最近考完试了。闲下来就正好刷刷以前没刷完的搜索专题。
简单搜索就没啥好讲的啦。就是暴力bfs和dfs。
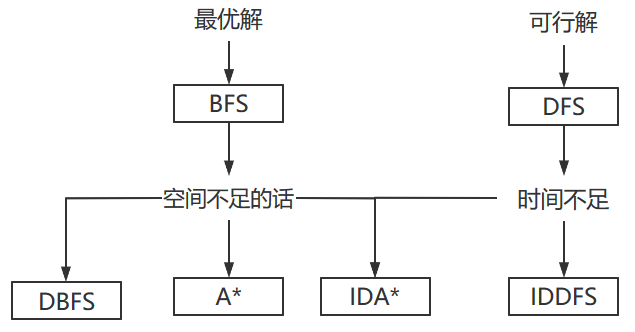
这篇博客是kuangbin搜索进阶的专题的总结
八数码问题太经典啦。通过它来学习搜索的进阶技巧就很舒服。
首先是最简单的康拓优化。
康托展开(Hash序列权值,可以用于序列打表:
int jc[10] = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880};
int cantor(int a[])//康托展开
{
int ans = 0, k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
k=0;
for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++)
if (a[i] > a[j]) k++;
ans += k * jc[n-1-i];
}
return ans;
}
既然说到康托展开那就继续讲讲使用康托展开有什么需要注意的吧。
1.康托展开对于有重复元素的情况不成立,直接套用下方式子显然不对,而笔者暂时也未找到相关文献或自己想出,证明含有重复元素的情况能用类似康托展开的方法或其他简单方法求解。如果您对此有想法,恳请在下方留言区告诉我,我会非常感激。
2. longlong最多能存下20!,21!就爆了,所以说逆康托展开只在20个元素以下的排列有用。但是康托展开的值可以取模,用处还是不小的。
3. 当题目给出不一样的字符大小关系时,完全可以根据题目要求hash字符,将其抽象为数字在进行康托展开。
关于八数码问题的四种解法:
①康托展开+逆向BFS预处理

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 400000; struct path { char oper; int fa; }p[N]; int jc[10] = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880}; int in[9]; int goal[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; int vis[N]; int dic[4][2] = {1,0, -1,0, 0,1, 0,-1}; struct node { int maze[9]; int num; }; int cantor(int a[])//康托展开 { int ans = 0, k; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { k = 0; for (int j = i+1; j < 9; j++) if (a[i] > a[j]) k++; ans += k * jc[8-i]; } return ans; } void bfs(int qin[]) { queue<node> q; vis[cantor(qin)] = 1; node st; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) st.maze[i] = qin[i]; p[0].fa = -1; st.num = 8; q.push(st); while (!q.empty()) { node top = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int tx = top.num % 3 + dic[i][0]; int ty = top.num / 3 + dic[i][1]; if (tx < 0) continue; if (tx >= 3) continue; if (ty < 0) continue; if (ty >= 3) continue; node temp; memcpy(temp.maze, top.maze, sizeof(top.maze)); temp.num = ty*3+tx; swap(temp.maze[top.num], temp.maze[temp.num]); int ct2 = cantor(temp.maze); int ct1 = cantor(top.maze); if (!vis[ct2]) { vis[ct2] = 1; q.push(temp); if (i == 0) p[ct2].fa = ct1, p[ct2].oper = 'l'; else if (i == 1) p[ct2].fa = ct1, p[ct2].oper = 'r'; else if (i == 2) p[ct2].fa = ct1, p[ct2].oper = 'u'; else if (i == 3) p[ct2].fa = ct1, p[ct2].oper = 'd'; //cout << p[ct2].oper << endl; } } } } int main() { cin.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(0); bfs(goal); char temp[9]; while (cin >> temp[0] >> temp[1] >> temp[2] >> temp[3] >> temp[4] >> temp[5] >> temp[6] >> temp[7] >> temp[8]) { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) if (temp[i] == 'x') in[i] = 9; else in[i] = temp[i]-'0'; int cont = cantor(in); if (!vis[cont]) cout << "unsolvable" << endl; else { while (p[cont].fa != -1) { cout << p[cont].oper; cont = p[cont].fa; } cout << endl; } } return 0; }
②A*+康托展开+逆序对判断(这个A*真的难改。大概TLE了10发才弄出来

