
上图是本篇博客所要写的类的继承图
java.util.Collection
添加
boolean add(E e) // append the element
boolean addAll(Collection c) // append all element in c, must be the same type
清空
void clear() // delete all the element in Collection, but the collection still work
查找
boolean contains(Object o) //Returns true if this collection contains the specified element.

Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>(); Collection<String> c2 = new ArrayList<>(); coll.add("h"); coll.add("e"); System.out.println(coll); // [h, e] c2.add("h"); c2.add("a"); coll.addAll(c2); // [h, e, l, l] 把c2中元素全部加入coll中,类型必须相同 c2.clear(); // [] 只是清空元素,容器还在 boolean b = coll.contains("h"); // true 是否包含指定元素
迭代器
Iterator<E> iterator() // return a iterator object
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) System.out.print(it.next());
删除
boolean remove(Object o) // return false if not found the element , or true
boolean removeIf(Predicate<? extends E> filter) // functional interface

Collection<Integer> coll = new ArrayList<>(); coll.add(1); coll.add(2); coll.add(3); coll.add(4); coll.add(5); // 匿名内部类 coll.removeIf(new Predicate<Integer>(){ @Override public boolean test(Integer t) { return t > 3; } }); System.out.println(coll); // [1, 2, 3] // lambda表达式 coll.removeIf(t->{ return t > 3; });
大小
int size()
遍历
default void forEach(Consumer<? extends T> action) // Consumer is a functional interface

// anonymous inner class coll.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>(){ @Override public void accept(Integer t) { System.out.print(t); // 12345 } }); // lambda expression coll.forEach(t->{ System.out.print(t); // 12345 });
其他
Object[] toArray() // Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection.
List接口,父类方法就不赘述了,只写下子类方法
java.util.List;
添加
void add(int index, E e) // add the specified value at the specified position in list
获取
E get(int index) // Returns the element at the specified position in this list
查找
int indexOf(Object o) // same as lastIndexOf()
Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element , or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
删除
E remove(index) //Removes the element at the specified position.
修改
void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) // repalce each element with the method return value in functional interface

// anonymous inner class list.replaceAll(new UnaryOperator<Integer>() { @Override public Integer apply(Integer t) { return t+10; //[11, 12, 13, 14, 15] } }); // lambda expression list.replaceAll(t->{ return t + 10; });
E set(int index, E e) // Replaces the element at the specified position
排序
void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) // Sorts this list according to the order induced by the specified Comparator.

