风瘦马,夕阳西下,断肠人在天涯"; String [] printword = new String[100]; System.out.println("----原诗词的格式---- "+words); printword = words.split(","); System.out.println("====拆分后的诗词为===="); for (int i = 0; i < printword.length; i++) { System.out.println(printword[i]); } }

3、StringBuffer类的方法
①append方法
字符串.append(参数);
②insert()方法
字符串.insert(位置,参数);
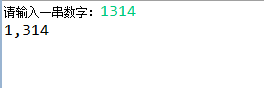
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); // 接收数字串,存放于StringBuffer类型的对象中 System.out.print("请输入一串数字:"); String nums = input.next(); StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer(nums); // 从后往前每隔三位添加逗号 for (int i = str.length()-3; i > 0; i-=3) { str.insert(i, ","); } System.out.println(str); }
四、日期类
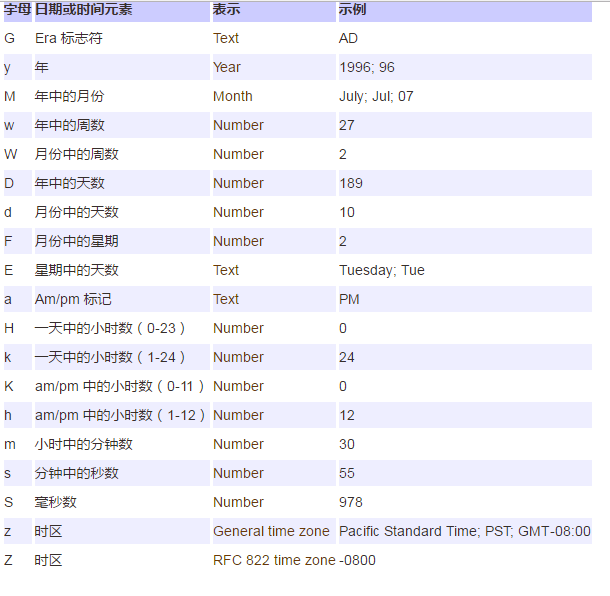
①simpleDateFormat
Calendar中些陷阱,很容易掉下去:
1、Calendar的星期是从周日开始的,常量值为0。
2、Calendar的月份是从一月开始的,常量值为0。
3、Calendar的每个月的第一天值为1。
public static void main(String[] args) { SimpleDateFormat formater = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日HH点mm分ss秒 E"); Date date = new Date(); System.out.println(date); System.out.println("当前时间为:"+formater.format(date)); Date date2 = new Date(115,4,23,10,59,59); String format = formater.format(date2); System.out.println(format); }
输出结果为:
Tue May 23 11:01:44 CST 2017
当前时间为:2017年05月23日11点01分44秒 星期二
2015年05月23日10点59分59秒 星期六
查看Date的源码
public Date(int year, int month, int date, int hrs, int min, int sec) { int y = year + 1900; // month is 0-based. So we have to normalize month to support Long.MAX_VALUE. if (month >= 12) { y += month / 12; month %= 12; } else if (month < 0) { y += CalendarUtils.floorDivide(month, 12); month = CalendarUtils.mod(month, 12); } BaseCalendar cal = getCalendarSystem(y); cdate = (BaseCalendar.Date) cal.newCalendarDate(TimeZone.getDefaultRef()); cdate.setNormalizedDate(y, month + 1, date).setTimeOfDay(hrs, min, sec, 0); getTimeImpl(); cdate = null; }