![题目链接https://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1032
题目描述
Problems in Computer Science are often classified as belonging to a certain class of problems (e.g., NP, Unsolvable, Recursive). In this problem you will be analyzing a property of an algorithm whose classification is not known for all possible inputs.
Consider the following algorithm:
1. input n
2. print n
3. if n = 1 then STOP
4. if n is odd then n <- 3n + 1
5. else n <- n / 2
6. GOTO 2
Given the input 22, the following sequence of numbers will be printed 22 11 34 17 52 26 13 40 20 10 5 16 8 4 2 1
It is conjectured that the algorithm above will terminate (when a 1 is printed) for any integral input value. Despite the simplicity of the algorithm, it is unknown whether this conjecture is true. It has been verified, however, for all integers n such that 0 < n < 1,000,000 (and, in fact, for many more numbers than this.)
Given an input n, it is possible to determine the number of numbers printed (including the 1). For a given n this is called the cycle-length of n. In the example above, the cycle length of 22 is 16.
For any two numbers i and j you are to determine the maximum cycle length over all numbers between i and j.
因为题目数据很水,所以暴力15ms过。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int x, y, ans;
int main() {
while (scanf("%d%d", &x, &y) != EOF) {
printf("%d %d ", x, y);
if(x > y) swap(x, y);
ans = 0;
for(int i = x; i <= y; ++i){
ll s = i;
int cnt = 1;
while(s != 1){
if(s % 2) s = s * 3 + 1;
else s = s >> 1;
++cnt;
}
ans = ans > cnt ? ans : cnt;
}
printf("%d
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
因为一开始不知道数据怎么水,所以想了一个记忆化的做法。记忆每一次新产生数的次数,减少重复计算。
虽然题目给定的n < 1000000, 但在运算中会出现大于1000000的数造成数组越界,所以在记忆化的过程中要对大于1000000的数要特别处理。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int x, y, ans;
int a[N];
inline void init() {
a[1] = 1, a[2] = 2;
}
inline bool judge(ll x) {
if (x < N)
if (a[(int)x]) return 1;
return 0;
}
int GT(int t) {
if (t <= 2) return t;
if (t > N) {
ll s = t;
int cnt = 1;
while (s) {
if (judge(s)) return a[(int)s] + cnt - 1;
if (s % 2) s = s * 3 + 1;
else s = s >> 1;
++cnt;
}
return a[s] + cnt;
}
if (t % 2) a[t] = GT(t * 3 + 1) + 1;
else a[t] = GT(t >> 1) + 1;
return a[t];
}
int main() {
init();
while (scanf("%d%d", &x, &y) != EOF) {
printf("%d %d ", x, y);
ans = 0;
if (x > y) swap(x, y);
for (int i = x; i <= y; ++i) {
if(!a[i]) a[i] = GT(i);
ans = ans > a[i] ? ans : a[i];
}
printf("%d
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
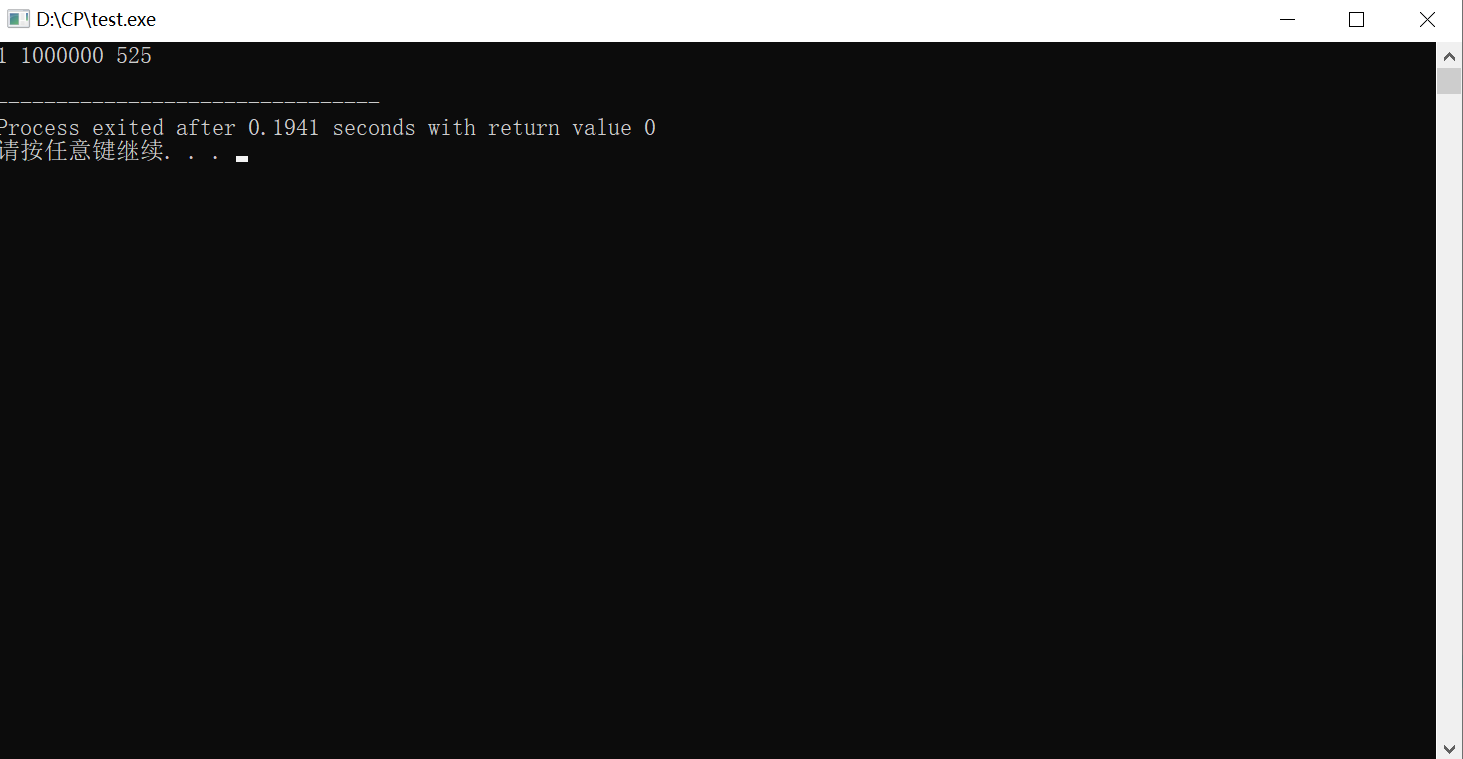
因为n <= 1000000时最大次数是525次,所以面对极限数据时可以预处理1~1000000,在加st表优化查询,这样理论上可以得到约等于
另外附上大佬的线段树做法https://blog.csdn.net/cowboy90/article/details/14225693]()