目录
Scanner的概述和方法介绍
- Scanner的构造方法原理
- Scanner(InputStream source)
- System类下有一个静态的字段:
- public static final InputStream in; 标准的输入流,对应着键盘录入。
- 一般方法
- hasNextXxx() 判断是否还有下一个输入项,其中Xxx可以是Int,Double等。如果需要判断是否包含下一个字符串,则可以省略Xxx
- nextXxx() 获取下一个输入项。Xxx的含义和上个方法中的Xxx相同,默认情况下,Scanner使用空格,回车等作为分隔符

package com.hwh.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo1_Scanner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //键盘录入
if(sc.hasNextInt()) { //判断键盘录入的是否是int类型的数据
int i = sc.nextInt(); //键盘录入的数据存储在i中
System.out.println(i);
}else {
System.out.println("输入的类型错误");
}
}
}
若输入字母的话, 运行结果为输入的类型错误
Scanner获取数据出现的小问题及解决方案
- 两个常用的方法:
- public int nextInt():获取一个int类型的值
- public String nextLine():获取一个String类型的值
- 案例演示
- a:先演示获取多个int值,多个String值的情况
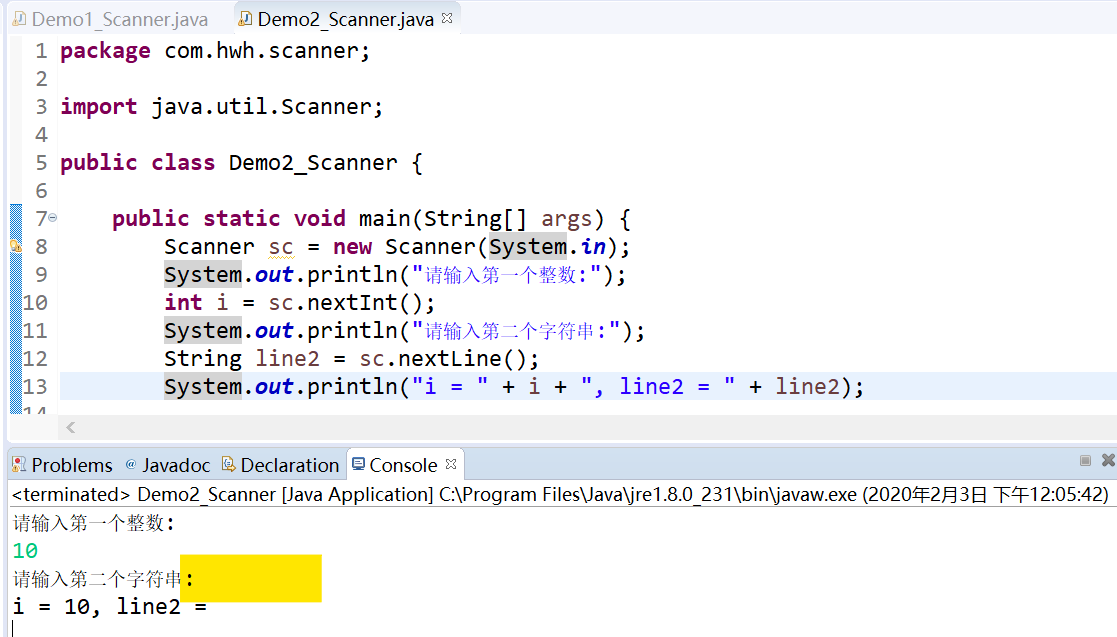
- b:再演示先获取int值,然后获取String值出现问题
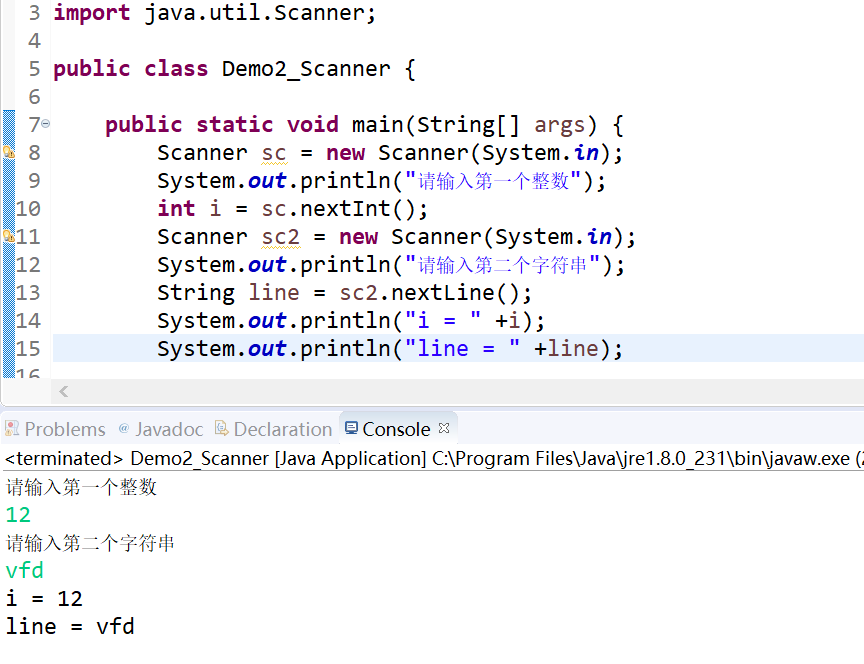
- c:问题解决方案
- 第一种:先获取一个数值后,再创建一个新的键盘录入对象获取字符串,但是浪费空间
- 第二种:把所有的数据都先按照字符串获取,然后要什么,你就对应的转换为什么,使用整数字符串转换成整数的方法[推荐]
String类的概述
- 通过JDK提供的API,查看String类的说明
- 可以看到这样的两句话。
- a:字符串字面值"abc"也可以看成是一个字符串对象。
- b:字符串是常量,一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。
package com.heima.string;
public class Demo1_String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abc"; //"abc"可以看成一个字符串对象
str = "def"; //当把"def"赋值给str,原来的"abc"就变成了垃圾
System.out.println(str); //String类重写了toString方法返回的是该对象本身
}
}
运行结果为def
String类的构造方法
package com.hwh.string;
public class Demo2_String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String();
System.out.println(s1);
byte[] arr1 = {97,98,99};
String s2 = new String(arr1); //解码,将计算机读的懂的转换成我们读的懂
System.out.println(s2);
byte[] arr2 = {97,98,99,100,101,102};
String s3 = new String(arr2,2,3); //将arr2字节数组从2索引开始转换3个
System.out.println(s3);
char[] arr3 = {'a','b','c','d','e'}; //将字符数组转换成字符串
String s4 = new String(arr3);
System.out.println(s4);
String s5 = new String(arr3,1,3); //将arr3字符数组,从1索引开始转换3个
System.out.println(s5);
String s6 = new String("hwh");
System.out.println(s6);
}
}
运行结果为
abc
cde
abcde
bcd
hwh
String类的判断功能
- String类的判断功能
- boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写
- boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
- boolean contains(String str):判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串
- boolean startsWith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
- boolean endsWith(String str):判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
- boolean isEmpty():判断字符串是否为空。
package com.hwh.string;
public class Demo4_StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//demo2();
String s1 = "hwh";
String s2 = "";
String s3 = null;
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); //false
System.out.println(s2.isEmpty()); //true
//System.out.println(s3.isEmpty()); //错误 java.lang.NullPointerException
}
public static void demo2() {
//demo1();
String s1 = "我是hwh,哈哈";
String s2 = "hwh";
String s3 = "www";
String s4 = "我是";
String s5 = "哈哈";
System.out.println(s1.contains(s2)); //true//判断是否包含传入的字符串
System.out.println(s1.contains(s3)); //false
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(s1.startsWith(s4)); //true//判断是否以传入的字符串开头
System.out.println(s1.startsWith(s5)); //false
