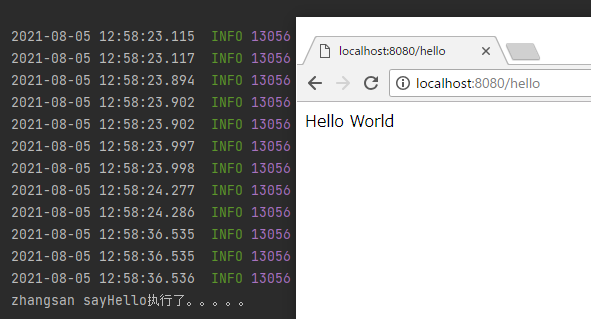
springboot主要是帮助我们简化开发中繁琐的配置,如何简化???
pom.xml
父依赖
管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本,如果导入的包没有被管理就需要手动配置版本
启动器 spring-boot-starter
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是spring-boot的场景启动器
spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
starter就是实现自动装配的核心,如何实现????
启动类
启动类
由两部分组成@SpringBootApplication、run方法
@SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
@SpringBootApplication
作用:标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类 , SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用;
@SpringBootApplication结构
|-- @SpringBootConfiguration :表示为SpringBoot的配置类
|-- @EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能
|-- @AutoConfigurationPackage:自动包配置
|-- @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}):导入组件到spring容器中
|-- @ComponentScan :自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean , 并加载到Spring容器中
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class

protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. " + "If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; } // 获取注解类 protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() { return EnableAutoConfiguration.class; }

SpringFactoriesLoader

public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader; if (classLoader == null) { classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader(); } String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName(); return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList()); } private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) { Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } else { HashMap result = new HashMap(); try { Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()); String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames; int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length; for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) { String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12]; ((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> { return new ArrayList(); })).add(factoryImplementationName.trim()); } } } result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> { return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)); }); cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException var14) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14); } } }

