
二
package com.aaa.threaddemo; /* * 一 实现多线程有哪四种方式? * 1.继承Thread类 * 2.实现runnable接口 * */ public class CreatThreadMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo2 thread2 = new Demo2(); //实例化 我们的demo2 thread Thread thread = new Thread(thread2); //把new的 demo2 thread 对象,放入Thread中 ,然后开启start方法。 thread.start(); } } /* * 1 继承一个thread类 * thread是runnable的实现类,代表一个线程的实例。 * 里面有个一个native方法 start()方法,他可以启动一个新的线程, * 并执行run方法 */ class Demo1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("继承thread 重写run方法 调用start, 开启一个多线程"); } } /* * 二 实现runnable接口 * 注意!Java中只有单继承机制,已经有继承的子类如何实现多线程? * 可以考虑runnable接口。 * * 当我们的实例对象demo2实现runnable接口之后,还需要new一个Thread, * 把 demo2 当做target 传入到Thread中,才能调用star方法,开启多线程。 */ class Demo2 extends CreatThreadMethod implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("在继承的基础上,实现runnable接口,开启多线程"); } }
三 有返回值的线程?
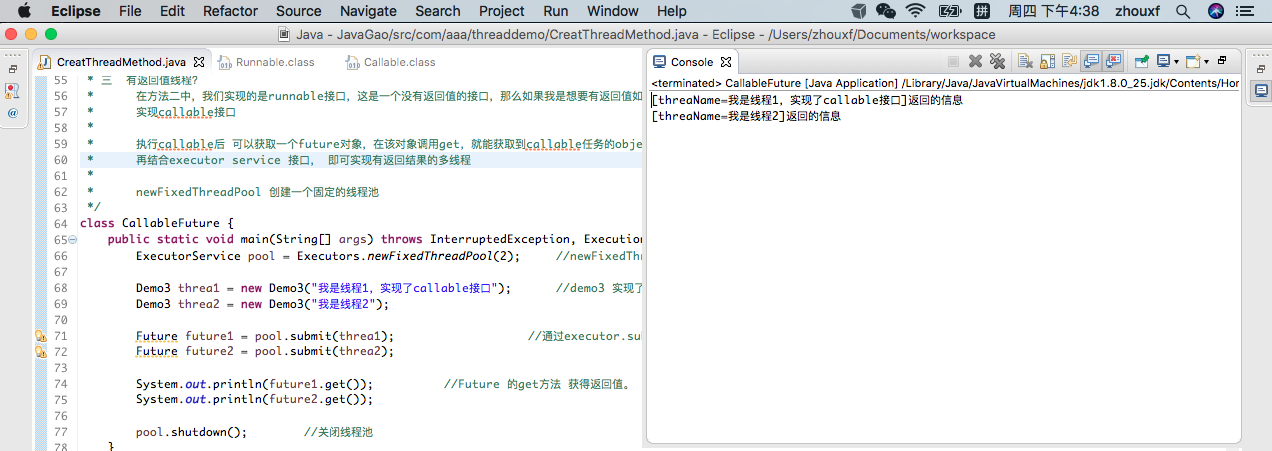
package com.aaa.threaddemo; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; /* * 一 实现多线程有哪四种方式? * 1.继承Thread类 * 2.实现runnable接口 * 3.ExecutorService、Callable<Class>、Future 有返回值线程 * */ public class CreatThreadMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo2 thread2 = new Demo2(); //实例化 我们的demo2 thread Thread thread = new Thread(thread2); //把new的 demo2 thread 对象,放入Thread中 ,然后开启start方法。 thread.start(); } } /* * 1 继承一个thread类 * thread是runnable的实现类,代表一个线程的实例。 * 里面有个一个native方法 start()方法,他可以启动一个新的线程, * 并执行run方法 */ class Demo1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("继承thread 重写run方法 调用start, 开启一个多线程"); } } /* * 二 实现runnable接口 * 注意!Java中只有单继承机制,已经有继承的子类如何实现多线程? * 可以考虑runnable接口。 * * 当我们的实例对象demo2实现runnable接口之后,还需要new一个Thread, * 把 demo2 当做target 传入到Thread中,才能调用star方法,开启多线程。 */ class Demo2 extends CreatThreadMethod implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("在继承的基础上,实现runnable接口,开启多线程"); } } /* * 三 有返回值线程? * 在方法二中,我们实现的是runnable接口,这是一个没有返回值的接口,那么如果我是想要有返回值如何处理? * 实现callable接口 * * 执行callable后 可以获取一个future对象,在该对象调用get,就能获取到callable任务的object。 * 再结合executor service 接口, 即可实现有返回结果的多线程 * * newFixedThreadPool 创建一个固定的线程池 */ class CallableFuture { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //newFixedThreadPool(); 创建一个固定的线程池 2 个 Demo3 threa1 = new Demo3("我是线程1,实现了callable接口"); //demo3 实现了callable接口 Demo3 threa2 = new Demo3("我是线程2"); Future future1 = pool.submit(threa1); //通过executor.submit提交一个Callable,返回一个Future,然后通过这个Future的get方法取得返回值。 Future future2 = pool.submit(threa2); System.out.println(future1.get()); //Future 的get方法 获得返回值。 System.out.println(future2.get()); pool.shutdown(); //关闭线程池 } } /* ExecutorService 接口? <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task); <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result); Future<?> submit(Runnable task); 一 callable 和 runnable接口的区别 public interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception; } 可以看到在callable里面, 有一个泛型V call方法中返回一个这个类型的值 interface Runnable { public abstract void run(); } runnable 这里是没有返回值的 二 Future 是个啥? public interface Future<V> { boolean cancel(boolean var1); boolean isCancelled(); boolean isDone(); V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; V get(long var1, TimeUnit var3) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException; } Future 也是一个接口,使用它的get()方法,可以获得任务执行的返回值。 */ class Demo3 implements Callable<Object>{ private String threadName; public Demo3(String threadName) { this.threadName = threadName; } @Override public Object call() throws Exception { return "[threaName=" + threadName + "]" + "返回的信息"; } }
