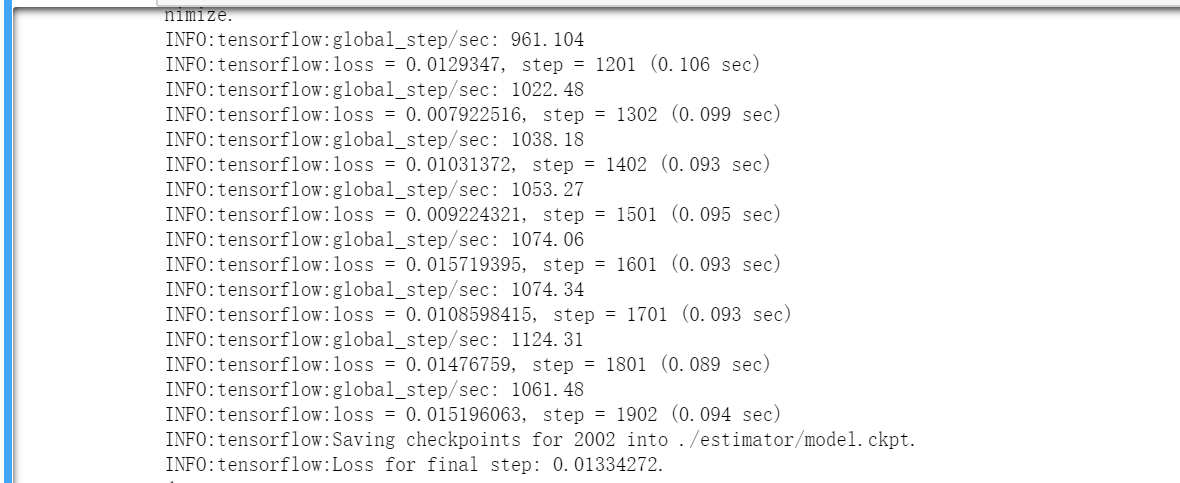
再次使用tensorflow的时候,已经用过三四个机器学习工具了,最近应实习公司的要求,从Pytorch又回来了!
吐槽
这次学习tensorflow和keras的过程是痛苦的。
我先去学tensorflow,tf 的工具真是细致,除了求导不用自己写啥都要慢慢搭建,想写一个稍微复杂一点的模型都要一个矩阵一个矩阵来搞,刚开始的时候还动力满满,但后来觉得这也太麻烦了吧。习惯了pytorch写class之后,这种写法写的又慢又不容易维护,痛苦万分。
相比之下,keras就十分精简了,一个线性回归要不了几行,但同时,灵活性(那些小零件)好像就不如 tf 丰富了(tf 已经丰富到冗余了)。后来了解到,tf也有一些中高级的封装,于是我就去学习estimator等技巧了。
早已听说,tensorflow 2相比1变化不小,这对我又是一个挑战,只是网上资料感觉有限,真正对于tensorflow2 的教程也讲得总是不完全对自己的问题,看来学习还是要自己看文档啊!
整个过程来来回回,我的tensorflow安装也一直有问题,包括版本问题,平台问题,以及我一直搞不清为什么在vscode上没有补全(现在没有补全简直要了我的命,为了方便都是看补全来学习了QAQ),现在我知道了,是因为tensorflow的文档比较混乱,各种混用,输入正确的目录才能 peek definition,否则虽然能用,但是在编辑阶段简直是在写vim。
线性回归
经过这几天的学习,我决定接收tensorflow2,在tf2里面使用keras,感觉这样应该还能保留大部分 customized feature 吧!
一个简单的Linear Regression 模型:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.python import keras
from tensorflow.python.keras import Sequential, layers
def input_fn(x_data, y_data, shuffle=True,
batch_size=20, num_epoches=100):
""" tensorflow `input_fn` """
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_data, y_data))
if shuffle:
ds = ds.shuffle(1000)
ds = ds.batch(batch_size).repeat(num_epoches)
return ds
class MyCallBack(keras.callbacks.Callback):
""" Call back Class, for details during traing and prediction. """
def on_batch_begin(self, epoch, logs={}):
print('this is begin on batch')
def on_epoch_begin(self, epoch, logs={}):
print('this is epoch begin')
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs={}):
print('this is end on batch')
def TotalDataGen():
""" data generation """
train_x = np.random.randn(100)
train_y = 3 * train_x + 1.2 + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, train_x.shape)
return train_x, train_y
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_x, train_y = TotalDataGen()
# clarify a model structure
model = Sequential([
layers.Dense(1, input_shape=(1,))
])
model.compile(
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01),
loss=tf.losses.mean_squared_error,
metrics=['mse']
)
# data settings
boundary = 80
train_data = input_fn(train_x[: boundary], train_y[: boundary])
eval_data = input_fn(train_x[boundary:], train_y[boundary:])
# training
model.fit(train_data, callbacks=[MyCallBack()])
# evaluation
model.evaluate(eval_data)
print('done')
estimator & keras model
如果相比keras,你更需要estimator,可以这样用。
estimator_model = keras.estimator.model_to_estimator(
keras_model=model, model_dir='./estimator/')
estimator_model.train(lambda : input_fn(train_x, train_y))