The GCD table G of size n × n for an array of positive integers a of length n is defined by formula
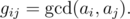
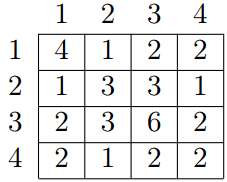
Let us remind you that the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two positive integers x and y is the greatest integer that is divisor of both x and y, it is denoted as 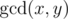 . For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:
. For example, for array a = {4, 3, 6, 2} of length 4 the GCD table will look as follows:
Given all the numbers of the GCD table G, restore array a.
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 500) — the length of array a. The second line contains n2space-separated numbers — the elements of the GCD table of G for array a.
All the numbers in the table are positive integers, not exceeding 109. Note that the elements are given in an arbitrary order. It is guaranteed that the set of the input data corresponds to some array a.
In the single line print n positive integers — the elements of array a. If there are multiple possible solutions, you are allowed to print any of them.
首先我们假设得到的数组a是非递减的,即a1<=a2<=a3<=...<=an
易知所有数中最大的是gcd(an,an) = an,则首先删除这个数确定an,然后剩下的最大的即为gcd(an-1,an-1),确定他,由于an也确定,则可以删除gcd(an,an-1),gcd(an-1,an),同理一个一个推

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define LL long long #define SIZE 1001 int n; int ans[SIZE]; map<int,int> cnt; int gcd(int a, int b) { return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b); } int main() { // freopen("test.in","r",stdin); int n; scanf("%d", &n); for(int i=1;i<=n * n;i++) { int a; scanf("%d", &a); cnt[-a]++; } int pos = n - 1; for (map <int, int> :: iterator it = cnt.begin(); it != cnt.end(); ++it) { int x = -it->first; while (it->second) { ans[pos] = x; --it->second; for (int i = pos + 1; i < n; ++i) cnt[-gcd(ans[pos], ans[i])] -= 2; pos--; } } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) printf("%d ", ans[i]); return 0; }