四 线程池的方式
package com.aaa.threaddemo; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; /* * 一 实现多线程有哪四种方式? * 1.继承Thread类 * 2.实现runnable接口 * 3.ExecutorService、Callable<Class>、Future 有返回值线程 * 4.基于线程池的方式 * */ public class CreatThreadMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo2 thread2 = new Demo2(); //实例化 我们的demo2 thread Thread thread = new Thread(thread2); //把new的 demo2 thread 对象,放入Thread中 ,然后开启start方法。 thread.start(); } } /* * 1 继承一个thread类 * thread是runnable的实现类,代表一个线程的实例。 * 里面有个一个native方法 start()方法,他可以启动一个新的线程, * 并执行run方法 */ class Demo1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("继承thread 重写run方法 调用start, 开启一个多线程"); } } /* * 二 实现runnable接口 * 注意!Java中只有单继承机制,已经有继承的子类如何实现多线程? * 可以考虑runnable接口。 * * 当我们的实例对象demo2实现runnable接口之后,还需要new一个Thread, * 把 demo2 当做target 传入到Thread中,才能调用star方法,开启多线程。 */ class Demo2 extends CreatThreadMethod implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("在继承的基础上,实现runnable接口,开启多线程"); } } /* * 三 有返回值线程? * 在方法二中,我们实现的是runnable接口,这是一个没有返回值的接口,那么如果我是想要有返回值如何处理? * 实现callable接口 * * 执行callable后 可以获取一个future对象,在该对象调用get,就能获取到callable任务的object。 * 再结合executor service 接口, 即可实现有返回结果的多线程 * * newFixedThreadPool 创建一个固定的线程池 */ class CallableFuture { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //newFixedThreadPool(); 创建一个固定的线程池 2 个 Demo3 threa1 = new Demo3("我是线程1,实现了callable接口"); //demo3 实现了callable接口 Demo3 threa2 = new Demo3("我是线程2"); Future future1 = pool.submit(threa1); //通过executor.submit提交一个Callable,返回一个Future,然后通过这个Future的get方法取得返回值。 Future future2 = pool.submit(threa2); System.out.println(future1.get()); //Future 的get方法 获得返回值。 System.out.println(future2.get()); pool.shutdown(); //关闭线程池 } } /* ExecutorService 接口? <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task); <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result); Future<?> submit(Runnable task); 一 callable 和 runnable接口的区别 public interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception; } 可以看到在callable里面, 有一个泛型V call方法中返回一个这个类型的值 interface Runnable { public abstract void run(); } runnable 这里是没有返回值的 二 Future 是个啥? public interface Future<V> { boolean cancel(boolean var1); boolean isCancelled(); boolean isDone(); V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; V get(long var1, TimeUnit var3) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException; } Future 也是一个接口,使用它的get()方法,可以获得任务执行的返回值。 */ class Demo3 implements Callable<Object>{ private String threadName; public Demo3(String threadName) { this.threadName = threadName; } @Override public Object call() throws Exception { return "[threaName=" + threadName + "]" + "返回的信息"; } } /* * 为啥使用线程池? * 1 资源的宝贵性 一个线程系统中的创建是一个复杂的过程。 * 2 便于管理 提高效率 * 3 缓存的策略 线程池 * * */ class ThreadPool{ public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //创建一个线程池 固定容量是5 while(true){ pool.execute(new Runnable() { //提交多个线程任务 并执行 @Override public void run() { System.out.println( "当前线程【" +Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】 正在运行"); try { Thread.sleep(3000); //让线程睡一会 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } } }