Strategic Game
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2892 Accepted Submission(s): 1206
Problem Description
Bob enjoys playing computer games, especially strategic games, but sometimes he cannot find the solution fast enough and then he is very sad. Now he has the following problem. He must defend a medieval city, the roads of which form a tree. He has to put the minimum number of soldiers on the nodes so that they can observe all the edges. Can you help him?
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:
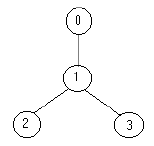
the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0 < n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:

the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the following table:
Sample Input
4 0:(1) 1 1:(2) 2 3 2:(0) 3:(0) 5 3:(3) 1 4 2 1:(1) 0 2:(0) 0:(0) 4:(0)
Sample Output
1 2
Source
Recommend
JGShining
邻接矩阵,枚举时可以省去很多不必要的点。
第一组测试数据:

code:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include <fstream> 4 #include <sstream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <set> 8 #include <utility> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <stack> 11 #include <list> 12 #include <vector> 13 #include <cstdio> 14 #include <cstdlib> 15 #include <cstring> 16 #include <cmath> 17 #include <ctime> 18 #include <ctype.h> 19 using namespace std; 20 21 #define MAXN 1510 22 23 int map[MAXN][MAXN]; 24 bool vst[MAXN]; 25 int path[MAXN]; 26 int cnt[MAXN]; 27 int n; 28 29 bool dfs(int v) 30 { 31 int i; 32 for(i=0;i<cnt[v];i++) 33 { 34 if(!vst[map[v][i]]) 35 { 36 vst[map[v][i]]=1; 37 if(path[map[v][i]]==-1||dfs(path[map[v][i]])) 38 { 39 path[map[v][i]]=v; 40 return true; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 return false; 45 } 46 47 int hungary() 48 { 49 int ans=0; 50 memset(path,-1,sizeof(path)); 51 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 52 { 53 memset(vst,0,sizeof(vst)); 54 if(dfs(i)) 55 ans++; 56 } 57 return ans/2; 58 } 59 60 int main() 61 { 62 int a; 63 int k; 64 while(~scanf("%d",&n)) 65 { 66 memset(map,0,sizeof(map)); 67 memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt)); 68 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 69 { 70 scanf("%d:(%d)",&a,&k); 71 while(k--) 72 { 73 int b; 74 scanf("%d",&b); 75 map[a][cnt[a]++]=b; 76 map[b][cnt[b]++]=a; 77 } 78 } 79 printf("%d\n",hungary()); 80 } 81 return 0; 82 }
再复习一遍:
对于任意图:
|最小边覆盖|+|最大匹配|=|V|
二分图的最大匹配=最小点覆盖数
对于二分图:
以下数值等价.
最大匹配
最小点覆盖
|V|-最大独立集(二分图or有向无环图)
|V|-最小边覆盖数
|V|-最小路径覆盖数(有向无环图)
|V|-最小路径覆盖数/2(无向图)
(上面括号里有有向无环图的,均是将一个点拆成两个点连边匹配)
由于任意图的那几个几乎用不到于是这里只贴二分图的定义
最小点覆盖(Konig定理):理解为点覆盖边,即用最小的点覆盖所有的边。(若一条边的其中一个端点被选用,这条边就被覆盖了)
最大独立集:求一个最大的点集,里面的点不存在任何的边相连。
最小边覆盖:理解为边覆盖点,用最少的边把图中的点全部覆盖。
最小路径覆盖:用最少的路径把图中的所有点覆盖。
另外:最大独立集与最小覆盖集互补。
需要明确的是:
“图的顶点数目等于顶点覆盖数与最大独立集合的大小之和”对于所有无向图有效
“最大匹配数=最小顶点覆盖数”只针对二部图有效