sem_t分为有名和无名。有名的sem_t通过sem_open来创建, 而无名的sem_t通过sem_init的初始化。 用有名的sem_t来进程间同步是件很容易的事情,百度上一搜很多想相关的例子。
有名和无名的sem_t主要区别:
1. 效率:有名sem_t是放在文件,无名的sem_t是放在内存。
2.限制:有名的sem_t可以用来同步多线程,任意多进程。而无名的sem_t可以用来同步多线程,以及Fork出来的进程间的同步。
网上想关的例子很多,本文主要是测试一下用无名sem_t进程同步,比如你在使用nginx的时候,nginx会fork出很多works,如果在works间你希望能同步一些操作,那么这个时候就可以用它,注意下面API描述中的红色部分,明确说了需要放到共享内存(shared memory)。
Name
sem_init - initialize an unnamed semaphore Synopsis #include <semaphore.h> int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value); Link with -pthread. Description sem_init() initializes the unnamed semaphore at the address pointed to by sem. The value argument specifies the initial value for the semaphore. The pshared argument indicates whether this semaphore is to be shared between the threads of a process, or between processes. If pshared has the value 0, then the semaphore is shared between the threads of a process, and should be located at some address that is visible to all threads (e.g., a global variable, or a variable allocated dynamically on the heap). If pshared is nonzero, then the semaphore is shared between processes, and should be located in a region of shared memory (see shm_open(3), mmap(2), and shmget(2)). (Since a child created by fork(2) inherits its parent's memory mappings, it can also access the semaphore.) Any process that can access the shared memory region can operate on the semaphore using sem_post(3), sem_wait(3), etc. Initializing a semaphore that has already been initialized results in undefined behavior.
下面是一段简单的测试代码
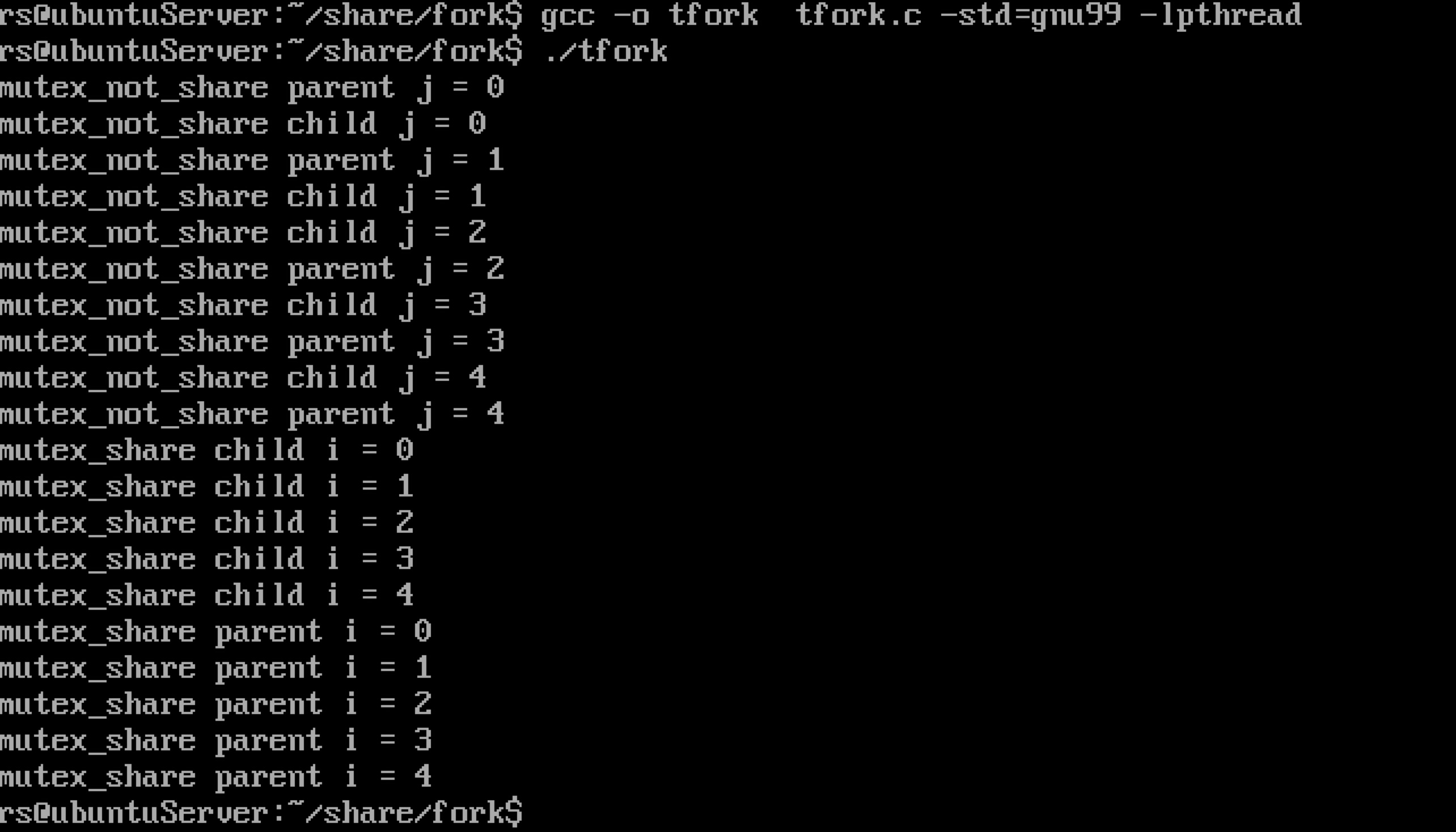
#include <semaphore.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/mman.h> void *createSharedMemory(size_t size) { void *addr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_ANON | MAP_SHARED, -1, 0); if (addr == MAP_FAILED) { return NULL; } return addr; } void freeSharedMemory(void *addr, size_t size) { if (munmap(addr, size) == -1) { printf("munmap(%p, %d) failed", addr, (int)size); } } int main(int argc, char *argv[] ) { sem_t* mutex_share = createSharedMemory(sizeof(sem_t)); sem_t mutex_not_share; if (mutex_share == NULL) { printf("creat share memory error "); return 0; } if( sem_init(mutex_share,1,1) < 0 || sem_init(&mutex_not_share,1,1) < 0) { printf("semaphore initilization "); return 0; } if (fork() == 0) { sem_wait(&mutex_not_share); for(int j = 0;j<5;j++) { printf("mutex_not_share child j = %d ", j); usleep(50000); } sem_post(&mutex_not_share); sem_wait(mutex_share); for (int i = 0;i<5;i++) { printf("mutex_share child i = %d ", i); usleep(50000); } sem_post(mutex_share); } else { sem_wait(&mutex_not_share); for(int j = 0;j<5;j++) { printf("mutex_not_share parent j = %d ", j); usleep(50000); } sem_post(&mutex_not_share); sem_wait(mutex_share); for (int i = 0;i<5;i++) { printf("mutex_share parent i = %d ", i); usleep(50000); } sem_post(mutex_share); } freeSharedMemory(mutex_share,sizeof(sem_t)); return 0; }
运行结果可以看出,如果没有放到共享内存,就算将pshared设置为1,也起不了作用。