2924 数独挑战
“芬兰数学家因卡拉,花费3个月时间设计出了世界上迄今难度最大的数独游戏,而且它只有一个答案。因卡拉说只有思考能力最快、头脑最聪明的人才能破解这个游戏。”这是英国《每日邮报》2012年6月30日的一篇报道。这个号称“世界最难数独”的“超级游戏”,却被扬州一位69岁的农民花三天时间解了出来。
看到这个新闻后,我激动不已,证明我们OI的实力的机会来了,我们虽然不是思考能力最快、头脑最聪明的人,但是我们可以保证在1s之内解题。
好了废话不多说了……
数独是一种填数字游戏,英文名叫Sudoku,起源于瑞士,上世纪70年代由美国一家数学逻辑游戏杂志首先发表,名为Number Place,后在日本流行,1984年将Sudoku命名为数独,即“独立的数字”的省略,解释为每个方格都填上一个个位数。2004年,曾任中国香港高等法院法官的高乐德(Wayne Gould)把这款游戏带到英国,成为英国流行的数学智力拼图游戏。
玩家需要根据9×9盘面上的已知数字,推理出所有剩余位置(数据表示为数字0)的数字,并满足每一行、每一列、每一个粗线宫内的数字均含1-9,不重复。
现在给你一个数独,请你解答出来。每个数独保证有解且只有一个。
9行9列。
每个数字用空格隔开。0代表要填的数
行末没有空格,末尾没有回车。
输出答案。
排成9行9列。
行末没有空格,结尾可以有回车。
2 0 0 0 1 0 8 9 0
0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 9 0 0 0 0 7
0 6 0 0 0 1 3 0 0
0 9 0 7 3 4 0 8 0
0 0 3 6 0 0 0 5 0
6 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 5 9 0 8 0 0 0 3
2 4 5 3 1 7 8 9 6
9 1 7 2 6 8 5 3 4
3 8 6 9 4 5 2 1 7
4 6 2 8 5 1 3 7 9
5 9 1 7 3 4 6 8 2
8 7 3 6 2 9 4 5 1
6 3 8 1 7 2 9 4 5
7 2 4 5 9 3 1 6 8
1 5 9 4 8 6 7 2 3
纯搜索,用empty[]数组记录下每个没有填数的位置,设n[i][l]=true数组表示第i行数l已经被填过,m[j][l]表示第j列数l已经被填过,k数组如下图所示
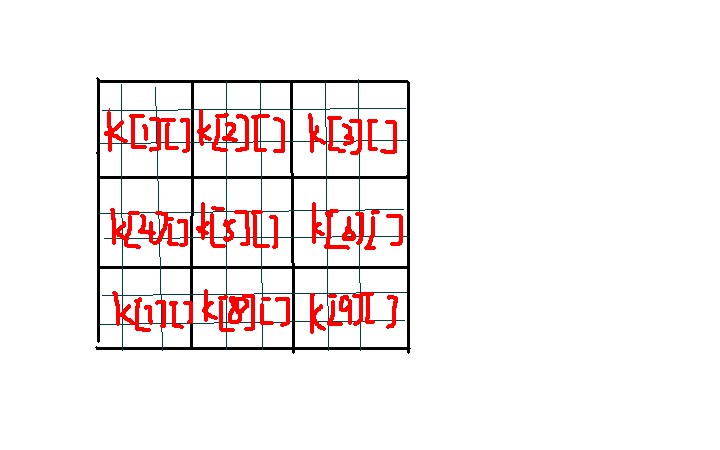
从第一个没有被填数的位置开始搜,填入一个数,更新m,n,k数组,注意回溯时也要更新m,n,k数组。
注意如果第i行j列没有填数,搜索时由于前面填的数的限制,什么数也不能填,那么此时一定要回退,直至这个格填上数再进行下一个,否则死循环。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; int a[10][10],empty[82],cnt; bool n[10][10],m[10][10],k[10][10]; bool find(int i,int j,int l)//判断位置i,j填p是否合适 { if(i<=3&&j<=3&&k[1][l]) return false; if(i<=3&&j>=4&&j<=6&&k[2][l]) return false; if(i<=3&&j>=7&&k[3][l]) return false; if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j<=3&&k[4][l]) return false; if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=4&&j<=6&&k[5][l]) return false; if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=7&&k[6][l]) return false; if(i>=7&&j<=3&&k[7][l]) return false; if(i>=7&&j>=4&&j<=6&&k[8][l]) return false; if(i>=7&&j>=7&&k[9][l]) return false; if(n[i][l]) return false; if(m[j][l]) return false; return true; } void mark(int i,int j,int l)//标记i,j位置填上了l { if(i<=3&&j<=3) k[1][l]=true; else if(i<=3&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[2][l]=true; else if(i<=3&&j>=7)k[3][l]=true; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j<=3) k[4][l]=true; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[5][l]=true; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=7) k[6][l]=true; else if(i>=7&&j<=3) k[7][l]=true; else if(i>=7&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[8][l]=true; else if(i>=7&&j>=7) k[9][l]=true; n[i][l]=true; m[j][l]=true; } void back(int i,int j,int l)//位置i,j撤回l { if(i<=3&&j<=3) k[1][l]=false; else if(i<=3&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[2][l]=false; else if(i<=3&&j>=7)k[3][l]=false; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j<=3) k[4][l]=false; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[5][l]=false; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=7) k[6][l]=false; else