一.数组的定义
int[] x = new int[100]; /*内存中定义了100个int类型的变量*/
获取数组的长度:length属性
public class ArrayDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr; // 声明变量 arr = new int[3]; // 创建数组对象 System.out.println("arr[0]=" + arr[0]); // 访问数组中的第一个元素 System.out.println("arr[1]=" + arr[1]); // 访问数组中的第二个元素 System.out.println("arr[2]=" + arr[2]); // 访问数组中的第三个元素 System.out.println("数组的长度是:" + arr.length); // 打印数组长度 } } /*arr[0]=0 arr[1]=0 arr[2]=0 数组长度为3*/
当数组被成功创建后,数组中元素会被自动赋予一个默认值,根据元素类型的不同,默认初始化的值也是不一样的
|
数据类型 |
默认初始化值 |
|
byte、short、int、long |
0 |
|
float、double |
0.0 |
|
char |
一个空字符(空格),即’u0000’ |
|
boolean |
false |
|
引用数据类型 |
null,表示变量不引用任何对象 |
数组的静态初始化方式
①类型[] 数组名 = new 类型[]{元素,元素,……};
②类型[] 数组名 = {元素,元素,元素,……};
二.数组的遍历
public class ArrayDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; // 定义数组 // 使用for循环遍历数组的元素 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); // 通过索引访问元素 } } } /*1 *2 *3 *4 *5 */
三.数组中常见的问题
1.数组的最值
public class ArrayDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 4, 1, 6, 3, 9, 8 }; // 定义一个数组 int max = arr[0]; // 定义变量max用于记住最大数,首先假设第一个元素为最大值 // 下面通过一个for循环遍历数组中的元素 for (int x = 1; x < arr.length; x++) { if (arr[x] > max) { // 比较 arr[x]的值是否大于max max = arr[x]; // 条件成立,将arr[x]的值赋给max } } System.out.println("max=" + max); // 打印最大值 } } //结果为max=9
2.数组的异常
①数组越界异常
public class ArrayDemo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[4]; // 定义一个长度为4的数组 System.out.println("arr[0]=" + arr[4]); // 通过角标4访问数组元素 } }

上图运行结果中所提示的错误信息是数组越界异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,出现这个异常的原因是数组的长度为4,其索引范围为0~3,而上述代码中的第4行代码使用索引4来访问元素时超出了数组的索引范围
②空指针异常
public class ArrayDemo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[3]; // 定义一个长度为3的数组 arr[0] = 5; // 为数组的第一个元素赋值 System.out.println("arr[0]=" + arr[0]); // 访问数组的元素 arr = null; // 将变量arr置为null System.out.println("arr[0]=" + arr[0]); // 访问数组的元素 } }
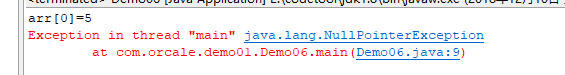
上述代码中第4、5行代码都能通过变量arr正常地操作数组。第6行代码将变量置为null,当第7行代码再次访问数组时就出现了空指针异常NullPointerException