Binary Tree Traversals
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 7357 Accepted Submission(s):
3378
Problem Description
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is
either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the
left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the
vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are
preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees
T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
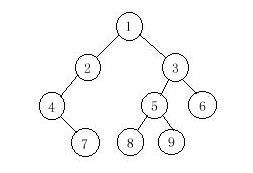
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.

Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line
of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of
vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the
preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always
correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
Output
For each test case print a single line specifying the
corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
9
1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6
4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
题意:知道二叉树的前序和中序遍历,求二叉树的后续序遍历。
思路:数据结构题,前序遍历的数列中(或数列的某个子串)中的找到第一个字符,在中序遍历中查找位置,找到位置后即可确定该字符的左右儿子,分别再递归查找,建立出二叉树,再进行后序遍历即可。
AC代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<set> #include<map> #include<vector> #include<queue> using namespace std; const int N_MAX = 1000+4; struct treeNode { int data; treeNode* left; treeNode* right; }; treeNode tree[N_MAX]; int preorder[N_MAX], inorder[N_MAX]; bool what = 0; treeNode* create(int *a,int *b,int n) { treeNode *tree; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (a[0] == b[i]) {//找到了父亲节点,此时i代表左子树的节点数量 tree = new treeNode; tree->data = b[i]; tree->left = create(a + 1, b, i); tree->right = create(a+i+1,b+i+1,n-i-1); return tree; } } return NULL; } void postorder(treeNode* root) { if (root != NULL) { postorder(root->left); postorder(root->right); if (what)printf(" "); else what++; printf("%d", root->data); } } int main() { int n; while (scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d",&preorder[i]); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d",&inorder[i]); treeNode*root = create(preorder, inorder, n); what = 0; postorder(root); printf(" "); } return 0; }