#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <cstring> using namespace std; const int N = 400000; struct path { char oper; int fa; }p[N]; struct node { int maze[9]; int num; int g, h; friend operator < (node a1, node a2) { return a1.g+a1.h == a2.g+a2.h ? a1.g < a2.g : a1.g+a1.h > a2.g+a2.h; //return a1.g < a2.g; } }st, ed; int jc[10] = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880}; int in[9], goal[9] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; int vis[N]; int dic[4][2] = {1,0, -1,0, 0,1, 0,-1}; int cal(node temp) { int res = 0; for (int i=0;i<9;i++) { int px=(temp.maze[i]-1)/3,py=(temp.maze[i]-1)%3; res+=abs(px-i/3)+abs(py-i%3); } return res; } void output1(int k) { if (p[k].fa == -1) return ; else { output1(p[k].fa); cout << p[k].oper; } } int cantor(int a[]) { int ans = 0, k; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { k = 0; for (int j = i+1; j < 9; j++) if (a[i] > a[j]) k++; ans += k * jc[8-i]; } return ans; } void Astar() { memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); priority_queue<node> pq; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) st.maze[i] = in[i]; p[cantor(st.maze)].fa = -1; vis[cantor(st.maze)] = 1; pq.push(st); while (!pq.empty()) { node top = pq.top(); pq.pop(); int cur = cantor(top.maze); if (cur == 0) { output1(0); cout << endl; return ; } for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int tx = top.num % 3 + dic[i][0]; int ty = top.num / 3 + dic[i][1]; if (tx < 0) continue; if (tx >= 3) continue; if (ty < 0) continue; if (ty >= 3) continue; node temp; memcpy(temp.maze, top.maze, sizeof(top.maze)); temp.num = ty*3+tx; swap(temp.maze[top.num], temp.maze[temp.num]); temp.h = top.h+1; int aft = cantor(temp.maze); temp.g = cal(temp); if (!vis[aft]) { vis[aft] = 1; pq.push(temp); if (i == 0) p[aft].fa = cur, p[aft].oper = 'r'; else if (i == 1) p[aft].fa = cur, p[aft].oper = 'l'; else if (i == 2) p[aft].fa = cur, p[aft].oper = 'd'; else if (i == 3) p[aft].fa = cur, p[aft].oper = 'u'; } } } } int main() { cin.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(0); char temp[9]; while (cin >> temp[0] >> temp[1] >> temp[2] >> temp[3] >> temp[4] >> temp[5] >> temp[6] >> temp[7] >> temp[8]) { for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) if (temp[i] == 'x') in[i] = 9, st.num = i; else in[i] = temp[i]-'0'; int rev = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) for (int j = i+1; j < 9; j++) if (in[i] == 9) continue; else if (in[i] > in[j]) rev++; if (rev & 1) cout << "unsolvable" << endl; else Astar(); } return 0; }
顺便讲讲A*常见的启发策略:
1.曼哈顿距离
2.曼哈顿距离+深度
③IDA*+康托展开+逆序对判断(这其实是一个严重被低估的算法

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 400000; struct path { char oper; int fa; }p[N]; int jc[10] = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320,362880}; int in[9]; int goal[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; int vis[N]; int dic[4][2] = {1,0, 0,1, 0,-1, -1,0}; char dic_rec[5] = {'d', 'r', 'l', 'u'}; int flag = 0; //end condition check char ans_rec[N]; int cal() { int res = 0; for (int i=0;i<9;i++) { if (in[i] == 9) continue; int px=(in[i]-1)/3,py=(in[i]-1)%3; res+=abs(px-i/3)+abs(py-i%3); } return res; } int cantor(int a[]) { int ans = 0, k; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { k = 0; for (int j = i+1; j < 9; j++) if (a[i] > a[j]) k++; ans += k * jc[8-i]; } return ans; } void IDAstar(int limit, int depth, int x, int y, int pre) { if (flag) return ; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { if (flag) return ; int tx = x + dic[i][0]; int ty = y + dic[i][1]; if (tx < 0 || tx > 2 || ty < 0 || ty > 2) continue; if (i + pre == 3) continue; //与之前的方向相反的优化剪枝 swap(in[x*3+y], in[tx*3+ty]); int manha = cal(); if (!manha) { ans_rec[depth] = dic_rec[i]; ans_rec[depth+1] = '�'; cout << ans_rec << endl; flag = 1; return ; } if (depth <= limit) { if (flag) return ; ans_rec[depth] = dic_rec[i]; IDAstar(limit, depth+1, tx, ty, i); } swap(in[x*3+y], in[tx*3+ty]); } } int main() { char temp[9]; while (cin >> temp[0] >> temp[1] >> temp[2] >> temp[3] >> temp[4] >> temp[5] >> temp[6] >> temp[7] >> temp[8]) { flag = 0; int x_pos = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) if (temp[i] == 'x') in[i] = 9, x_pos = i; else in[i] = temp[i]-'0'; int rev = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) for (int j = i+1; j < 9; j++) if (in[i] == 9) continue; else if (in[i] > in[j]) rev++; int cont = cantor(in); if (rev & 1) cout << "unsolvable" << endl; else if (cont == 0) cout << endl; else { for (int i = 1; !flag; i++) IDAstar(i, 0, x_pos/3, x_pos%3, -1); } } return 0; }
这里讲讲IDA*常用的剪枝:
1. 曼哈顿距离+深度 <= 限制深度
2. 不走跟上次反相的方向
关于搜索进阶的比较好的题目讲解:
题解:HASH + BFS(其实网上有IDA*的做法,但是根本过不了极端样例——HDU数据太水,我个人跟倾向于这种做法

