一、通过debug模式验证jdbc中mysql管理事务的默认方式(自动提交)示例
package edu.aeon.jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; import edu.aeon.aeonutils.AeonJdbcUtils; /** * [说明]:验证jdbc中mysql管理事务的默认方式(自动提交) * @author aeon */ public class TestJDBC { /** * 使用jdbc中mysql管理事务的默认方式(自动提交)验证 */ public static void jdbc_insert(){ Connection connection=null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { connection = AeonJdbcUtils.getMySqlConnection(); String sql="insert into user(userid,username,userpw) values (?,?,?)"; //第一条数据 //将sql语句进行预编译然后保存到preparedStatement对象中 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10006); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon6"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon6"); int rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(rowCount+"条数据被插入!"); //第二条数据 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10007); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon7"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon7"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(rowCount+"条数据被插入!"); //第三条数据 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10008); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon8"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon8"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(rowCount+"条数据被插入!"); //第四条 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10006);//模拟错误 preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon9"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon9"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(rowCount+"条数据被插入!"); //第五条数据 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 100010); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon10"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon10"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(rowCount+"条数据被插入!"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { AeonJdbcUtils.closeDB(null, preparedStatement, connection); } } public static void main(String[] args) { jdbc_insert(); } }
执行结果截图:
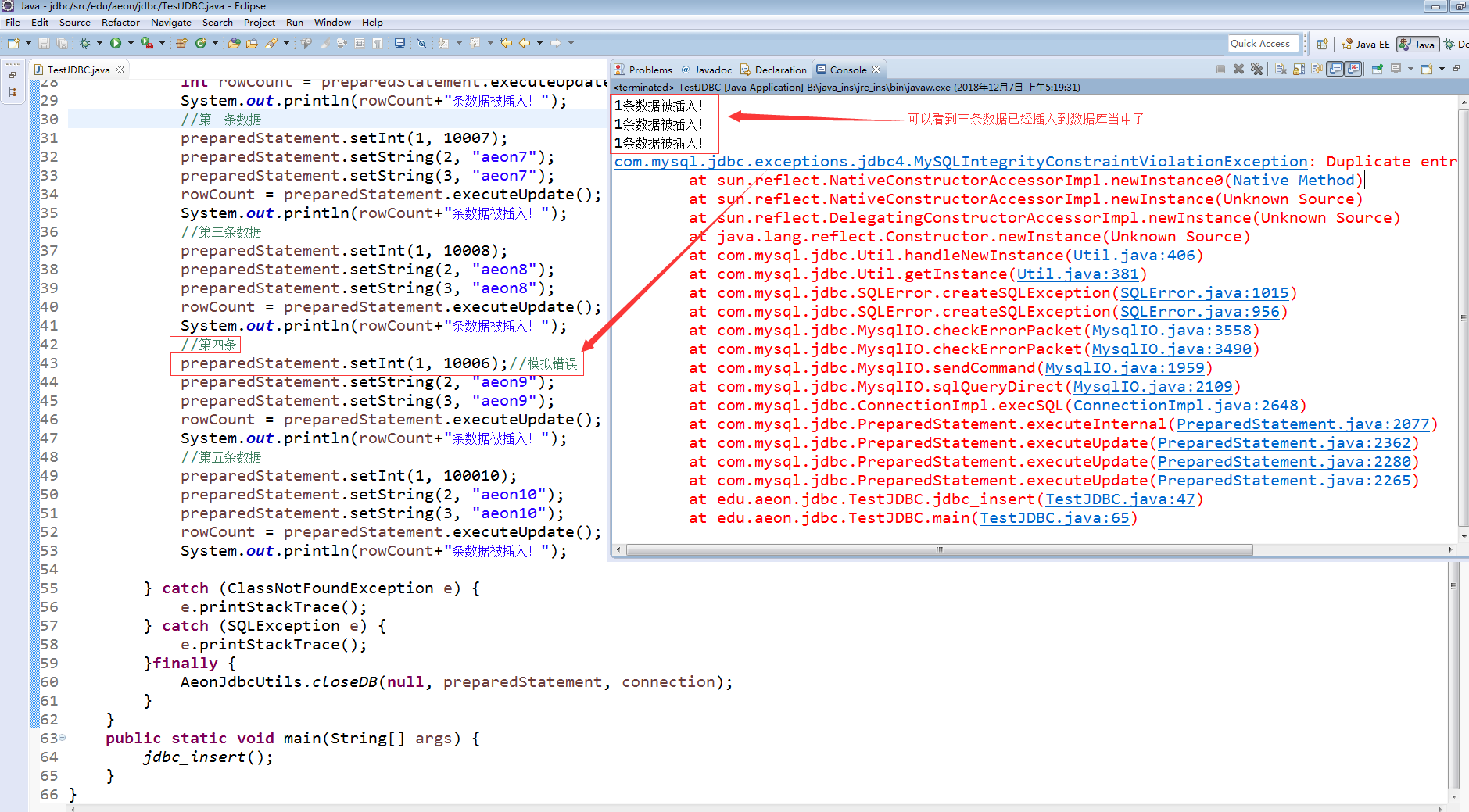
数据库截图:
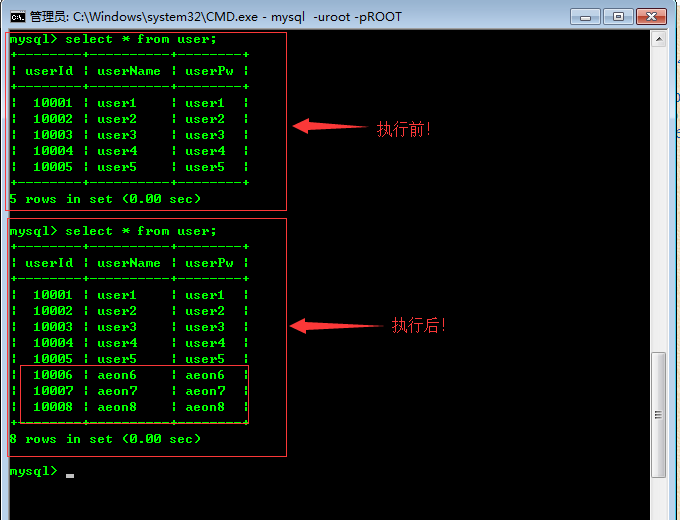
当我们在debug模式下执行完第一条数据后执行第二条数据前,我们可以看到第一条数据已经被插入到数据库当中了、因此可以判断出第一条事务被默认的提交到数据库当中了。
当在执行第四条语句的时候出了主键冲突作用、但是这个错误不会影响到前三条数据的正常执行(这就是鉴于事物的原子行)
当第四条语句(事务)出错后,那么第五条数据是不会被正常执行的!
二、这种jdbc中mysql的默认提交事务在某些场合下并不使用
比如说进行转账操作时、a 卡向b卡转账 100万元
当程序跑到a卡里面的钱被扣了100万元后、b卡里面的钱没有被加前、突然停电了、那么这种情况就是a持卡人说我向你转了100万、而b持卡人说我根本没有收到100万、我们怎么在程序里面避免这种现象的发生?(将a卡扣钱事务和b卡的加钱事务放到一个事务当中)、当扣钱和加钱同时执行成功,则本次转账成功、否则当次事务中的任何一个操作出现异常的情况下视为本事务执行失败,恢复到转账前。
2.1实现(在事务执行之前将事务的提交方式改为手动提交)
此处由于本人比较小懒、就不模拟转账操作了(设计到转账还要从新见测试表)、我们拿之前的例子说明即可(因为原理一样):
package edu.aeon.jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; import edu.aeon.aeonutils.AeonJdbcUtils; /** * [说明]:修改jdbc中事务的提交方式 * @author aeon */ public class TestJDBC { /** * @throws SQLException */ public static void jdbc_insert() throws SQLException{ Connection connection=null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { connection = AeonJdbcUtils.getMySqlConnection(); //设置事务的提交方式为手动提交 connection.setAutoCommit(false); String sql="insert into user(userid,username,userpw) values (?,?,?)"; //第一条数据 //将sql语句进行预编译然后保存到preparedStatement对象中 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10006); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon6"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon6"); int rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //第二条数据 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10007); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon7"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon7"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //第三条数据 