20191323王予涵第三章学习笔记
一、知识点归纳
1、多任务处理
通过对cpu进行时分复用来实现进程的并发运行,若有多个cpu或cpu有多个内核,则可以并行运行多个进程。
struct proc{
struct proc *next;
int *ksp;
int pid;
int ppid;
int status;
int priority;
int kstack[1024];
}
上下文切换:
- 将当前寄存器保存到调用切换任务的堆栈中,并将堆栈指针保存到proc.ksp中
| body | eax | ecx | edx | ebx | ebp | esi | edi | eflags |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | -2 | -3 | -4 | -5 | -6 | -7 | -8 | -9 |
- 系统对进程进行调度,将活动就绪队列中的第一进程运行
- 恢复目前运行进程上下文
2、进程同步
P1进程:
- 除P0之外所有进程的祖先
- 所有孤儿进程的父进程
- 处理所有僵尸进程
僵尸进程:
一个子进程在其父进程还没有调用wait()或waitpid()的情况下退出。这个子进程就是僵尸进程。任何一个子进程(init除外)在exit()之后,并非马上就消失掉,而是留下一个称为僵尸进程(Zombie)的数据结构,等待父进程处理。这是每个子进程在结束时都要经过的阶段。
孤儿进程:
父进程退出,而它的一个或多个子进程还在运行,那么那些子进程将成为孤儿进程。P1进程会wait()该进程结束,收集必要信息。
3、Unix/Linux中的进程
进程的产生:
- 内核启动代码强制创建P0进程,设置优先级为最低
- P0进程初始化系统,并挂载根文件系统
- 创建子进程P1,将进程切换到P1
- P1创建守护进程
- 系统启动完毕
守护进程:
提供系统服务,并在后台运行,不直接与用户交互
syslogd
inetd
httpd
进程执行模式切换:
- 中断:外部设备发送给cpu信号,请求服务
- 陷阱:程序运行出现错误
- 系统调用:执行内核函数
更改进程执行映像:
#include <unistd.h>
int execl( const char *pathname, const char *arg0, ... /* (char *)0 */ );
int execv( const char *pathname, char *const argv[] );
int execle( const char *pathname, const char *arg0, ... /* (char *)0, char *const envp[] */ );
int execve( const char *pathname, char *const argv[], char *const envp[] );
int execlp( const char *filename, const char *arg0, ... /* (char *)0 */ );
int execvp( const char *filename, char *const argv[] );
最终发出系统调用:
int execve(const char *filename, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
- filename为可执行文件路径名
- argv为向可执行文件传入的参数
