国有 n 个大城市和 m 条道路,每条道路连接这 n 个城市中的某两个城市。任意两个城市之间最多只有一条道路直接相连。这 m 条道路中有一部分为单向通行的道路,一部分为双向通行的道路,双向通行的道路在统计条数时也计为 1 条。
C 国幅员辽阔,各地的资源分布情况各不相同,这就导致了同一种商品在不同城市的价格不一定相同。但是,同一种商品在同一个城市的买入价和卖出价始终是相同的。
商人阿龙来到 C 国旅游。当他得知同一种商品在不同城市的价格可能会不同这一信息之后,便决定在旅游的同时,利用商品在不同城市中的差价赚回一点旅费。设 C 国 n 个城市的标号从 1~ n,阿龙决定从 1 号城市出发,并最终在 n 号城市结束自己的旅行。在旅游的过程中,任何城市可以重复经过多次,但不要求经过所有 n 个城市。阿龙通过这样的贸易方式赚取旅费:他会选择一个经过的城市买入他最喜欢的商品――水晶球,并在之后经过的另一个城市卖出这个水晶球,用赚取的差价当做旅费。由于阿龙主要是来 C 国旅游,他决定这个贸易只进行最多一次,当然,在赚不到差价的情况下他就无需进行贸易。
假设 C 国有 5 个大城市,城市的编号和道路连接情况如下图,单向箭头表示这条道路为单向通行,双向箭头表示这条道路为双向通行。
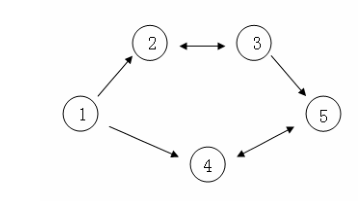
假设 1~n 号城市的水晶球价格分别为 4,3,5,6,1。
阿龙可以选择如下一条线路:1->2->3->5,并在 2 号城市以 3 的价格买入水晶球,在 3号城市以 5 的价格卖出水晶球,赚取的旅费数为 2。
阿龙也可以选择如下一条线路 1->4->5->4->5,并在第 1 次到达 5 号城市时以 1 的价格买入水晶球,在第 2 次到达 4 号城市时以 6 的价格卖出水晶球,赚取的旅费数为 5。
现在给出 n 个城市的水晶球价格,m 条道路的信息(每条道路所连接的两个城市的编号以及该条道路的通行情况)。请你告诉阿龙,他最多能赚取多少旅费。
题目可以用缩点 + 搜索的方法过。
用tarjan将原图每一个强联通块缩点用两个数组记录每一个块中价格的最小值和最大值,在重新建图。在之后的dfs中用变量flag记录是否可以达到终点,然后进行ans对比。
注意卖出东西的那一个城市一点用与终点n联通。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 5e5 + 10;
int n, m, tot1, top, tot2, cnt, tot, ans, flag;
int r[N], a[N], minn[N], maxx[N], stk[N], head1[N], dfn[N], head2[N], v[N], low[N], id[N];
struct Edg {
int to, nxt;
}e1[M], e2[M];
template <typename T>
inline void read(T& x) {
x = 0;
char c = getchar();
T op = 1;
for (; c < '0' || c > '9'; c = getchar())
if (c == '-') op = -1;
for (; c <= '9' && c >= '0'; c = getchar())
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + c - '0';
x *= op;
}
inline void add1(int x, int y) {
e1[++tot1].to = y;
e1[tot1].nxt = head1[x];
head1[x] = tot1;
}
inline void add2(int x, int y) {
e2[++tot2].to = y;
e2[tot2].nxt = head2[x];
head2[x] = tot2;
}
inline int min(int x, int y) {
return x < y ? x : y;
}
inline int max(int x, int y) {
return x > y ? x : y;
}
void tarjan(int x) {
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++cnt;
stk[++top] = x, v[x] = 1;
for (int i = head1[x]; i; i = e1[i].nxt) {
int to = e1[i].to;
if (!dfn[to])
tarjan(to), low[x] = min(low[x], low[to]);
else if (v[to]) low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[to]);
}
if (dfn[x] == low[x]) {
++tot;
while (stk[top + 1] != x) {
id[stk[top]] = tot;
minn[tot] = min(minn[tot], a[stk[top]]);
maxx[tot] = max(maxx[tot], a[stk[top]]);
v[stk[top]] = 0;
--top;
}
if(id[n] == tot) ans = max(ans, maxx[tot] - minn[tot]);
}
}
void dfs(int x) {
v[x] = 1;
if(x == id[n]) {flag = 1; return;}
for (int i = head2[x]; i; i = e2[i].nxt) {
if (!v[e2[i].to]) dfs(e2[i].to);
minn[e2[i].to] = min(minn[x], minn[e2[i].to]);
if(flag) ans = max(maxx[e2[i].to] - minn[e2[i].to], ans);
}
if(flag) ans = max(ans, maxx[x] - minn[x]);
}
int main() {
//freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
read(n), read(m);
memset(minn, 0x3f, sizeof(minn));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) read(a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int x, y, z;
read(x), read(y), read(z);
if (z == 1) add1(x, y);
else add1(x, y), add1(y, x);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = head1[i]; j; j = e1[j].nxt)
if (id[i] != id[e1[j].to]) add2(id[i], id[e1[j].to]), ++r[id[e1[j].to]];
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i, flag = 0)
if (!r[i]) dfs(i);
printf("%d
", ans);
return 0;
}