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10008); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon8"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon8"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //第四条 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10006);//模拟错误 preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon9"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon9"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //第五条数据 preparedStatement.setInt(1, 100010); preparedStatement.setString(2, "aeon10"); preparedStatement.setString(3, "aeon10"); rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //提交事务 connection.commit(); System.out.println("本次操作成功!"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { connection.rollback(); System.out.println("本次操作失败!"); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { AeonJdbcUtils.closeDB(null, preparedStatement, connection); } } public static void main(String[] args) { try { jdbc_insert(); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("本次操作失败!"); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
执行结果截图:

数据库截图:

当我们将这个模拟异常去掉后、执行结果截图:
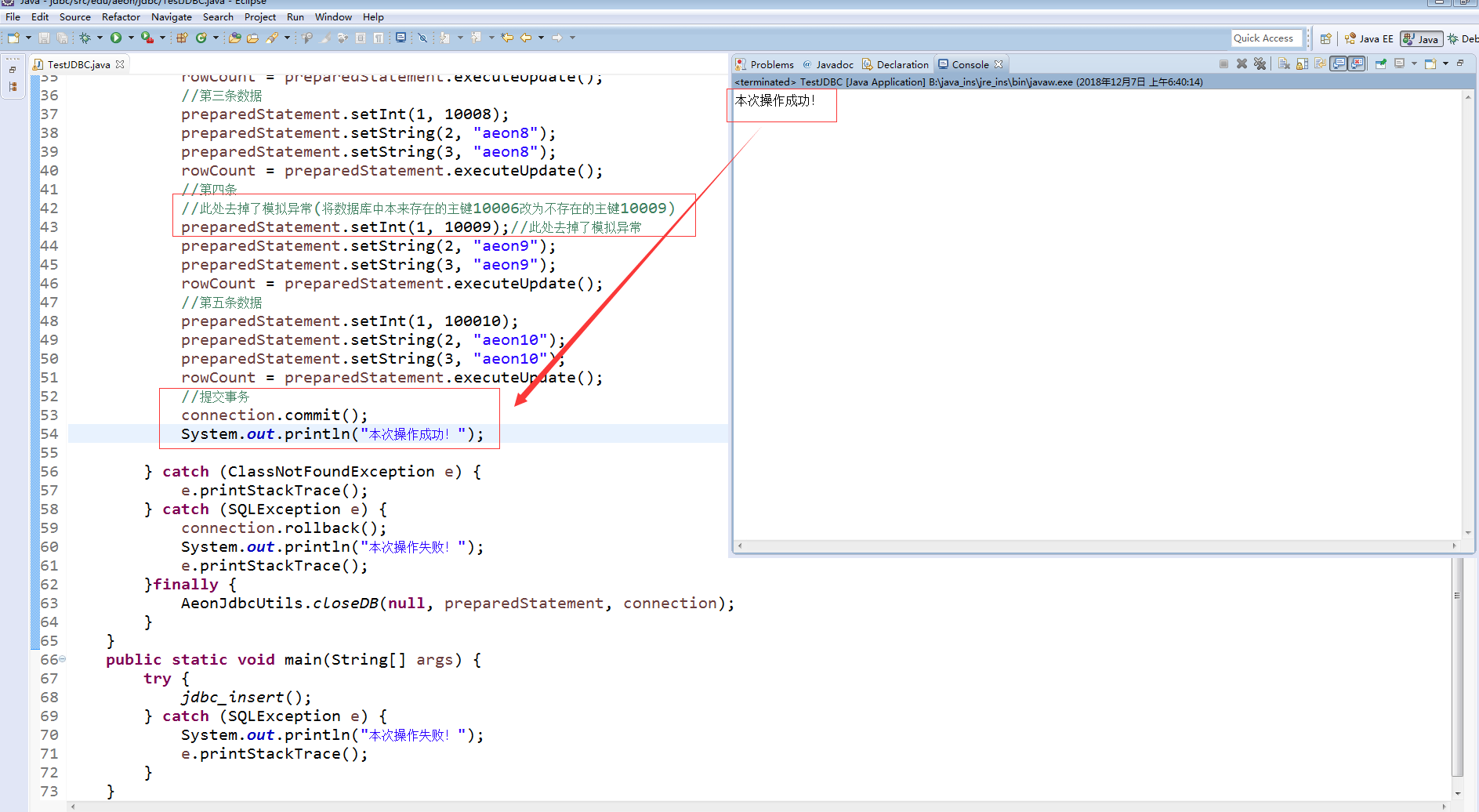
再去看看数据库:

可见数据已经进来了!
当使用jdbc修改了事务的提交方式为手动提交后、那么接下来执行的所有操作都将被放入到一个事务中了(commit()、rollback()之前的操作都将是一个事务)、当遇到commit()时将当前事务提交到数据库中、当遇到rollback()时,当前事务中的所有操作都将被撤回到事务执行之前(又恢复jdbc提交事务的默认方式)。
jdbc中使用行级锁:
1.关闭自动提交(connection.setAutoCommit(false))
2.使用for update锁定要操作的数据(如select * from users where userid in(1,2) for update)锁住id 为1和2的两条数据,然后再执行其它操作(如update。。。)
3.然后修改
4.事务的提交回滚
mysql数据库中默认的事务管理方式是默认自动提交,mysql中认为每个DML语句都会引起一个单独的事务,每执行一个DML语句,事务就默认自动提交。
statement编译一次执行一次,是因为sql在java中是字符串,statement需要把字符串格式的sql语句编译成网络数据,传输给数据库服务器,然后由数据库服务器去执行。
在mysql中关闭事务的自动提交时通过start transaction,以这种方式只能关闭本次的自动提交,事务结束后,会恢复到mysql默认的事务提交机制。
在事务开始之后,只要事务没有结束,无论我们执行多少个DML语句,这些DML语句都隶属于同一个事务中,根据事务的一致性及原子性,要么事务中的数据同时执行成功,要么都失败。结束事务的两种方式(commit/rollback)
