一 对象锁和类锁的关系
/* * 对象锁和【类锁】 全局锁的关系? 对象锁是用于对象实例方法,或者一个对象实例上的 this 类锁是用于类的静态方法或者一个类的class对象上的。 Ag.class 我们知道,类的对象实例可以有很多个,但是每个类只有一个class对象, 所以不同对象实例的对象锁是互不干扰的,但是每个类只有一个类锁。 */
对象锁, 不同对象。
public class SynchrDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(); Thread1 thread2 = new Thread1(); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class Ag{ public void show(){ // this 是当前对象的实例,由于新建两个对象,不是同一对象。所以这里是锁不住的。 代码快的方式,比修饰在方法上更细化控制。 synchronized (this) { for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i=" + i); } } } } class Thread1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { //这里是新建对象 主方法中new了两个thread,就是new了两个Ag对象 Ag ag = new Ag(); ag.show(); } }
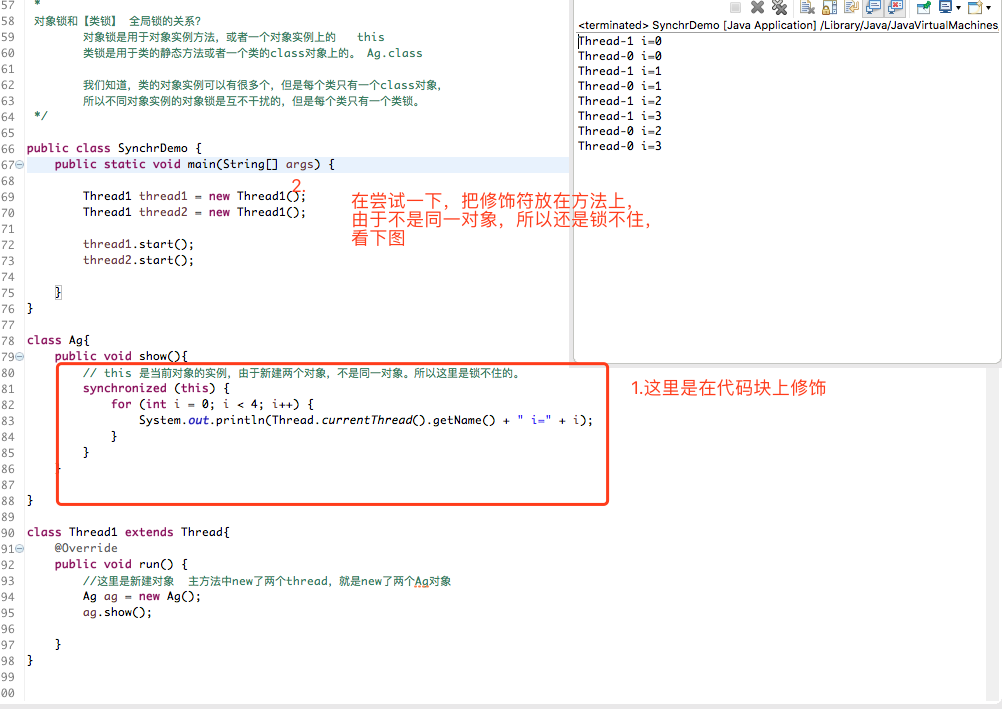
关键字修饰方法
public class SynchrDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(); Thread1 thread2 = new Thread1(); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class Ag{ // 这次修饰的是方法,范围比代码块要大,意味着在这个区域内,锁生效的时候,都是在阻塞,其他线程的等待时间就会增加。 // 这次实验的非同一对象,所以这里的锁是不起作用的。 