在关联关系中,很多情况下我们的多重性并不是多对一或者一对多的,而是多对多的。

不过因为我们要考虑里面的导航性,如果直接搞的话就是需要去维护两群对象之间多对多的互指链接,这就十分繁杂且易错。那么我们怎么办呢?可以将多对多的多重性尝试拆解为两组一对多的设计。

我们可以改为上图的这种拆解方法。就是说在账户与基金之间多搞一个申购交易,这样就可以化解多对多的复杂度。一个账户底下可以记录多笔申购交易,而每一个申购交易将指定某一档基金。虽然可以重复申购同一档基金,不过每一个申购交易只能设定一档基金。

一个账户对象可以链接多个申购交易对象,而每个申购交易对象只能链接到一个基金对象。
下面我们来看一个“多对多”的例子
Account.h
1 #include <cstdlib> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include "Bid.h" 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Account 7 { 8 public: 9 void setBid(Bid*); 10 int calcAsset(); 11 private: 12 vector<Bid*> bidObj; 13 };
Account.cpp
1 #include "Account.h" 2 3 void Account::setBid(Bid *theBid) 4 { 5 bidObj.push_back(theBid); 6 } 7 8 int Account::calcAsset() 9 { 10 int size,theAsset=0; 11 size=bidObj.size(); 12 for(int i=0;i<size;i++) 13 theAsset=theAsset+bidObj[i]->calcAsset(); 14 return theAsset; 15 }
Bid.h
1 #include "Fund.h" 2 3 class Bid 4 { 5 public: 6 Bid(float); 7 void setFund(Fund*); 8 int calcAsset(); 9 float getUnit(); 10 private: 11 float unit; 12 Fund *fundObj; 13 };
Bid.cpp
1 #include "Bid.h" 2 3 Bid::Bid(float theUnit) 4 { 5 unit=theUnit; 6 } 7 8 void Bid::setFund(Fund *theFund) 9 { 10 fundObj=theFund; 11 } 12 13 int Bid::calcAsset() 14 { 15 return unit*fundObj->getPrice(); 16 } 17 18 float Bid::getUnit() 19 { 20 return unit; 21 }
Fund.h
1 class Fund 2 { 3 public: 4 Fund(float); 5 float getPrice(); 6 private: 7 float price; 8 };