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; char str[10][10]; int dig[10]={1,6,36,216,1296,7776,46656,279936,1679616,10077696}; int len[9], n; ll res = 0; char dic[5]="ACGT"; map<int, bool> vis; struct node { int hash_val; int step; node(int h_val=0, int _step=0): hash_val(h_val),step(_step){} }; inline int BFS() { queue<node> q; q.push(node()); vis[0] = 1; while (!q.empty()) { node top = q.front(); q.pop(); if (top.hash_val == res) return top.step; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int h_val = top.hash_val; ll temp = 0; for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { int digit = h_val % 6; h_val /= 6; //如果当前的字符串已经完全匹配或者当前加入的字符不能与下一个字符匹配, //那么就将已匹配的位数*权值加到hashval if (len[j] == digit || str[j][digit+1] != dic[i]) temp += digit * dig[j-1]; //如果当前加入字符与字符串的下一个字符匹配 //那么就将(已匹配的位数+1)*权值加到hashval else temp += (digit+1) * dig[j-1]; } if (!vis[temp]) q.push(node(temp, top.step+1)), vis[temp] = 1; } } } int main(){ int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { cin >> n; res = 0; vis.clear(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { cin >> str[i]+1; // 这里代表的意思是从s[i][1]开始读入 len[i] = strlen(str[i]+1); //上面同理 res += dig[i-1]*len[i]; //每一位需要匹配的字符数*每一个字符串的权值 } cout << BFS() << endl; } return 0; }
HDU - 3085 Nightmare Ⅱ
题解:双向BFS模板

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int N = 1005; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; char G[N][N]; bool vis[2][N][N]; int n, m, k; int dic[4][2] = {1,0, 0,1, -1,0, 0,-1}; struct node { int x, y; node(int _x=0, int _y=0) { x = _x, y = _y; } }MM, GG, ZZ[2]; queue<node> q[2]; int step = 0; inline bool check(int x, int y) { if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= n || y >= m || G[x][y] == 'X') return true; for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) if (abs(ZZ[i].x-x)+abs(ZZ[i].y-y) <= 2*step) return true; return false; } inline bool BFS(int person) { int SZ = q[person].size(); while (SZ--) { node top = q[person].front(); q[person].pop(); if (check(top.x, top.y)) continue; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int tx = top.x + dic[i][0]; int ty = top.y + dic[i][1]; if (check(tx, ty)) continue; if (!vis[person][tx][ty]) { if (vis[person^1][tx][ty]) return true; q[person].push(node(tx,ty)); vis[person][tx][ty] = 1; } } } return false; } int solve() { memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); while (!q[0].empty()) q[0].pop(); while (!q[1].empty()) q[1].pop(); vis[1][GG.x][GG.y] = vis[0][MM.x][MM.y] = 1; q[0].push(MM), q[1].push(GG); step = 0; while (!q[0].empty() || !q[1].empty()) { step++; if (BFS(0)) return step; if (BFS(0)) return step; if (BFS(0)) return step; if (BFS(1)) return step; } return -1; } int main(){ int T; cin.tie(0); ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin >> T; while (T--) { cin >> n >> m; int ZZ_num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) { cin >> G[i][j]; if (G[i][j] == 'Z') ZZ[ZZ_num].x = i, ZZ[ZZ_num].y = j, ZZ_num++; else if (G[i][j] == 'M') MM.x = i, MM.y = j; else if (G[i][j] == 'G') GG.x = i, GG.y = j; } } cout << solve() << endl; } return 0; }