- envp为执行时的环境变量
需要注意的时Umode映像改变,但进程不会改变
4、I/O重定向
文件流和文件描述符
标准输入:
FILE *stdin -----------> FILE structure
fd = 0
标准输出:
FILE *stdout -----------> FILE structure
fd = 1
标准错误:
FILE *stderr -----------> FILE structure
fd = 2
5、管道FIFO
- pd[0]:用于从管道中读取
- pd[1]:用于向管道中写入
写进程必须关闭pd[0],都进程必须关闭pd[1]
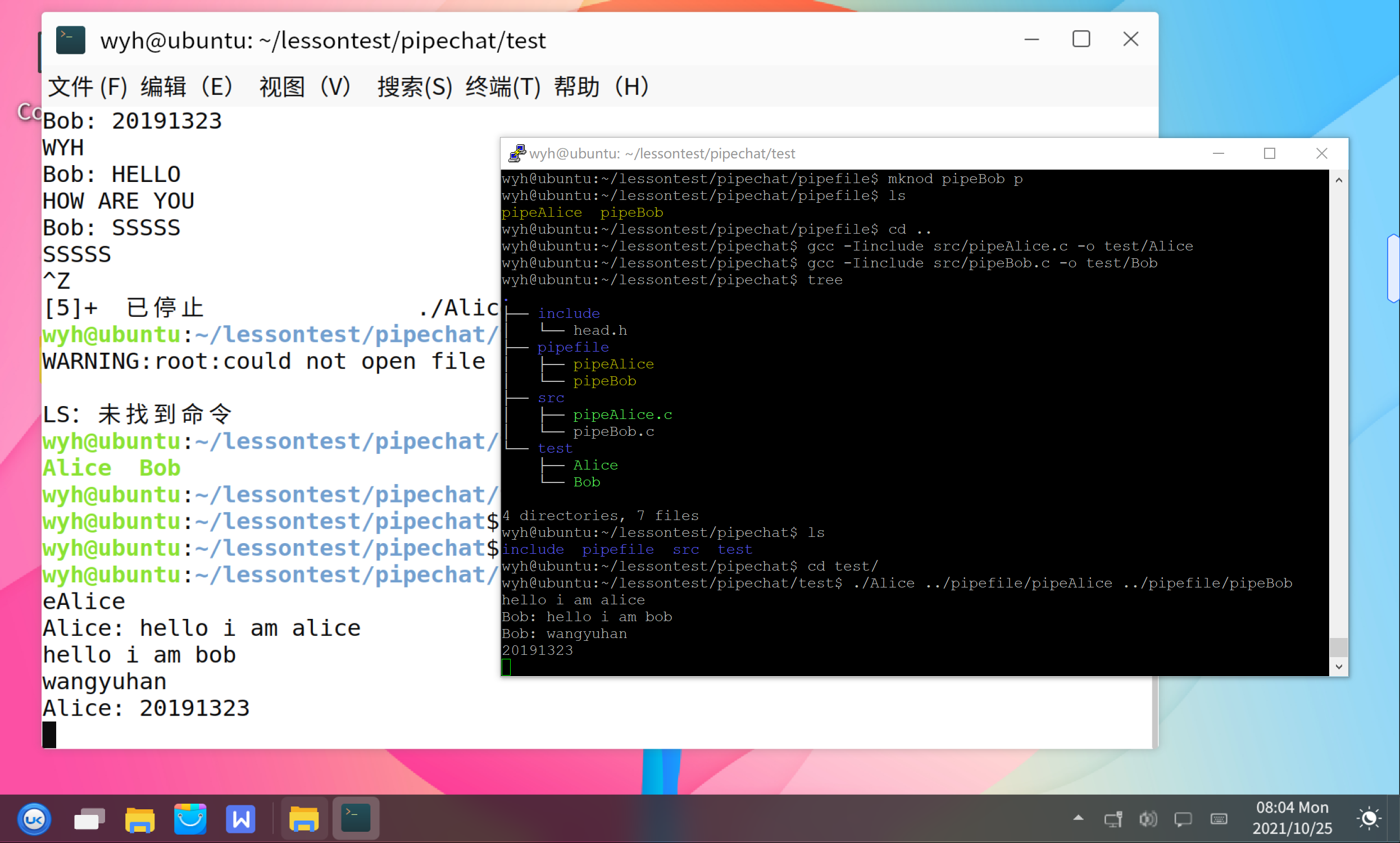
二、实践基于命名管道的聊天通信
源代码:
"head.h"
#ifndef head
#define heda
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SIZE 512
#endif
"pipeAlice.c"
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pid = fork();
if(pid)
{
char buf1[SIZE];
int fdw = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY);
while(1)
{
memset(buf1, 0, sizeof(buf1));
fgets(buf1, sizeof(buf1), stdin);
write(fdw, buf1, sizeof(buf1));
}
close(fdw);
}
else if( pid == 0)
{
char buf2[SIZE];
int fdr = open(argv[2], O_RDONLY);
while(1)
{
memset(buf2, 0, sizeof(buf2));
read(fdr, buf2, sizeof(buf2));
printf("Bob: %s", buf2);
}
close(fdr);
}
return 0;
}
"pipeBob.c"
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pid = fork();
if(pid)
{
char buf1[SIZE];
int fdw = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY);
while(1)
{
memset(buf1, 0, sizeof(buf1));
fgets(buf1, sizeof(buf1), stdin);
write(fdw, buf1, sizeof(buf1));
}
close(fdw);
}
else if( pid == 0)
{
char buf2[SIZE];
int fdr = open(argv[2], O_RDONLY);
while(1)
{
memset(buf2, 0, sizeof(buf2));
read(fdr, buf2, sizeof(buf2));
printf("Alice: %s", buf2);
}
close(fdr);
}
return 0;
}
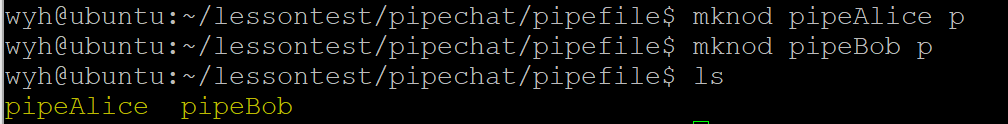
1、创建命名FIFO
2、编译聊天点对点聊天程序

3、运行程序进行聊天