配置文件 通过configpaser 模块进行读取

import configparser
class ReadConfig:
"""
完成配置文件的读取
"""
def __init__(self):
self.config = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.config.read(contants.global_file) # 先加载global
switch = self.config.getboolean('switch', 'on')
if switch: # 开关打开的时候,使用online的配置
self.config.read(contants.online_file, encoding='utf-8')
else: # 开关关闭的时候,使用test的配置
self.config.read(contants.test_file, encoding='utf-8')
def get(self, section, option):
return self.config.get(section, option)
config = ReadConfig()
正则是通过 re 模块
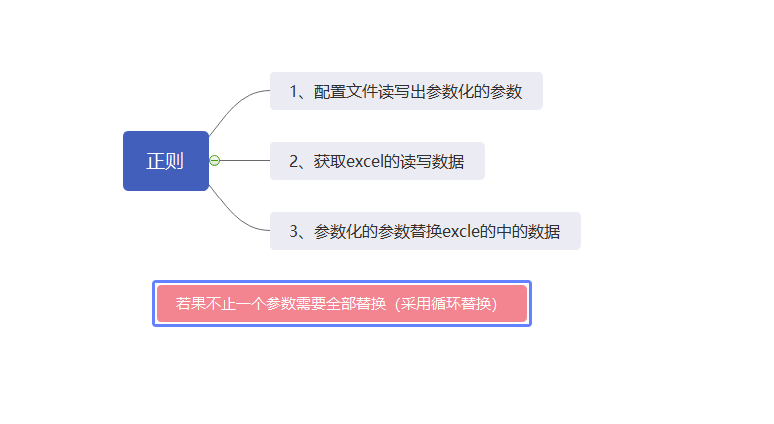
def DoRe(data):
"""
1.用正则表达式来匹配测试数据中的指定字符
2.根据指定字符获取到配置文件中对应的值
3.然后进行替换
"""
pattern = '#(.*?)#' # 正则表达式 匹配组当中多次或者最多一次单个字符
while re.search(pattern, data):
search = re.search(pattern, data) # 从任意位置开始找,找第一个就返回Match object, 如果没有找None
group = search.group(1) # 拿到参数化的KEY
value = config.get_value('data', group) # 根据KEY取配置文件里面的值
"""
记得替换后的内容,继续用data接收
"""
data = re.sub(pattern, value, data, count=1) # 查找替换,count查找替换的次数
print(data)
return data
if __name__ == '__main__':
a=DoRe('{"mobilephone":"#user_mobile#","pwd":"#user_password#"}')
print(a)
数据库通过pymsql
class DoMysql:
"""
初始化:
1.从配置文件获取到数据库的连接信息
2.建立光标
方法:
1.执行sql语句,获取一个或者全部数据
2.关闭光标和数据库
"""
def __init__(self):
self.mysql = pymysql.connect(host=config.get_value('testdb', 'host'),
port=int(config.get_value('testdb', 'port')),
user=config.get_value('testdb', 'user'),
password=config.get_value('testdb', 'password'),
db=config.get_value('testdb', 'db'),
charset=config.get_value('testdb', 'charset'))
#self.cursor = self.mysql.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) # 查询的数据以键值对返回
self.cursor = self.mysql.cursor() # 值返回查询的结果
def fetch_one(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
return self.cursor.fetchone()
def fetch_all(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
return self.cursor.fetchall()
def close(self):
self.cursor.close()
self.mysql.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
result = DoMysql().fetch_all('select id from loan where memberid=241;')
print(result)