META-INF/spring.factories
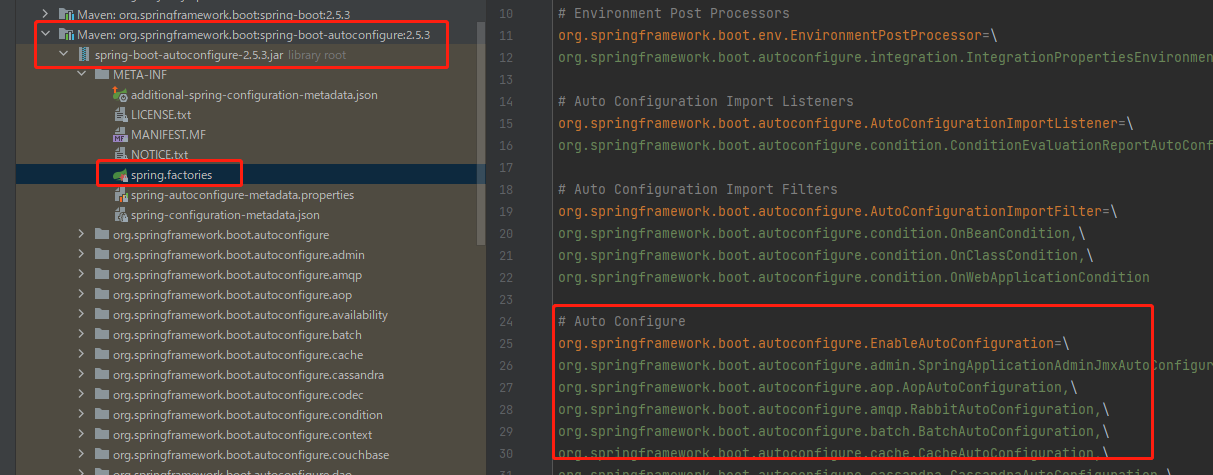
以org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration为例
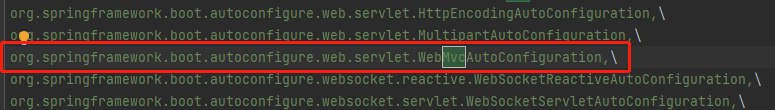
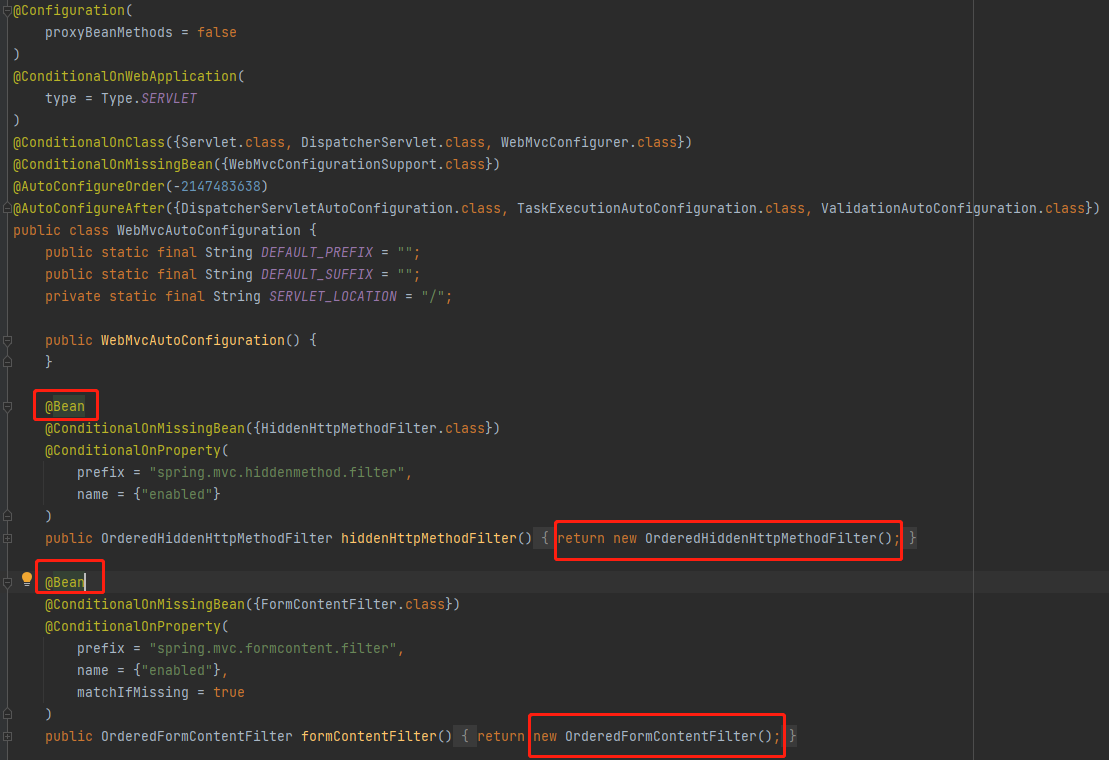
自动装配的本质:将开发所需的对象都放到spring容器中
分析:
1、loadSpringFactories方法获取META-INF/spring.factories数据保存到Map集合
2、通过与Map集合key(EnableAutoConfiguration名称)获取AutoConfiguration类的全名称集合
3、根据配置类的全名称和注解实例化配置类对象
4、实例化配置类过程中的会将组件(具体类)一并实例化并放入到spring容器中
自定义starter
自定义starter需要哪些文件
1、META-INF/spring.factories
2、spring管理的类
3、AutoConfiguration配置类文件
创建项目
1、创建maven工程
项目结构
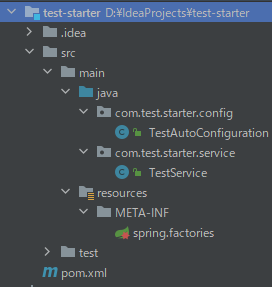
2、添加依赖(这里使用spring-boot-maven-plugin插件会有问题)
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.5.3</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId> <version>2.5.3</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <!-- 打包插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5.3</version> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
3、META-INF/spring.factories,以下红字是固定的,上面分析中有原因
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration= com.test.starter.config.TestAutoConfigure
4、组件(具体类)

public class TestService { public void sayHello(){ System.out.println("TestService 的sayHello方法执行了。。。。。"); } public TestService(){ System.out.println("TestService 已经实例化了。。。。。"); } }
3、AutoConfiguration类,实例化组件

