Spring框架:
传统JavaEE解决企业级应用问题时的“重量级”架构体系,使它的开发效率,开发难度和实际的性能都令人失望。Spring是以一个
救世主的身份降临在广大的程序员面前。Spring致力于JavaEE应用的各种解决方案,而不是仅仅专注于某一层的方案也可以说Spring
是一个企业级应用开发的一站式选择。Spring贯穿表现层,业务层,持久层。然而,Spring并不是为了取代他们而出现而是以高度的
开放性与它们无缝整合。
Spring核心:
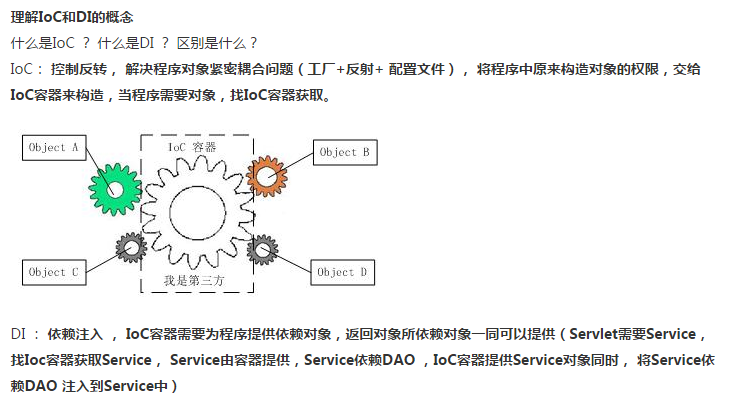
IOC控制反转(Inversion of Control )也被称为依赖注入(Dependency Injection ,DI)是面向对象编程中的一种设计理念,用来减低
程序代码之间的耦合度
AOP面向切面编程(Aspect Oriented Programming,AOP)是软件编程思想发展到一定阶段的产物是面向对象编程(Object Oriented Programming)
的有益补充。AOP一般适用于有横切逻辑的场合,如访问控制,事务管理,性能检测等。
AOP Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
面向对象编程是从【静态角度】考虑程序的结构,而面向切面编程是从【动态角度】考虑程序运行过程。
AOP底层,就是采用【动态代理】模式实现的。采用了两种代理:JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态代理。
基本术语(一些名词):
(1)切面(Aspect)
切面泛指[*交叉业务逻辑*]。事务处理和日志处理可以理解为切面。常用的切面有通知(Advice)与顾问(Advisor)。实际就是对主业务逻辑的一种增强。
(2)织入(Weaving)
织入是指将切面代码插入到目标对象的过程。代理的invoke方法完成的工作,可以称为织入。
(3) 连接点(JoinPoint)
连接点是指可以被切面织入的方法。通常业务接口的方法均为连接点
(4)切入点(PointCut)
切入点指切面具体织入的方法
注意:被标记为final的方法是不能作为连接点与切入点的。因为最终的是不能被修改的,不能被增强的。
(5)目标对象(Target)
目标对象指将要被增强的对象。即包含主业务逻辑的类的对象。
(6)通知(Advice)
通知是切面的一种实现,可以完成简单的织入功能。通知定义了增强代码切入到目标代码的时间点,是目标方法执行之前执行,还是执行之后执行等。切入点定义切入的位置,通知定义切入的时间。
(7)顾问(Advisor)
顾问是切面的另一种实现,能够将通知以更为复杂的方式织入到目标对象中,是将通知包装为更复杂切面的装配器。
6.AOP是一种思想,而非实现
AOP是基于OOP,而又远远高于OOP,主要是将主要核心业务和交叉业务分离,交叉业务就是切面。例如,记录日志和开启事务。
=====通知Advice
7.前置通知 MethodBeforeAdvice
定义前置通知,需要实现MethodBeforeAdvice接口,该接口中有一个方法before(),会在目标方法执行之前执行。
特点:
1.在目标方法之前执行
8.后置通知 AfterReturningAdvice
9.环绕通知 MethodInterceptor
10.异常通知 ThrowsAdvice
定义异常通知,需要实现接口ThrowAdvice接口 。该接口的主要作用是,在目标方法抛出异常后,根据异常的不同做出相应的处理。当该接口处理完异常后,会简单地将异常再次抛出给目标方法。
=====顾问Advisor
11.通知Advice是Spring提供的一种切面(Aspect)。但其功能过于简单,只能
将切面织入到目标类的所有目标方法中,无法完成将切面织入到指定目标方法中。
顾问Advisor是Spring提供的另一种切面。其可以完成更为复杂的切面织入功能。PointcutAdvisor是顾问的一种,可以指定具体的切入点。顾问将通知进行了包装,会根据不同的通知类型,在不同的时间点,将切面织入到不同的切入点。
PointcutAdvisor接口有两个较为常用的实现类:
*:NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor 名称匹配方法切入点顾问
*:RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor 正则表达式匹配方法切入点顾问
<property name="pattern" value=".*do.*"></property> 表示方法全名(包名,接口名,方法名)
运算符 名称 意义
. 点号 表示任意单个字符
+ 加号 表示前一个字符出现一次或者多次
* 星号 表示前一个字符出现0次或者多次
=====默认Advisor自动代理生成器
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
=====BeanName自动代理生成器
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
=====AspectJ对AOP的实现
对于AOP这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现。Spring就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程。然而,AspectJ也实现了AOP的功能,且实现方式更为简捷,使用更加方便,而且还支持注解式开发。所以,Spring又将AspectJ对于AOP的实现也引入到了自己的框架中。
在Spring中使用AOP开发时,一般使用AspectJ的实现方式。
IOC和AOP使用扩展
使用多种方式实现依赖注入:
第一步创建出Car类
package cn.happy.day01.entity; public class Car { private String color; @Override public String toString() { return "Car [color=" + color + "]"; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } }
第二步创建出一个实体类Student
package cn.happy.day01.entity; public class Student { private String name; private int age; private Car myCar; public Student() { System.out.println("init student"); } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", myCar=" + myCar + "]"; } public Student(String name, int age, Car myCar) { System.out.println("i am has args constructor"); this.name = name; this.age = age; this.myCar = myCar; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Car getMyCar() { return myCar; } public void setMyCar(Car myCar) { this.myCar = myCar; } }
