自定义排序
将两列数据进行排序,第一列按照升序排列,当第一列相同时,第二列升序排列。
在map和reduce阶段进行排序时,比较的是k2。v2是不参与排序比较的。如果要想让v2也进行排序,需要把k2和v2组装成新的类,作为k2,才能参与比较。
1 package sort; 2 3 import java.io.DataInput; 4 import java.io.DataOutput; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.net.URI; 7 8 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; 12 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 13 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 14 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 15 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 16 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 17 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 18 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; 19 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 20 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; 21 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.HashPartitioner; 22 23 public class SortApp { 24 static final String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://chaoren:9000/input"; 25 static final String OUT_PATH = "hdfs://chaoren:9000/out"; 26 27 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 28 final Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); 29 30 final FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI(INPUT_PATH), 31 configuration); 32 if (fileSystem.exists(new Path(OUT_PATH))) { 33 fileSystem.delete(new Path(OUT_PATH), true); 34 } 35 36 final Job job = new Job(configuration, SortApp.class.getSimpleName()); 37 38 // 1.1 指定输入文件路径 39 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, INPUT_PATH); 40 // 指定哪个类用来格式化输入文件 41 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); 42 43 // 1.2指定自定义的Mapper类 44 job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class); 45 // 指定输出<k2,v2>的类型 46 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(NewK2.class); 47 job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class); 48 49 // 1.3 指定分区类 50 job.setPartitionerClass(HashPartitioner.class); 51 job.setNumReduceTasks(1); 52 53 // 1.4 TODO 排序、分区 54 55 // 1.5 TODO (可选)合并 56 57 // 2.2 指定自定义的reduce类 58 job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class); 59 // 指定输出<k3,v3>的类型 60 job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class); 61 job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class); 62 63 // 2.3 指定输出到哪里 64 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(OUT_PATH)); 65 // 设定输出文件的格式化类 66 job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); 67 68 // 把代码提交给JobTracker执行 69 job.waitForCompletion(true); 70 } 71 72 static class MyMapper extends 73 Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NewK2, LongWritable> { 74 protected void map( 75 LongWritable key, 76 Text value, 77 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<LongWritable, Text, NewK2, LongWritable>.Context context) 78 throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { 79 final String[] splited = value.toString().split(" "); 80 final NewK2 k2 = new NewK2(Long.parseLong(splited[0]), 81 Long.parseLong(splited[1])); 82 final LongWritable v2 = new LongWritable(Long.parseLong(splited[1])); 83 context.write(k2, v2); 84 }; 85 } 86 87 static class MyReducer extends 88 Reducer<NewK2, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable> { 89 protected void reduce( 90 NewK2 k2, 91 java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> v2s, 92 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer<NewK2, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) 93 throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException { 94 context.write(new LongWritable(k2.first), new LongWritable( 95 k2.second)); 96 }; 97 } 98 99 /** 100 * 问:为什么实现该类? 答:因为原来的v2不能参与排序,把原来的k2和v2封装到一个类中,作为新的k2 101 * 102 */ 103 // WritableComparable:Hadoop的序列化 104 static class NewK2 implements WritableComparable<NewK2> { 105 Long first; 106 Long second; 107 108 public NewK2() { 109 } 110 111 public NewK2(long first, long second) { 112 this.first = first; 113 this.second = second; 114 } 115 116 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 117 this.first = in.readLong(); 118 this.second = in.readLong(); 119 } 120 121 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 122 out.writeLong(first); 123 out.writeLong(second); 124 } 125 126 /** 127 * 当k2进行排序时,会调用该方法. 当第一列不同时,升序;当第一列相同时,第二列升序 128 */ 129 public int compareTo(NewK2 o) { 130 final long minus = this.first - o.first; 131 if (minus != 0) { 132 return (int) minus; 133 } 134 return (int) (this.second - o.second); 135 } 136 137 @Override 138 public int hashCode() { 139 return this.first.hashCode() + this.second.hashCode(); 140 } 141 142 @Override 143 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 144 if (!(obj instanceof NewK2)) { 145 return false; 146 } 147 NewK2 oK2 = (NewK2) obj; 148 return (this.first == oK2.first) && (this.second == oK2.second); 149 } 150 } 151 152 }

Hadoop序列化
序列化概念:
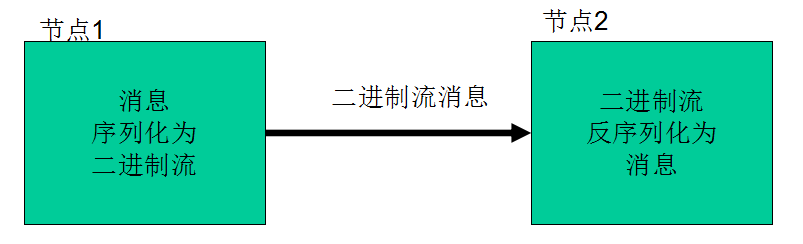
序列化:把结构化对象转化为字节流。
反序列化:是序列化的逆过程。即把字节流转回结构化对象。
Hadoop序列化的特点:
1、紧凑:高效使用存储空间。
2、快速:读写数据的额外开销小。
3、可扩展:可透明的读取老格式的数据。
4、互操作:支持多语言的交互。
Hadoop的序列化格式:Writable
Hadoop序列化的作用:
序列化在分布式环境的两大作用:进程间通信,永久存储。
Hadoop节点间通信:
Writable接口
Writable接口,是根据DataInput和DataOutput实现的简单、有效的序列化对象。
MR的任意key和value必须实现Writable接口。
MR的任意key必须实现WritableComparable接口。
自定义Writable类(上面代码中有)
实现Writable:
1、write是把每个对象序列化到输出流。
2、readFields是把输入流字节反序列化。
实现WritableComparable:
Java值对象的比较:一般需要重写toString(),hashCode(),equals()方法。