list.sort(new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) { return o2 - o1; // [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] } }); list.sort((o1, o2)->{ return o1 - o2; // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] });
ArrayList 底层是数组实现,查找快,在任意位置增删较慢,尽量不使用索引增删
复制 Object clone() // Returns a shallow copy of this ArrayList instance.
LinkedList 底层是双向链表,因此可以实现栈,队列,链表等数据结构
增加
void addFirst(E e) // equals to boolean offerFirst(E e)
void addLast(E e) // equals to boolean offerLast(E e) offer(E e) push(E e)
获取值
E getFirst() // E element() E peek() E peekFirst() is equals to this method
E getLast() // E peekLast()
删除
E removeFisrt() // E pop() pollFirst() E poll() Retrieves and removes the first element of this list, or returns null if this list is empty.
E removeLast() // E pollLast() Retrieves and removes the last element of this list, or returns null if this list is empty.
Set接口与Collection接口方法一致
HashSet底层用哈希表实现
,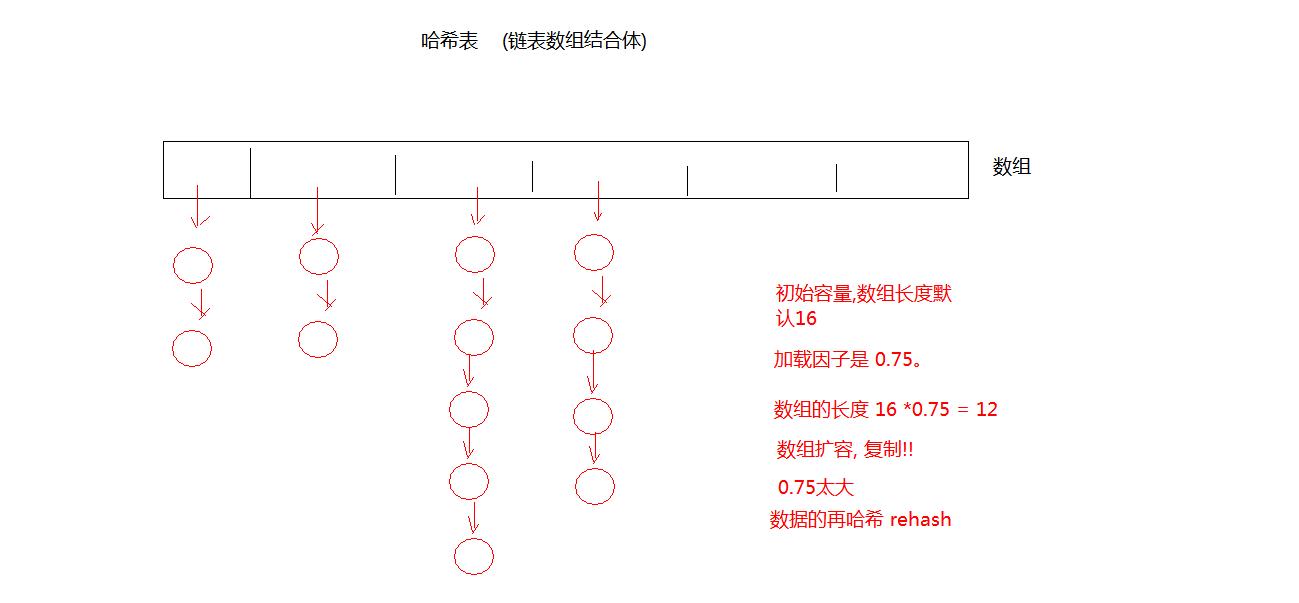
哈希表存储原理
1.首先调用本类的hashCode()方法算出哈希值
2.在容器中找是否与新元素哈希值相同的老元素,如果没有直接存入,如果有转到第三步
3.新元素会与该索引位置下的老元素利用equals方法一一对比
一旦新元素.equals(老元素)返回true,停止对比,说明重复,不再存入
如果与该索引位置下的老元素都通过equals方法对比返回false,说明没有重复,存入
字符串对象的哈希值

public int hashCode() { int h = hash;//hash初值为0 if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) { char val[] = value; for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) { h = 31 * h + val[i]; } hash = h; } return h; }
迭代器的并发修改异常 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException

public class ListDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("abc1"); list.add("abc2"); list.add("abc3"); list.add("abc4"); //对集合使用迭代器进行获取,获取时候判断集合中是否存在 "abc3"对象 //如果有,添加一个元素 "ABC3" Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ String s = it.next(); //对获取出的元素s,进行判断,是不是有"abc3" if(s.equals("abc3")){ list.add("ABC3"); } System.out.println(s); } } } 不能用两个迭代器同时操作集合,否则就会引起java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常 但下面的代码并没有引起异常 LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>(); list.add(2); list.add(3); list.add(4); System.out.println(list); Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { int a = it.next(); if(a == 3) it.remove(); }
如果两个对象的哈希值相同 ,两个对象的equals不一定返回true, 如String类的hashCode,不同的字符串有时会得到相同的哈希值
如果两个对象的equals方法返回true,两个对象的哈希值一定相同,这是java要求开发者的
Collections 集合工具类,静态方法
T binarySearch(List<? extends T> list, T key, Comparator<? extends T> c) // 无序也可以
int frequency(Collection<T> c, Object o) // 调用 对象的equals方法,返回 对象出现次数
T max(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp)
T min(Collection<? extends T> coll, Comparator<? super T> comp)

ArrayList<Heart> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Heart("good", 100)); list.add(new Heart("good", 80)); list.add(new Heart("good", 90)); list.add(new Heart("good", 110)); list.add(new Heart("good", 120)); // 匿名内部类 Heart h = Collections.max(list, new Comparator<Heart>() { @Override public int compare(Heart o1, Heart o2) { return o1.getJump() - o2.getJump(); // Heart [health=good, jump=120] } }); // lambda表达式 h = Collections.min(list,(h1, h2)->{ return h1.getJump() - h2.getJump(); //Heart [health=good, jump=80] });
反转
void reverse(List<?> list)
洗牌
void shuffle(List<?> list)
交换
void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j)
