1. css中定位机制有三种: 标准文档流, 浮动, 绝对定位
2. 绝对定位就属于第三种定位, 用到position属性, 下面就是具体设置

相对定位:
相对于自身原有位置(就是普通流的时候)进行偏移(设置top, left...后)
仍然处于标准文档流中
随即拥有偏移属性和z-index属性
绝对定位:
建立了以包含块为基准的定位
完全脱离了标准文档流
随即拥有偏移属性和z-index属性
3. 先上示例代码
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 6 <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> 7 <title>Document</title> 8 <style type="text/css"> 9 .class1 { 10 height: 100px; 11 background-color: blue 12 } 13 .class2 { 14 position:relative; /*去掉后子元素会以html为参照物*/ 15 height: 50px; 16 background-color: green; 17 } 18 .class3 { 19 height: 80px; 20 background-color: red; 21 } 22 .child { 23 height: 20; 24 position:absolute; 25 top: 10px; 26 left: 30px; 27 background-color:gold; 28 } 29 </style> 30 </head> 31 <body> 32 <div class="class1"></div> 33 <div class="class2"> 34 <div class="child"> 35 Jason Zeng 36 </div> 37 </div> 38 <div class="class3"></div> 39 </body> 40 </html>
祖先元素设置了定位
1 .class2 { 2 position:relative; /*去掉后子元素会以html为参照物*/ 3 height: 50px; 4 background-color: green; 5 }

祖先元素没有设置定位
1 .class2 { 2 height: 50px; 3 background-color: green; 4 }
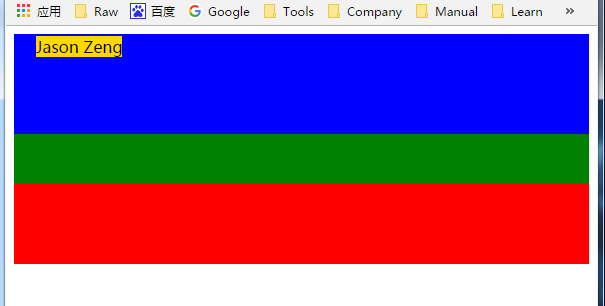
4.总结: 绝对定位时偏移参考物:
无已定位的祖先元素(包裹它的所有层都没有设置position属性): 以<html>为偏移参照物
有已定位的祖先元素: 以距其最近的已定位的祖先元素为偏移参照基准