Fund.cpp
1 #include "Fund.h" 2 3 Fund::Fund(float thePrice) 4 { 5 price=thePrice; 6 } 7 8 float Fund::getPrice() 9 { 10 return price; 11 }
main.cpp
1 #include <cstdlib> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "Bid.h" 4 #include "Account.h" 5 #include "Fund.h" 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 9 { 10 Fund *myFund; 11 Bid *myBid; 12 Account myAccount; 13 14 myFund=new Fund(19.84); 15 myBid=new Bid(100); 16 myBid->setFund(myFund); 17 myAccount.setBid(myBid); 18 cout << "大华大华基金单位及净值: " 19 << "(" << myBid->getUnit() << ")" 20 << "(" << myFund->getPrice() << ")" << endl; 21 22 myFund=new Fund(37.83); 23 myBid=new Bid(200); 24 myBid->setFund(myFund); 25 myAccount.setBid(myBid); 26 cout << "日盛上选基金单位及净值: " 27 << "(" << myBid->getUnit() << ")" 28 << "(" << myFund->getPrice() << ")" << endl; 29 30 myBid=new Bid(300); 31 myBid->setFund(myFund); 32 myAccount.setBid(myBid); 33 cout << "日盛上选基金单位及净值: " 34 << "(" << myBid->getUnit() << ")" 35 << "(" << myFund->getPrice() << ")" << endl << endl; 36 37 cout << "总资产为: " 38 << myAccount.calcAsset() << endl << endl; 39 40 system("PAUSE"); 41 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 42 }
下面我们来画一下UML图,并且用UML自动生成C++代码来做一个比较
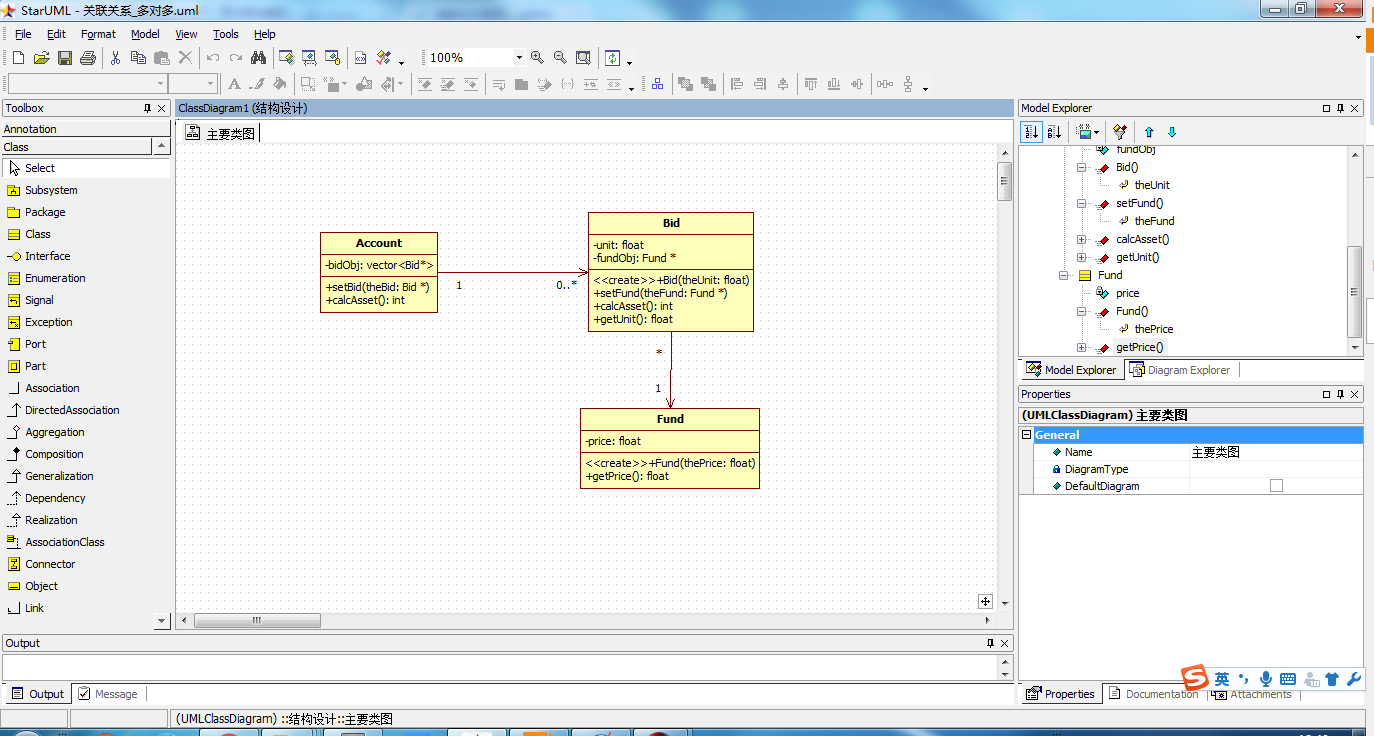
生成代码对比
Account.h
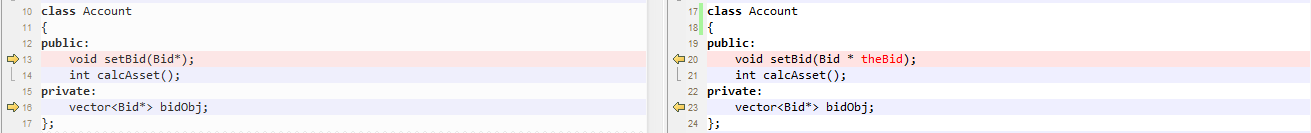
达到预期
Bid.h
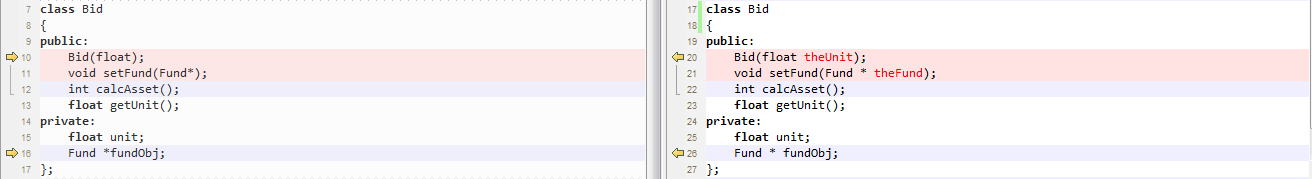
达到预期
Fund.h

达到预期