public synchronized void show(){ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i=" + i); } } } class Thread1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { //这里是新建对象 主方法中new了两个thread,就是new了两个Ag对象 Ag ag = new Ag(); ag.show(); } }
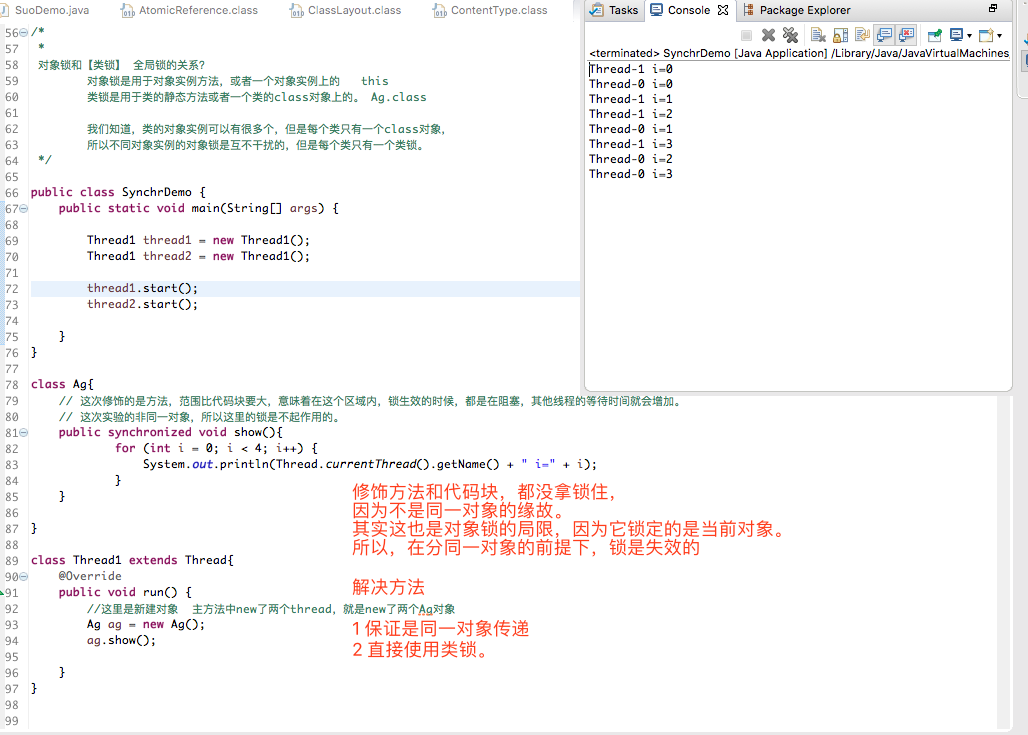
二 对象锁 同一对象
package com.aaa.threaddemo; /* * 一 Java中的关键字 synchronized 是啥? * synchronized是Java提供的一个并发控制的关键字。 * * 用法:同步方法 和 同步代码块。 * 可以修饰方法 也可以 修饰代码块。 * * 作用: 被synchronized修饰的代码块及方法,在同一时间,只能被单个线程访问。【保证线程安全】 1 修饰方法和代码块有什么不同? 二者的结果是一样的 修饰方法时,作用域是整个方法,控制的范围大。 synchronized 代码块 可控制具体的作用域,更精准控制提高效率。 减少阻塞带来的时间问题。 2 同步锁的给谁用的? 同步锁基于对象,只要锁的来源一致,即可达到同步的作用。 所以,但对象不一样,则不能达到同步效果。 3 synchronized修饰方法,代码块,锁未释放,此时,其他线程调用同一对象的其他被synchronized修饰的方法,代码块,会如何? 当线程 A 调用某对象的synchronized 方法 或者 synchronized 代码块时,若同步锁未释放, 其他线程调用同一对象的其他 synchronized 方法 或者 synchronized 代码块时将被阻塞,直至线程 A 释放该对象的同步锁。(注意:重点是其他) 4 调用非synchronized方法 ,代码快呢? 当线程 A 调用某对象的synchronized 方法 或者 synchronized 代码块时,无论同步锁是否释放, 其他线程调用同一对象的其他 非 synchronized 方法 或者 非 synchronized 代码块时可立即调用。 5 全局锁如何实现? 全局锁: 锁住整个 Class,而非某个对象或实例。1-4都是实例锁 实现: 静态 synchronized 方法 static 声明的方法为全局方法,与对象实例化无关, 所以 static synchronized 方法为全局同步方法,与对象实例化无关。 