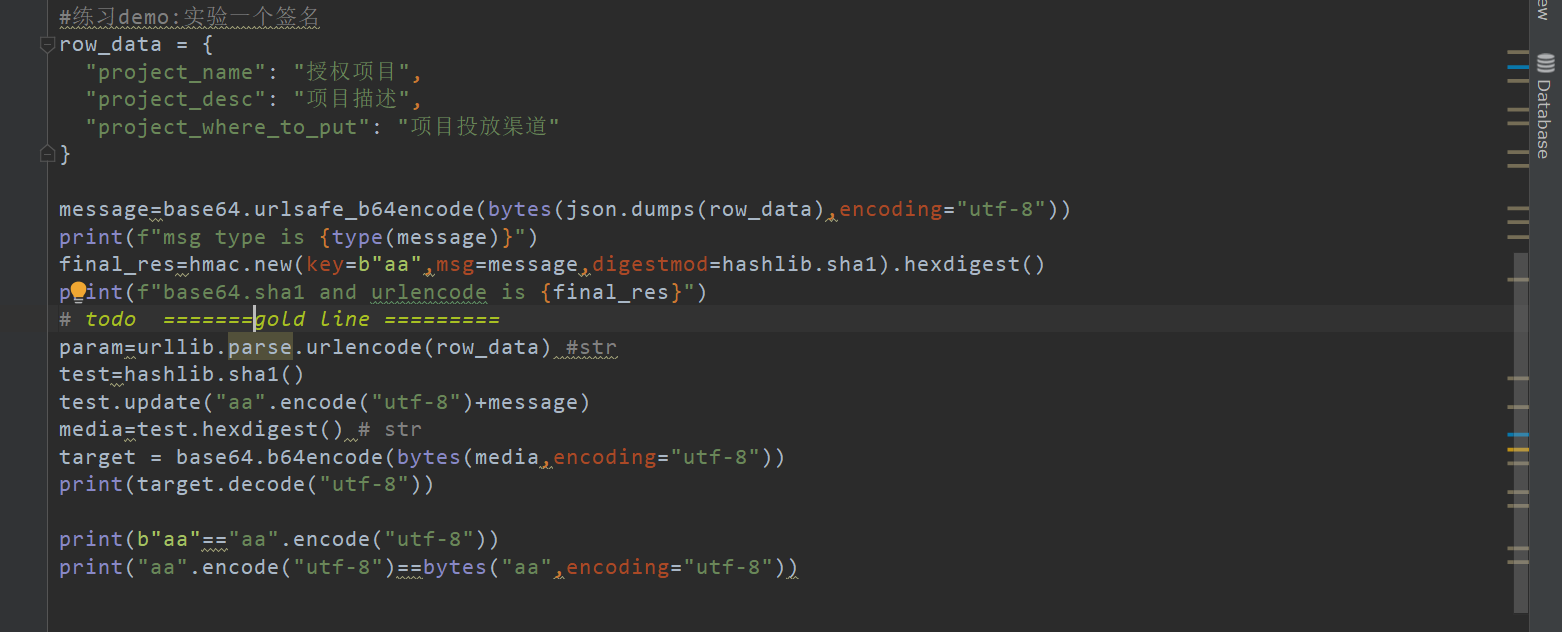
import hmac
import base64
import json
import urllib
import hashlib
#在进行hamc学习之前先进行基础只是的普及:hex,oct,digest,hexdigest
# # todo hex是将字符串转换为十六进制字节表示,oct是转八进制,digest是返回二进制的摘要字符串值,hexdigest是返回十六进制的字符串值
res1=hmac.new(key=b"aa",msg=b"bb",digestmod="sha1").hexdigest()
print(res1)
#bytes("aa",encoding="utf-8) <<==>>"aa".encode("utf-8")
res2=hmac.new(key=bytes("aa",encoding="utf-8"),msg=bytes("bb",encoding="utf-8"),digestmod="sha1").hexdigest()
print(res2)
#只能比较hmac进行的digest()摘要
print(hmac.compare_digest(res1,res2))
##
res3=hashlib.sha1()
#do sha1
res3.update(bytes("aa"+"bb",encoding="utf-8"))
print(res3.hexdigest())
#练习demo:实验一个签名
row_data = {
"project_name": "授权项目",
"project_desc": "项目描述",
"project_where_to_put": "项目投放渠道"
}
message=base64.urlsafe_b64encode(bytes(json.dumps(row_data),encoding="utf-8"))
print(f"msg type is {type(message)}")
final_res=hmac.new(key=b"aa",msg=message,digestmod=hashlib.sha1).hexdigest()
print(f"base64.sha1 and urlencode is {final_res}")
param=urllib.parse.urlencode(row_data) #str
test=hashlib.sha1()
test.update("aa".encode("utf-8")+message)
media=test.hexdigest() # str
target = base64.b64encode(bytes(media,encoding="utf-8"))
print(target.decode("utf-8"))
print(b"aa"=="aa".encode("utf-8"))
print("aa".encode("utf-8")==bytes("aa",encoding="utf-