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(s1.endsWith(s4)); //false//判断是否以传入的字符串结尾
System.out.println(s1.endsWith(s5)); //true
}
public static void demo1() { //抽取方法alt + shift + m
String s1 = "hwh";
String s2 = "hwh";
String s3 = "HwH";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true
System.out.println(s2.equals(s3)); //false
System.out.println("---------------");
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); //true
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); //true //不区分大小写
}
}
- ""和null的区别
- ""是字符串常量,同时也是一个String类的对象,既然是对象当然可以调用String类中的方法
- null是空常量,不能调用任何的方法,否则会出现空指针异常,null常量可以给任意的引用数据类型赋值
模拟用户登录
- 案例演示
- 需求:模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次。
- 用户名和密码都是admin
package com.hwh.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test1 {
// * 分析:
// * 1,模拟登录,需要键盘录入,Scanner
// * 2,给三次机会,需要循环,for
// * 3,并提示有几次,需要判断,if
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);//创建键盘录入对象
for(int i=2; i>=0; i--) {
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String userName = sc.nextLine(); //将键盘录入的用户名存储在userName中
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine(); //将键盘录入的密码存储在password中
//如果是字符串常量和字符串变量比较,通常都是字符串常量调用方法,将变量当作参数传递,防止空指针异常
if ("admin".equals(userName)&&"admin".equals(password)) {
System.out.println("欢迎"+userName+"登录");
break;//跳出循环
}else if(i==0){
System.out.println("登录失败, 机会用尽");
}else
{
System.out.println("登录失败, 你还有"+i+"次机会");
}
}
}
}
String类的获取功能
- String类的获取功能
- int length():获取字符串的长度。
- char charAt(int index):获取指定索引位置的字符
- int indexOf(int ch):返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
- int indexOf(String str):返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
- int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex):返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
- int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex):返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引。
- lastIndexOf
- String substring(int start):从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾。
- String substring(int start,int end):从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串。
package com.hwh.string;
public class Demo5_StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//demo1();
//demo2();
//demo3();
demo4();
}
private static void demo4() {
String s1 = "heimawudi";
String s2 = s1.substring(5);
System.out.println(s2); //wudi
String s3 = s1.substring(0, 5); //heima //包含头,不包含尾,左闭右开
System.out.println(s3);
}
private static void demo3() {
String s1 = "woaiheima";
int index1 = s1.indexOf('a', 3); //8 //从指定位置开始向后找
System.out.println(index1);
int index2 = s1.lastIndexOf('a'); //8 //从后向前找,第一次出现的字符
System.out.println(index2);
int index3 = s1.lastIndexOf('a', 7); //2 //从指定位置向前找
System.out.println(index3);
}
private static void demo2() {
String s1 = "heima";
int index = s1.indexOf('e'); //1 //参数接收的是int类型的,传递char类型的会自动提升
System.out.println(index);
int index2 = s1.indexOf('z'); //如果不存在返回就是-1
System.out.println(index2);
int index3 = s1.indexOf("ma"); //3 //获取字符串中第一个字符出现的位置
System.out.println(index3);
int index4 = s1.indexOf("ia"); //-1
System.out.println(index4);
}
private static void demo1() {
String s1 = "heima";