接下来就就是编写applicationContext.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd "> <bean id="mmCar" class="cn.happy.day01.entity.Car"> <property name="color" value="green color"></property> </bean> <!-- <bean id="stu1" class="cn.happy.day01.entity.Student"> <property name="name" value="微冷的雨"></property> <property name="age" value="18"></property> <property name="myCar" ref="mmCar"></property> </bean> --> <!--01.构造器注入 --> <bean id="stu2" class="cn.happy.day01.entity.Student"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="微冷的雨"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" value="18"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="2" ref="mmCar"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!--02.p命名空间注入 --> <bean id="stu3" class="cn.happy.day01.entity.Student" p:name="国庆放假买手机" p:age="18" p:myCar-ref="mmCar"> </bean> <!--05.各种类型注入之 集合 之 List--> <bean id="list" class="cn.happy.day01.entity.CollectionBean"> <property name="list"> <list> <value>方言</value> <value>李小龙</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!--06.各种类型注入之 集合 之 Set--> <bean id="set" class="cn.happy.day01.entity.CollectionBean"> <property name="set"> <set> <value>方言</value> <value>李小龙</value> </set> </property> </bean> <!--07.各种类型注入之 集合 之 Map--> <bean id="map" class="cn.happy.day01.entity.CollectionBean"> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="fy"> <value>方言</value> </entry> <entry key="lxl"> <value>李小龙</value> </entry> </map> </property> </bean> </beans>
关于上面注入集合的内容创建一个集合的类即可:
package cn.happy.day01.entity; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; /** * 集合Bean * @author Happy * */ public class CollectionBean { private List<String> list; private Set<String> set; private Map<String,String> map; private String [] empName;//数组 private Properties pp;//Properties的使用 public String[] getEmpName() { return empName; } public void setEmpName(String[] empName) { this.empName = empName; } public Properties getPp() { return pp; } public void setPp(Properties pp) { this.pp = pp; } public List<String> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public Set<String> getSet() { return set; } public void setSet(Set<String> set) { this.set = set; } public Map<String, String> getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) { this.map = map; } }
最后我们编写测试类测试即可
package cn.happy.day01.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.happy.day01.entity.CollectionBean; import cn.happy.day01.entity.Student; public class Spring_01Test { public static void main(String[] args) { testCollectionMap(); } /** * 1.1 spring容器创建的时候,会将所有配置的bean对象创建 */ /*@Test public void testOne(){ //容器一旦生成,bean都被加载到内存 ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Student stu = (Student)ctx.getBean("stu1"); System.out.println(stu); Student stu = (Student)ctx.getBean("stu1"); Student stu2 = (Student)ctx.getBean("stu1"); System.out.println(stu); System.out.println(stu2); }*/ static void testCollectionMap(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("map"); System.out.println(bean.getMap()); } //every type injection of Collection Set static void testCollectionSet(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("set"); System.out.println(bean.getSet()); } //every type injection of Collection List static void testCollectionList(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("list"); System.out.println(bean.getList()); } //04.域属性的注入 static void testJavaBean(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Student stu=(Student)ctx.getBean("stu1"); System.out.println(stu); } //03.普通属性注入 static void testUseful(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); } //02.P命名空间注入 static void testPInjection(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Student stu = (Student)ctx.getBean("stu3"); System.out.println(stu); } //01.1构造注入 static void testConstructorInjection2(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Student stu = (Student)ctx.getBean("stu2"); System.out.println(stu); } //01.构造注入 static void testConstructorInjection(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Student stu = (Student)ctx.getBean("stu2"); System.out.println(stu); } }