(1)多层的异常捕获1
package Demo1; public class CatchWho { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
结果:

(2)多层的异常捕获2
package Demo1; public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
结果:

(3)多层异常捕获3
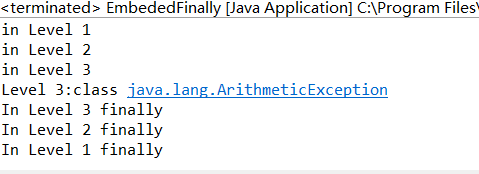
public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } // result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { . System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } }
结果:
(4)finally语句是否一定会执行?
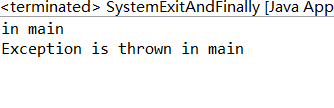
public static void main(String[] args) { try{ System.out.println("in main"); throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); //System.exit(0); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(0); } finally { System.out.println("in finally"); } }
结果:
结论:
很明显,根据结果来看,finally语句并不是一定要执行的,而不执行的条件根据调试便可以知道:
System.exit(0);
System.exit(0);语句是会打断finally的正常执行的。