运行循环,保证程序不退出
目的:
1.保住当前线程的生命
2.负责监听事件:iOS所有事件 触摸、时钟、网络等等!
3.要想保住一条线程的生命,让这条线程有执行不完的任务。(如果没有事件发送,会让程序进入休眠状态)
4.Runloop 它还需要做一件事 Ui的绘制,在RunLoop循环中要绘制屏幕上的点。
5.节省CPU资源,提高程序的性能,该做事做事,该休息休息。
runLoop跟主线程有关系;每一个分线程也都有一个runloop;主线程的runloop是默认开启的,而分线程的是需要手动开启。
01-时钟事件(保证UI和时钟同时进行,互不影响)
//NSDefaultRunLoopMode 默认模式!! //UITrackingRunLoopMode UI模式!! //NSRunLoopCommonModes 占位模式!! UI&&默认! UI和默认都可以进行,互不影响 //UI模式优先级最高!! UI模式只会被触摸事件所触发!! [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
002-加载大图
UI界面滑动视图时,分析卡顿的原因:
1.渲染图片耗时—-分段加载图片
2.每次RunLoop循环,最多需要加载18张大图!所以卡住了。
思路:每次RunLoop循环,只渲染一张大图
步骤:
1.监听Runloop的循环!!
2.将加载大图的代码!放在一个数组里面!!
3.每次Runloop循环,取出一个加载大图的任务执行!!
在创建UI滑动视图之后调用: addRunloopObserver
typedef void(^runloopBlock)(void);//Ref 引用 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSMutableArray * tasks; #pragma mark - <CFRunloop> -(void)addTasks:(runloopBlock)task{ [self.tasks addObject:task]; if (self.tasks.count > 18) {//Runloop 最大加载18张大图 [self.tasks removeObjectAtIndex:0]; } } -(void)addRunloopObserver{ //获取Runloop CFRunLoopRef runloop = CFRunLoopGetCurrent(); //定义一个context CFRunLoopObserverContext context = { 0, (__bridge void *)(self), &CFRetain, &CFRelease, NULL }; //定义观察者 static CFRunLoopObserverRef runloopObserver; runloopObserver = CFRunLoopObserverCreate(NULL, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting, YES, 0, &callBack, &context); //添加观察者 CFRunLoopAddObserver(runloop, runloopObserver, kCFRunLoopCommonModes); //C里面 一旦creat new copy 有堆空间 需要自己手动释放 CFRelease(runloopObserver); } void callBack(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity, void *info){ //activity BeforeWaiting NSLog(@"%@",info); ViewController * vc = (__bridge ViewController *)info; if(vc.tasks.count == 0){ return; } runloopBlock block = vc.tasks.firstObject; block(); [vc.tasks removeObjectAtIndex:0]; } 使用: - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:0.0001 target:self selector:@selector(timerMethod) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; _tasks = [NSMutableArray array]; //setupUI [self addRunloopObserver]; } -(void)timerMethod{ //不干任何事情! } - (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:IDENTIFIER]; cell.selectionStyle = UITableViewCellSelectionStyleNone; //干掉contentView上面的子控件!! 节约内存!! for (NSInteger i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { //干掉contentView 上面的所有子控件!! [[cell.contentView viewWithTag:i] removeFromSuperview]; } //添加文字 [ViewController addlabel:cell indexPath:indexPath]; //添加图片 [self addTasks:^{ [ViewController addImage1With:cell]; }]; [self addTasks:^{ [ViewController addImage2With:cell]; }]; [self addTasks:^{ [ViewController addImage3With:cell]; }]; return cell; }
003-图片延迟加载
//当我设置成UITrackingRunLoopMode或者NSRunLoopCommonModes我就能获取点击或者拖拽的事件 [self.imagView performSelector:@selector(setImage:) withObject:[UIImage imageNamed:@"002"] afterDelay:2.0f inModes:@[NSRunLoopCommonModes]];
004.自动释放池:autoreleasepool
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; _thread = [[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(testThread) object:nil]; [_thread start]; } - (void) testThread { //加一个池子,当runloop在休眠之前会自动释放自动释放池,当runloop在启动时,就会再次创建池子。 @autoreleasepool { //定时器生效的方式,一定要保证runloop开启,并且mode不为空 //此方法的定时器,默认已经加了mode,只需要开启runloop就可以了 [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:1.0f target:self selector:@selector(testAgain) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop]run]; } } - (void) testAgain { NSLog(@"-----------------%@",[NSThread currentThread]); }
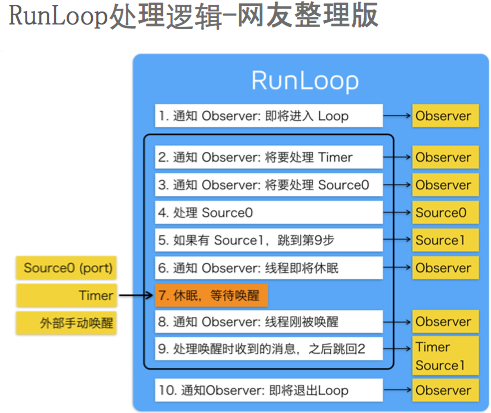
应用:子线程执行两个事件,怎么保证两个事件都执行。
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { NSThread * t = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(demo) object:nil]; [t start]; self.finished = NO; [self performSelector:@selector(otherMethod) onThread:t withObject:nil waitUntilDone:NO]; //t 线程执行完demo 事件后就被销毁了,无法执行otherMethod事件 } - (void)demo { NSLog(@"demo -- %@ ",[NSThread currentThread]); //[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] run];//提高优先级,继续问有没有其他事件,死循环 不会打印 come here. while (!self.finished) { [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:0.1]]; } NSLog(@"Come here "); } - (void)otherMethod { for (int i = 0; i<10; i++) { NSLog(@"otherMethod -- %@ ",[NSThread currentThread]); } self.finished = YES; }