System.out.println(s1.length()); //5 //length()是一个方法,获取的是每一个字符的个数
String s2 = "你要减肥,造吗?";
System.out.println(s2.length()); //8
char c = s2.charAt(5); //造 //根据索引获取对应位置的字符
System.out.println(c);
char c2 = s2.charAt(10); //错误StringIndexOutOfBoundsException字符串索引越界异常
System.out.println(c2);
}
}
字符串的遍历
package com.hwh.test;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hanwenhao";
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { //通过for循环获取到字符串中每个字符的索引
System.out.println(s.charAt(i)); //通过索引获取每一个字符
/*也可以char c = s.charAt(i);
System.out.println(c);*/
}
}
}
统计不同类型字符个数
- 案例演示
- 需求:统计一个字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数,其他字符出现的次数。
- ABCDEabcd123456!@#$%^
package com.hwh.test;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "ABCDEabcd123456!@#$%^";
int big = 0;
int small = 0;
int num = 0;
int other = 0;
//1,获取每一个字符,通过for循环遍历
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i); //通过索引获取每一个字符
//2,判断字符是否在这个范围内
if(c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') {
big++; //如果满足是大写字母,就让其对应的变量自增
}else if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') {
small++;
}else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
num++;
}else {
other++;
}
}
//3,打印每一个计数器的结果
System.out.println(s + "中大写字母有:" + big + "个,小写字母有:" + small + "个,数字字符:"
+ num + "个,其他字符:" + other + "个");
}
}
String类的转换功能
- A:String的转换功能:
-
byte[] getBytes():把字符串转换为字节数组。
-
char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组。
-
static String valueOf(char[] chs):把字符数组转成字符串。
-
static String valueOf(int i):把int类型的数据转成字符串。
- 注意:String类的valueOf方法可以把任意类型的数据转成字符串
-
String toLowerCase():把字符串转成小写。(了解)
-
String toUpperCase():把字符串转成大写。
-
String concat(String str):把字符串拼接。
-
package com.hwh.string;
import com.hwh.bean.Person;
public class Demo6_StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
demo1();
//demo2();
//demo3();
//demo4();
}
public static void demo4() {
String s1 = "hwh";
String s2 = "chengxuYUAN";
String s3 = s1.toLowerCase();
String s4 = s2.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s3); //hwh
System.out.println(s4); //CHENGXUYUAN
System.out.println(s3 + s4); //hwhCHENGXUYUAN //用+拼接字符串更强大,可以用字符串与任意类型相加
System.out.println(s3.concat(s4)); //hwhCHENGXUYUAN //concat方法调用的和传入的都必须是字符串
}
private static void demo3() {
char[] arr = {'a','b','c'};
String s = String.valueOf(arr); //底层是由String类的构造方法完成的
System.out.println(s); //abc
String s2 = String.valueOf(100); //将100转换为字符串
System.out.println(s2 + 100); //100100
Person p1 = new Person("张三", 23);
System.out.println(p1); //Person [name=张三, age=23]
String s3 = String.valueOf(p1); //调用的是对象的toString方法
System.out.println(s3); //Person [name=张三, age=23]
}
private static void demo2() {
String s = "hwh";
char[] arr = s.toCharArray(); //将字符串转换为字符数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); //h w h
}
}
private static void demo1() {
String s1 = "abc";
byte[] arr = s1.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");//97 98 99
}
String s2 = "你好你好";
byte[] arr2 = s2.getBytes(); //通过gbk码表将字符串转换成字节数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { //编码:把我们看的懂转换为计算机看的懂得
System.out.print(arr2[i] + " "); //gbk码表一个中文代表两个字节
} //-60 -29 -70 -61 -60 -29 -70 -61 //gbk码表特点,中文的第一个字节肯定是负数
