memset()函数
首先要知道memset函数是对字节为单位进行赋值的;
ios::binary和ios::text打开文件区别,fstream读写文件示例
1.text方式写入文件会将换行(/n)扩展成/r/n, 读文件时则自动转换回来
2.binary方式则不会作任何扩展,与读写内容一致
3.默认为text方式
转自博客:https://blog.csdn.net/wangpf2008/article/details/5637350
seekg()/seekp()与tellg()/tellp()的用法详解
对输入流操作:seekg()与tellg()
对输出流操作:seekp()与tellp()
下面以输入流函数为例介绍用法:
seekg()是对输入文件定位,它有两个参数:第一个参数是偏移量,第二个参数是基地址。
对于第一个参数,可以是正负数值,正的表示向后偏移,负的表示向前偏移。而第二个参数可以是:
ios::beg:表示输入流的开始位置
ios::cur:表示输入流的当前位置
ios::end:表示输入流的结束位置
tellg()函数不需要带参数,它返回当前定位指针的位置,也代表着输入流的大小。
转自博客:https://blog.csdn.net/mafuli007/article/details/7314917
C++通过Read函数读取文件
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <fstream> 3 #include <vector> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 7 template<typename T> 8 std::vector<T> ReadArray(std::ifstream &in, int size) //size标识vector的大小 9 { 10 std::vector<T> v(size, 0); 11 in.read((char*)(&v[0]), sizeof(T)*size); 12 return v; 13 } 14 15 int main() { 16 17 ifstream in("TEST.txt");//创建文件流并于txt文件绑定 18 19 //获取文件的大小 20 in.seekg(0, in.end); 21 int length = in.tellg(); 22 in.seekg(0, in.beg); 23 24 char* temp = new char[length]; 25 26 if (in.is_open()) { 27 cout << "Now reading..." << endl; 28 in.read(temp, length); //读取文件 29 } 30 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) 31 { 32 cout << temp[i] <<" "; 33 } 34 35 cout << endl; 36 37 //将流中的内容存储到容器中 38 in.seekg(0, in.beg); //将指针指向文件开头处 39 vector<char> textVec; 40 textVec = ReadArray<char>(in, length); 41 42 cout << textVec[1] << endl; 43 44 in.close(); 45 system("PAUSE"); 46 47 }
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/alex1997222/article/details/78976154
C语言中的pow()函数
原型:extern float pow(float x, float y);
用法:#include <math.h>
功能:计算x的y次幂。
说明:x应大于零,返回幂指数的结果
srand()和rand()函数
srand()函数用来保证rand()函数每次生成的随机数都不一样
且srand()函数只能执行一次
srand()默认参数为1,此时rand()函数每次生成的随机数还是一样的
srand()参数一般为0或者是time(0)或time(Null)
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/u013745804/article/details/82379266
assert()函数
assert宏的原型定义在<assert.h>中,其作用是如果它的条件返回错误,则终止程序执行。
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/lvchaoshun/p/7816288.html
memset()函数
memcmp (const void*, const void*, size_t)
第一个参数:目的地址
第二个参数:源地址
第三个参数:所需要复制的字节数
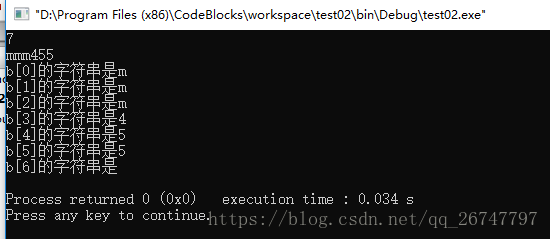
1 int main() 2 { 3 char a[4] = "mmmm"; 4 char b[7] = "123455"; 5 memcpy(b,a,3); 6 printf("%d ",sizeof(b)); 7 printf("%s ",b); 8 for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(b); i++) 9 printf("b[%d]的字符串是%c ",i,b[i]); 10 return 0; 11 }
执行结果;
C++读取含有逗号的数据
https://blog.csdn.net/techfield/article/details/77855620
https://blog.csdn.net/zsc201825/article/details/84939375
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_35821976/article/details/79412090 可用
strtok()函数
#include <string.h>
char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);
char *strtok_r(char *str, const char *delim, char **saveptr);
功能:分解字符串为一组标记串。str为要分解的字符串,delim为分隔符字符串。
说明:首次调用时,str必须指向要分解的字符串,随后调用要把s设成NULL。
strtok在str中查找包含在delim中的字符并用NULL('/0')来替换,直到找遍整个字符串。
返回指向下一个标记串。当没有标记串时则返回空字符NULL。

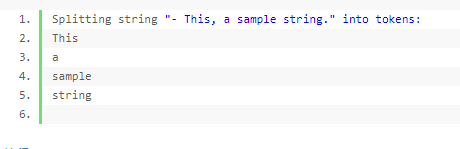
/* strtok example */ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main () { char str[] ="- This, a sample string."; char * pch; printf ("Splitting string "%s" into tokens: ",str); pch = strtok (str," ,.-"); while (pch != NULL) { printf ("%s ",pch); pch = strtok (NULL, " ,.-"); } return 0; }
输出:
c++传递二维数组方法

1 //二维静态数组 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void ces(int **num) 6 { 7 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 8 for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++){ 9 cout<<*((int *)num+5*i+j)<<" "; //这样可以 10 // cout<<((int *)num+5*i)[j]<<" "; //这样可以 11 // cout<<num[i][j]<<" "; //这样不可以 12 } 13 cout<<endl; 14 } 15 } 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 int num[5][5]; 20 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ 21 for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++){ 22 num[i][j] = i * j; 23 } 24 } 25 ces((int **)num); //这样可以 26 // ces(num); //这样不可以 27 return 0; 28 }

1 //二维动态数组 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void ces(int **num, int m, int n) 6 { 7 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){ 8 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){ 9 // cout<<*((int *)num+5*i+j)<<" "; //这样不行 10 // cout<<((int *)num+5*i)[j]<<" "; //这样不行 11 cout<<num[i][j]<<" "; //这样可以 12 } 13 cout<<endl; 14 } 15 } 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 int m = 5, n = 5, i, j; 20 int **num = new int*[m]; 21 for (i = 0; i < m; i++) 22 { 23 num[i] = new int[n]; 24 } 25 for (i = 0; i < m; i++){ 26 for (j = 0; j < n; j++){ 27 num[i][j] = i * j; 28 } 29 } 30 ces(num, m, n); //这样可以 31 32 // ces((int **)num, m, n); //这样可以 33 for (i = 0; i < m; i++) 34 { 35 delete[] num[i]; 36 } 37 delete[] num; 38 return 0; 39 }
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/usa007lhy/p/3286186.html
c_str()函数
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/renzhuang/articles/6092935.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/newzol/p/8686076.html
科学记数法相关
https://blog.csdn.net/lanzhihui_10086/article/details/39989841
mysql_affected_rows()
对于SELECT操作,mysql_affected_rows()等价于mysql_num_rows(),即查询结果的行数,但是显示使用mysql_num_rows()更加合适。
因此mysql_affected_rows()一般用来在DELETE, INSERT , REPLACE , UPDATE语句执行完成之后判断数据表中变化的行数(如果数据表没有变化,则行数为0)。
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/koastal/article/details/74783278
类似 error C4996: 'sprintf': This function or variable may be unsafe.解决方法
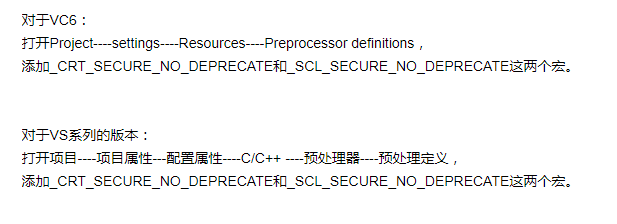
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/douzi2/p/3974959.html
关于scanf()、gets()等函数的讲解(很详细)
下面放出博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/xiao_yanci/article/details/80588934
另外如果在vs中使用gets(a)函数会报错标识符找不到,将gets()改为gets_s()就好了
