归一化交叉相关Normalization cross correlation (NCC)
NCC正如其名字,是用来描述两个目标的相关程度的,也就是说可以用来刻画目标间的相似性。一般NCC也会被用来进行图像匹配,即在一个图像中搜索与一小块已知区域的NCC最高的区域作为对应匹配,然后对准整幅图像。
假设两幅图像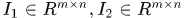 ,那么其NCC可如下计算:
,那么其NCC可如下计算:

其中 表示点乘运算。
表示点乘运算。
比如下面两幅图像,我们想对齐

part1.jpg

part2.jpg
首先在一幅图像中选取两个图像都有的区域作为templete

templete.jpg
然后在另一幅图像中选取包含templete的区域

region.jpg
最终对齐的结果如下

result.jpg
- function NCC
- close all
- part2 =imread('part1.png');
- part1 = imread('part2.png');
-
- imshow(part2);title('part2')
- figure, imshow(part1);title('part1');
- % 选取template和搜索区域region. Note:template的大小必须小于region
- figure,
- [sub_part2,rect_part2]=imcrop(part2);% template
- [sub_part1,rect_part1]=imcrop(part1);% region
-
- figure, imshow(sub_part2)
- figure, imshow(sub_part1);
-
- [x,y,z] = normcorr2(double(sub_part2(:,:,1)),double(sub_part1(:,:,1)));
- figure,surf(x,y,z),shading flat
- %% 寻找偏置
- [~,imax]=max(z(:));%
- [yoffset,xoffset]=ind2sub(size(z),imax(1));
- %% 图像对齐
- % 配对点在第一幅图像中到边界的距离
-
- rect_part1=floor(rect_part1);
- left1=rect_part1(1)+xoffset;
- right1=size(part1,2)-left1;
- up1=rect_part1(2)+yoffset;
- down1 = size(part1,1)-left1;
- % 配对点在第二幅图像中到边界的距离
- rect_part2=floor(rect_part2);
- left2=rect_part2(1);
- right2=size(part2,2)-left2;
- up2=rect_part2(2);
- down2 = size(part2,1)-up2;
-
- img=zeros(max(up1,up2)+max(down1,down2)+1,max(left1,left2)+max(right1,right2)+1,size(part1,3));
- sx=max(left1,left2)+1;
- sy=max(up1,up2)+1;
- img(sy-up1+1:sy-up1+size(part1,1),sx-left1+1:sx-left1+size(part1,2),:)=part1;
- img(sy-up2+1:sy-up2+size(part2,1),sx-left2+1:sx-left2+size(part2,2),:)=part2;
- imshow(uint8(img));
- end
-
-
-
- function [x,y,z]=normcorr2(I1,I2)
- % I1,I2是单通道图像,即矩阵
- % I1 is template
- % I2 is the region where match pairs are searched
- [m1,n1]=size(I1);
- [m2,n2]=size(I2);
- z=conv2(I2,rot90(I1,2),'valid');
- im2=cumsum(I2.^2,1);
- im2=cumsum(im2,2);
- sum1=sum(sum(I1.^2,1),2);
- % nz=zeros(m2-m1+1,n2-n1+1);
- wrapIm2=zeros(1+m2,1+n2);
- wrapIm2(2:end,2:end)=im2;
- nz=(wrapIm2(m1+1:m2+1,n1+1:n2+1)+wrapIm2(1:m2-m1+1,1:n2-n1+1)-wrapIm2(1:m2-m1+1,n1+1:n2+1)-wrapIm2(m1+1:m2+1,1:n2-n1+1))*sum1;
- nz=sqrt(nz);
- z=z./nz;
- [x,y]=meshgrid(1:n2-n1+1,1:m2-m1+1);
- end

1477398865849.jpg

1477398880386.jpg

1477398892560.jpg

1477398906100.jpg

1477398924878.jpg
有些文献在计算卷积的时候,总说要把矩阵逆排序之后再对应相乘,包括conv2这个函数也是这么计算的。但实际上我们有一个templete和region,直接就是对应位置乘积之后作为卷积结果,也只有这样才能保证在匹配的位置处NCC系数最大,所以在代码里,我先对templete进行了逆序操作,在使用conv2卷积。
另外matlab2016添加了image registration 工具箱,里面可以直接计算NCC系数了,具体参见
http://cn.mathworks.com/help/images/examples/registering-an-image-using-normalized-cross-correlation.html.