1.异常的传统处理方式
缺点:
[1] 通过判断影响执行效率。
[2] 判断逻辑和业务逻辑交织在一起,可维护性很差。
1 public class Test01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 4 System.out.println("请输入第一个数:"); 5 6 int num1 = 0; 7 if(sc.hasNextInt()) { 8 num1 = sc.nextInt(); 9 10 System.out.println("请输入第二个数:"); 11 int num2 = 0; 12 if(sc.hasNextInt()) { 13 num2 = sc.nextInt(); 14 15 if(0 == num2) { 16 System.out.println("除数不能为0!"); 17 }else { 18 int r = num1 / num2; 19 System.out.println("num1/num2 = "+r); 20 } 21 22 }else { 23 System.out.println("第二个数输入不是数字"); 24 } 25 26 }else { 27 System.out.println("第一个数输入不是数字!"); 28 } 29 } 30 }
2.Java异常处理的定义
异常是指在程序的运行过程中所发生的不正常的情况,它会中断正在运行的程序。
3.Java异常处理机制
java中通过异常处理机制为程序提供异常处理的能力,保持程序继续运行而不中断!
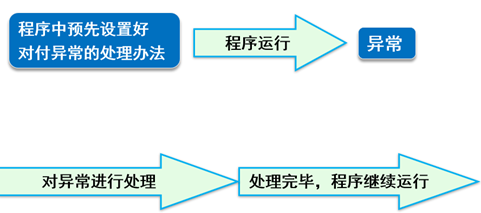
4.try/catch
把有可能产生异常的代码放到try代码块中,catch代码块负责捕获并处理异常。
[1]正常执行,没出现任何异常
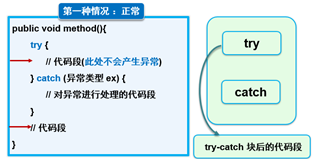
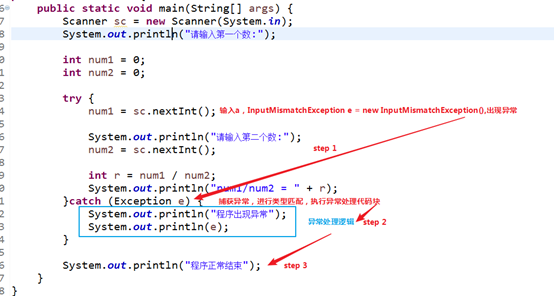
[2]出现异常,异常处理,正常结束
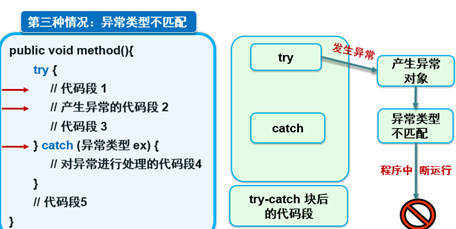
[3]异常类型不匹配
[4] 多重catch
1 public class Test03 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 4 System.out.println("请输入第一个数:"); 5 6 int num1 = 0; 7 int num2 = 0; 8 9 try { 10 num1 = sc.nextInt(); 11 12 System.out.println("请输入第二个数:"); 13 num2 = sc.nextInt(); 14 15 int r = num1 / num2; 16 System.out.println("num1/num2 = " + r); 17 }catch (ArithmeticException e) { 18 System.out.println("数学计算异常:"+e.getMessage()); 19 }catch(InputMismatchException e) { 20 System.out.println("输入不匹配异常:"+e.getMessage()); 21 }catch (Exception e) { 22 System.out.println("发送异常:"+e.getMessage()); 23 } 24 25 System.out.println("程序正常结束"); 26 } 27 }
5.try/catch/finally
把有可能产生异常的代码放到try中,catch负责匹配并处理异常,finally块用于进行收尾工作(关闭数据库、关闭文件、释放内存等资源),不管是否发生异常,finally都执行。
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 3 System.out.println("请输入第一个数:"); 4 5 int num1 = 0; 6 int num2 = 0; 7 8 try { 9 num1 = sc.nextInt(); 10 11 System.out.println("请输入第二个数:"); 12 num2 = sc.nextInt(); 13 14 int r = num1 / num2; 15 System.out.println("num1/num2 = " + r); 16 } catch (Exception e) { 17 System.out.println("程序出现异常"); 18 } finally { 19 System.out.println("不管是否出现异常,finally都执行"); 20 } 21 22 System.out.println("程序正常结束"); 23 }
6.异常的分类
Exception 根据是否处理分为两种情况。
RuntimeException:运行时异常。不要求程序必须做出处理。是所有运行时异常的父类。
CheckedException:检查时异常。要求程序必须处理,不处理编译不通过。
7.声明异常(throws关键字)
当一个方法可能存在异常,而此时自身又无法更好的处理,可以交给外界处理。此时用throws声明并抛出异常。
如果调用处也不知道如何处理异常,可选择继续声明异常,我们把这个过程称为异常上抛。
1 public class Test01 { 2 3 public static int div(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException{ 4 int r = 0; 5 r = a / b; 6 return r; 7 } 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 try { 11 Test01.div(10, 0); 12 } catch (ArithmeticException e) { 13 System.out.println("除数不能为0"); 14 } 15 } 16 }
8.手动抛出异常(throw关键字)
除了系统自动抛出异常外,有些问题需要开发者手动抛出异常,使用关键字throw。
1 package cn.sxt02.exception06; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private String gender; 6 7 public String getName() { 8 return name; 9 } 10 11 public void setName(String name) { 12 this.name = name; 13 } 14 15 public String getGender() { 16 return gender; 17 } 18 19 public void setGender(String gender) throws Exception{ 20 if(gender.equals("男") || gender.equals("女")) { 21 this.gender = gender; 22 }else { 23 throw new Exception("性别不合法!"); 24 } 25 } 26 27 public Student(String name, String gender) { 28 super(); 29 this.name = name; 30 this.gender = gender; 31 } 32 33 public Student() { 34 super(); 35 } 36 37 }
1 public class Test01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 Student stu = new Student(); 4 stu.setName("二狗"); 5 try { 6 stu.setGender("xxx"); 7 } catch (Exception e) { 8 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 9 } 10 } 11 }
9.自定义异常
如果开发者需要手动抛出的异常在系统不存在,可以自定义异常。
如果要自定义异常,首先要确定异常类型,如果异常是运行时异常,必须继承RuntimeException或其子类;如果异常是检查时异常,必须继承Exception或其子类。
异常的命名方式,参考系统命名方式,以Exception结尾。
1 public class AgeException extends Exception{ 2 3 public AgeException() { 4 super(); 5 } 6 7 public AgeException(String message) { 8 super(message); 9 } 10 11 }