}
}
按要求转换字符
- 需求:把一个字符串的首字母转成大写,其余为小写。(只考虑英文大小写字母字符)
- 链式编程:只要保证每次调用完方法返回的是对象,就可以继续调用
package com.hwh.test;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "woshiHAnwenhao";
String s2 = s.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase().concat(s.substring(1).toLowerCase());
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
把数组转成字符串
- 案例演示
- 需求:把数组中的数据按照指定个格式拼接成一个字符串
- 举例:
- int[] arr = {1,2,3};
- 输出结果:
- "[1, 2, 3]"
- 举例:
- 需求:把数组中的数据按照指定个格式拼接成一个字符串
package com.hwh.test;
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
String s = "["; //定义一个字符串用来与数组中元素拼接
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { //{1,2,3}
if(i == arr.length - 1) {
s = s + arr[i] + "]"; //[1, 2, 3]
}else {
s = s + arr[i] + ", "; //[1, 2,
}
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}
String类的其他功能
- A:String的替换功能及案例演示
- String replace(char old,char new)
- String replace(String old,String new)
- B:String的去除字符串两端空格及案例演示
- String trim()
- C:String的按字典顺序比较两个字符串及案例演示
- int compareTo(String str)
- int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
package com.hwh.string;
public class Demo7_StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//demo1();
//demo2();
String s1 = "a";
String s2 = "aaaa";
int num = s1.compareTo(s2); //按照码表值比较
System.out.println(num); //-3
String s3 = "韩";
String s4 = "文";
int num2 = s3.compareTo(s4);
System.out.println('韩' + 0); //38889 //查找的是unicode码表值
System.out.println('文' + 0); //25991
System.out.println(num2); //12898
String s5 = "hwh";
String s6 = "HWH";
int num3 = s5.compareTo(s6);
System.out.println(num3); //32
int num4 = s5.compareToIgnoreCase(s6);
System.out.println(num4); //0
}
private static void demo2() {
String s = " han wen h ao ";
String s2 = s.trim();
System.out.println(s2); //han wen h ao
}
private static void demo1() {
String s = "hanwenhao";
String s2 = s.replace('n', 'o'); //用o替换n
System.out.println(s2); //haoweohao
String s3 = s.replace('z', 'o'); //z不存在,保留原字符不改变
System.out.println(s3); //hanwenhao
String s4 = s.replace("an", "ao");
System.out.println(s4); //haowenhao
}
}
字符串反转
- A:案例演示
- 需求:把字符串反转
- 举例:键盘录入"abc"
- 输出结果:"cba"
- 需求:把字符串反转
package com.hwh.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test6 {
/*
*分析:
*1,通过键盘录入获取字符串Scanner
*2,将字符串转换成字符数组
*3,倒着遍历字符数组,并再次拼接成字符串
*4,打印
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //创建键盘录入对象
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String line = sc.nextLine(); //将键盘录入的字符串存储在line中
char[] arr = line.toCharArray(); //将字符串转换为字符数组
String s = "";
for(int i = arr.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { //倒着遍历字符数组
s = s + arr[i]; //拼接成字符串
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}
在大串中查找小串出现的次数
- 需求:统计大串中小串出现的次数
- 这里的大串和小串可以自己根据情况给出

package com.hwh.test;
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义大串
String max = "woaiheima,heimabutongyubaima,wulunheimahaishibaima,zhaodaogongzuojiushihaoma";
//定义小串
String min = "heima";
//定义计数器变量
int count = 0;
//定义索引
int index = 0;
//定义循环,判断小串是否在大串中出现
while((index = max.indexOf(min)) != -1) {
count++; //计数器自增
max = max.substring(index + min.length());
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
运行结果为3