if(i>=7&&j<=3) k[7][l]=false; else if(i>=7&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[8][l]=false; else if(i>=7&&j>=7) k[9][l]=false; n[i][l]=false; m[j][l]=false; } void dfs(int now,int s) { if(s==81) { for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=9;j++) cout<<a[i][j]<<' '; cout<<endl; } exit(0); } for(int i=now+1;i<=cnt;i++) { bool ok=false; if(!empty[i]) continue;//利用empty[i]是否为0来判断empty存的这个位置是否填上了数,0代表已经填上了 int x=empty[i]/10,y=empty[i]%10; int h=empty[i]; for(int p=1;p<=9;p++) if(find(x,y,p)) { empty[i]=0; mark(x,y,p);//标记 a[x][y]=p; dfs(i,s+1); back(x,y,p);//撤回标记 empty[i]=h; } if(empty[i]) return;//程序能运行的关键,没有这句就死循环了 } } int main() { for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) for(int j=1;j<=9;j++) { cin>>a[i][j]; if(!a[i][j]) {empty[++cnt]=i*10+j;continue;} n[i][a[i][j]]=true; m[j][a[i][j]]=true; if(i<=3&&j<=3) k[1][a[i][j]]=true; else if(i<=3&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[2][a[i][j]]=true; else if(i<=3&&j>=7) k[3][a[i][j]]=true; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j<=3) k[4][a[i][j]]=true; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[5][a[i][j]]=true; else if(i>=4&&i<=6&&j>=7) k[6][a[i][j]]=true; else if(i>=7&&j<=3) k[7][a[i][j]]=true; else if(i>=7&&j>=4&&j<=6) k[8][a[i][j]]=true; else k[9][a[i][j]]=true; } dfs(0,81-cnt); }


for(int i=now+1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
bool ok=false;//**********
if(!empty[i]) continue;
int x=empty[i]/10,y=empty[i]%10;
int h=empty[i];
for(int p=1;p<=9;p++)
if(find(x,y,p))
{
ok=true;//********
empty[i]=0;
mark(x,y,p);
a[x][y]=p;
dfs(i,s+1);
back(x,y,p);
empty[i]=h;
}
if(!ok) return; //************
}
利用ok变量来判断empty[i]位置是否填上了数,但忽略了ok在回溯中没有更改,当这个位置被标记之后标记不会撤回。
更改方法:回溯时添加ok=false
错误原因:深搜回溯问题
错误2:样例输出中,数与数之间有空格,这要是noip的话,100分就没了( ⊙ o ⊙ )!,注意注意!!!
上一个代码写的很丑,主要原因是k数组的调用,看了题解,发现k数组的第一维可以用如下式子计算:
(i-1)/3*3+(j-1)/3+1
代码长度优化版本:
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cstdlib> int a[10][10]; bool h[10][10],l[10][10],g[10][10]; void print() { for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=9;j++) printf("%d ",a[i][j]); printf(" "); } exit(0); } void go(int x,int y) { if(a[x][y]!=0) { if(x==9&&y==9) print(); if(y==9) go(x+1,1); else go(x,y+1); } if(a[x][y]==0) { for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) if(h[x][i]&&l[y][i]&&g[(x-1)/3*3+(y-1)/3+1][i]) { a[x][y]=i; h[x][i]=false; l[y][i]=false; g[(x-1)/3*3+(y-1)/3+1][i]=false; if(x==9&&y==9) print(); if(y==9) go(x+1,1); else go(x,y+1); a[x][y]=0; h[x][i]=true; l[y][i]=true; g[(x-1)/3*3+(y-1)/3+1][i]=true; } } } int main() { memset(h,true,sizeof(h)); memset(l,true,sizeof(l)); memset(g,true,sizeof(g)); for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) for(int j=1;j<=9;j++) { scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); if(a[i][j]>0) { h[i][a[i][j]]=false; l[j][a[i][j]]=false; g[(i-1)/3*3+(j-1)/3+1][a[i][j]]=false; } } go(1,1); }