6 synchronized 具体 Class 的代码块? synchronized (Ag.class) 获得的同步锁是全局的, static synchronized 获得的同步锁也是全局的,同一个锁,所以达到同步效果。 7 对象锁和【类锁】 全局锁的关系? 对象锁是用于对象实例方法,或者一个对象实例上的 this 类锁是用于类的静态方法或者一个类的class对象上的。 Ag.class 我们知道,类的对象实例可以有很多个,但是每个类只有一个class对象, 所以不同对象实例的对象锁是互不干扰的,但是每个类只有一个类锁。 * * */ /* * 对象锁和【类锁】 全局锁的关系? 对象锁是用于对象实例方法,或者一个对象实例上的 this 类锁是用于类的静态方法或者一个类的class对象上的。 Ag.class 我们知道,类的对象实例可以有很多个,但是每个类只有一个class对象, 所以不同对象实例的对象锁是互不干扰的,但是每个类只有一个类锁。 */ public class SynchrDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 改造后,可以确保是同一对象 验证 synchronized 是否生效 Ag ag = new Ag(); Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(ag); Thread1 thread2 = new Thread1(ag); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class Ag{ // 这次修饰的是方法,范围比代码块要大,意味着在这个区域内,锁生效的时候,都是在阻塞,其他线程的等待时间就会增加。 // 这次实验的同一对象,所以这里的锁是起作用的。 public synchronized void show(){ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i=" + i); } } } /* * 改造一些 对象的生成,确保在Thread1 中获得的是同一对象 */ class Thread1 extends Thread{ private Ag mag; public Thread1(Ag ag) { mag = ag; } @Override public void run() { mag.show(); } }