@Configuration public class TestAutoConfiguration { @Bean TestService testService(){ return new TestService(); } }
3、打成jar包
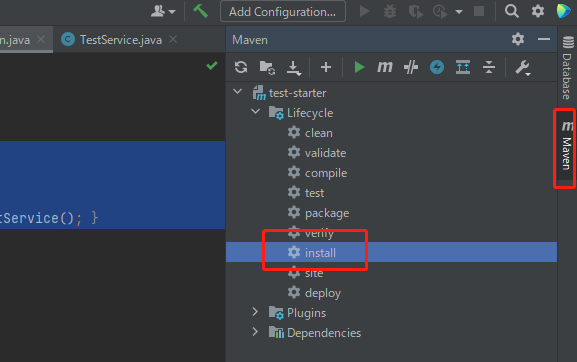
错误:Unable to find main class
猜测spring-boot-maven-plugin插件只能用于spring-boot项目,spring-boot需要main class
所以不使用spring-boot-maven-plugin插件,使用自己下载的maven
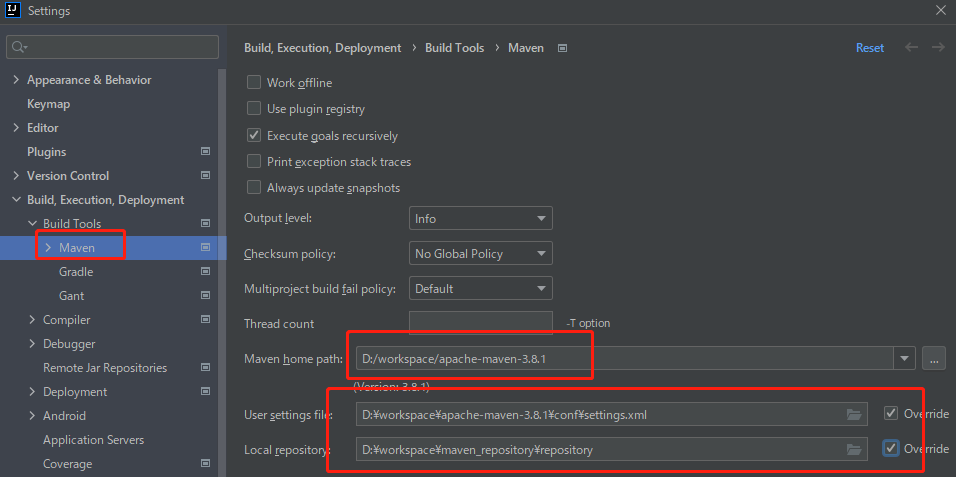
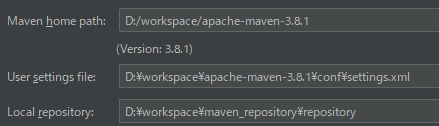
3.1、设置maven,
3.2、Sttings

使用自定义starter
使用自定义starter之前项目必须maven 仓库要一致
添加依赖(pom.xml)
<dependency> <groupId>org.marw</groupId> <artifactId>test-starter</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency>

编写Controller

@RestController public class DemoController { @Autowired TestService testService; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String sayHello() { testService.sayHello(); return "Hello World"; } }
启动项目
配置文件与JavaConfig绑定
如果想使用配置那么就需要一个Properties,正常情况下Properties和AutoConfiguration一起使用的
前期解决错误
创建一个TestProperties,并使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="org.xxx")注解
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="org.marw") public class TestProperties { private String name; }
出现Spring Boot Configuration Annotation Processor not configured
解决方法:添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
接着出现:Not registered via @EnableConfigurationProperties, marked as Spring component, or scanned via @ConfigurationPropertiesScan
在其对应的AutoConfiguration类上添加@EnableConfigurationProperties
@Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties({TestProperties.class}) public class TestAutoConfiguration {
编写properties

@Data // 提供类的get、set、equals、hashCode、canEqual、toString方法 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="org.marw") public class TestProperties { private String name; }
使用properties

public class TestService { String name; public void sayHello() { System.out.println(this.name + " sayHello执行了。。。。。"); } public TestService(TestProperties properties) { this.name = properties.getName(); } }
AutoConfiguration实例化带有properties的类
@Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties({TestProperties.class}) public class TestAutoConfiguration { @Autowired private TestProperties testProperties; @Bean TestService testService(){ return new TestService(testProperties); } }
打包,安装到maven仓库中。
使用上面的DemoController测试,刷新maven就可以了
编写配置application.properties
org.marw.name=zhangsan