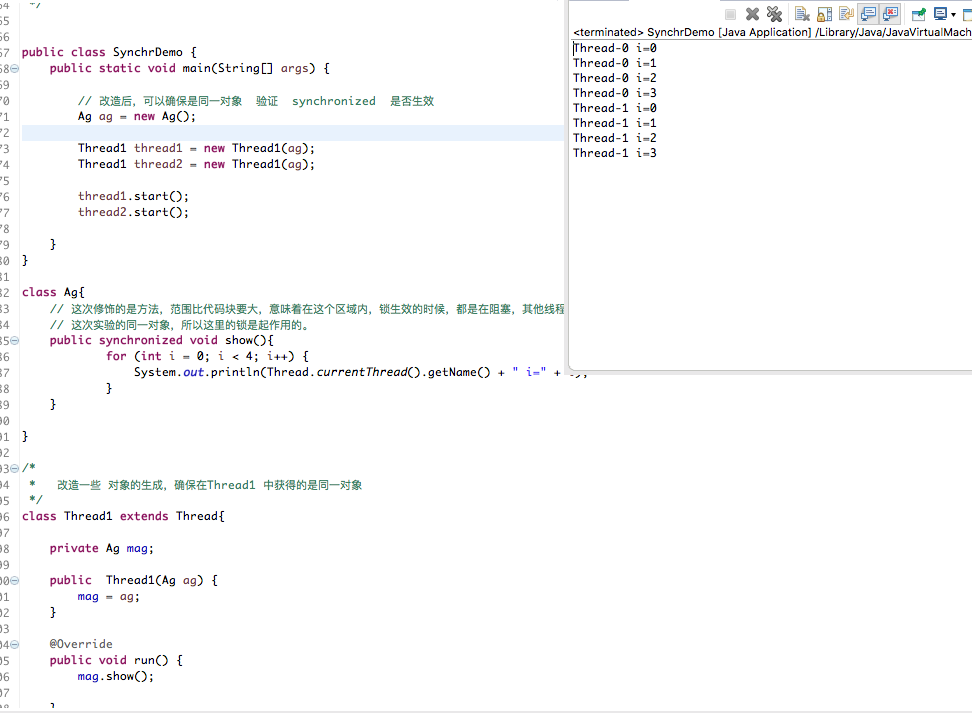
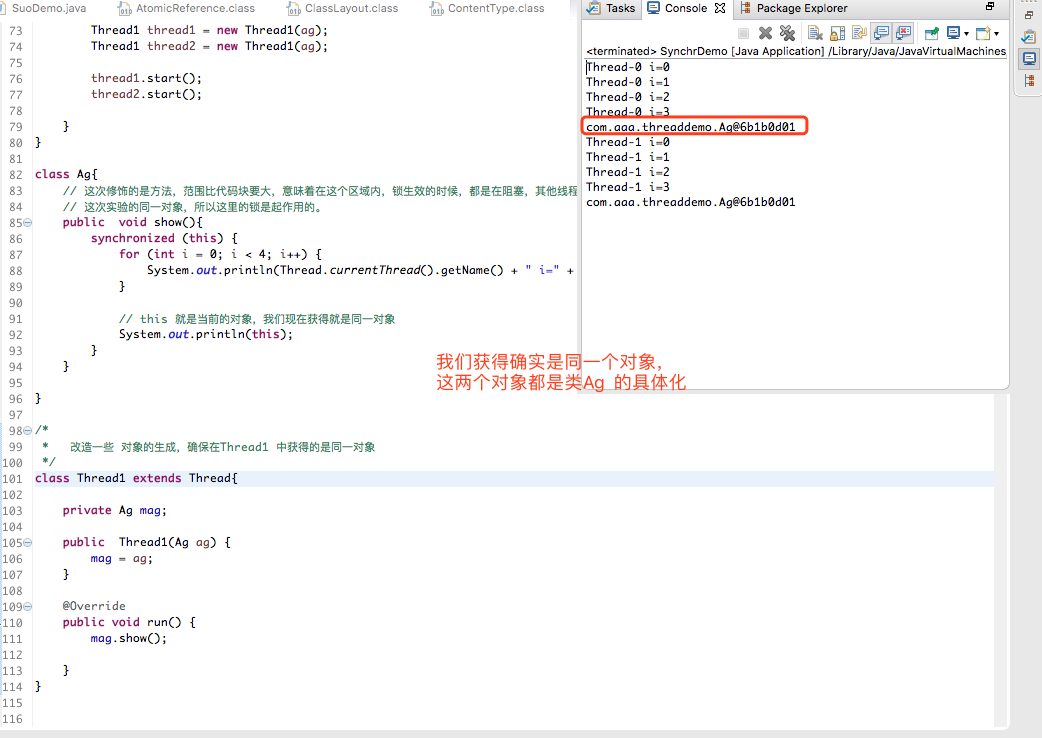
验证代码快的方式?
public class SynchrDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 改造后,可以确保是同一对象 验证 synchronized 是否生效 Ag ag = new Ag(); Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(ag); Thread1 thread2 = new Thread1(ag); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class Ag{ // 这次修饰的是方法,范围比代码块要大,意味着在这个区域内,锁生效的时候,都是在阻塞,其他线程的等待时间就会增加。 // 这次实验的同一对象,所以这里的锁是起作用的。 public void show(){ synchronized (this) { for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i=" + i); } // this 就是当前的对象,我们现在获得就是同一对象 System.out.println(this); } } } /* * 改造一些 对象的生成,确保在Thread1 中获得的是同一对象 */ class Thread1 extends Thread{ private Ag mag; public Thread1(Ag ag) { mag = ag; } @Override public void run() { mag.show(); } }
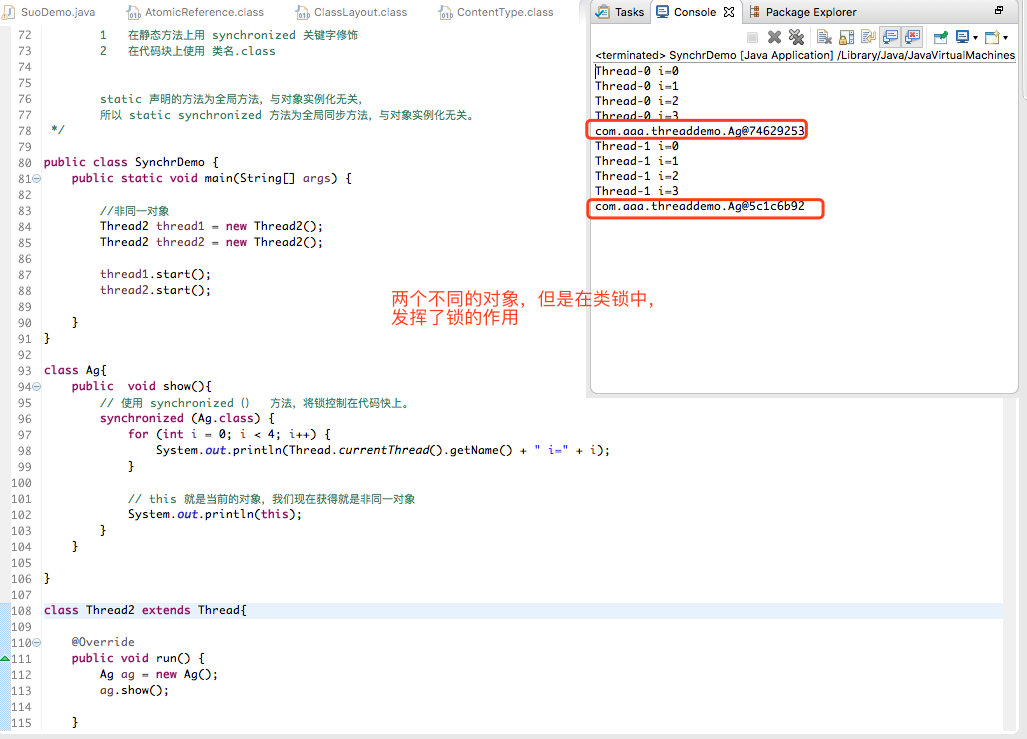
三 类锁? 非同一对象
/* * * 类锁,全局锁如何实现? 全局锁: 锁住整个 Class,而非某个对象或实例 实现: 1 在静态方法上用 synchronized 关键字修饰 2 在代码块上使用 类名.class static 声明的方法为全局方法,与对象实例化无关, 所以 static synchronized 方法为全局同步方法,与对象实例化无关。 */ public class SynchrDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //非同一对象 Thread2 thread1 = new Thread2(); Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2(); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class Ag{ public void show(){ // 使用 synchronized() 方法,将锁控制在代码快上。 synchronized (Ag.class) { for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i=" + i); } // this 就是当前的对象,我们现在获得就是非同一对象 System.out.println(this); } } } class Thread2 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { Ag ag = new Ag(); ag.show(); } }
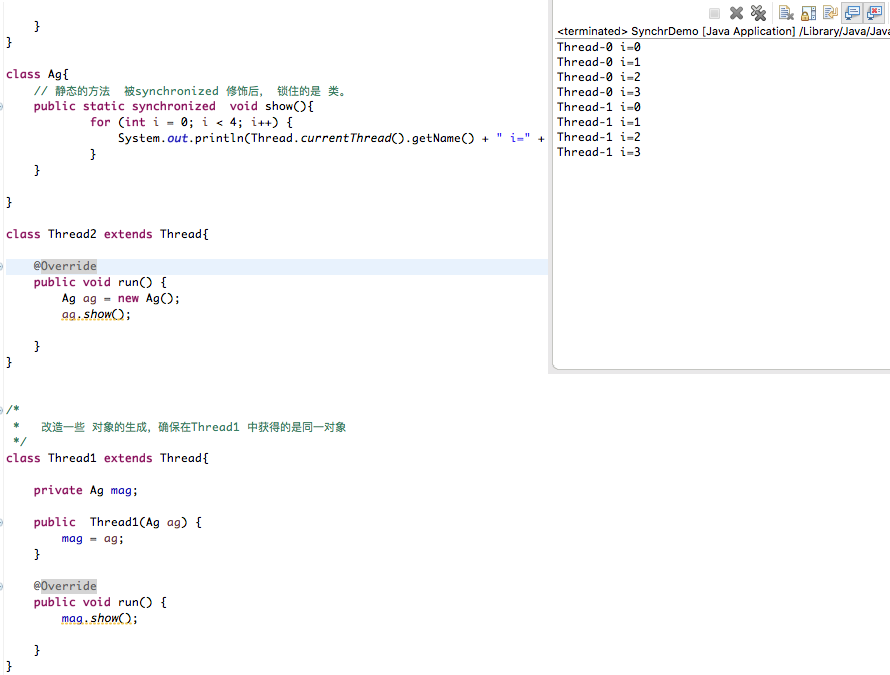
测试 关键字修饰 static 方法
public class SynchrDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //非同一对象 Thread2 thread1 = new Thread2(); Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2(); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class Ag{ // 静态的方法 被synchronized 修饰后, 锁住的是 类。 public static synchronized void show(){ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " i=" + i); } } } class Thread2 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { Ag ag = new Ag(); ag.show(); } }