FLUME CHANNEL
Flume Channel 和 Source 的结构有一定的相似性。
Channel 和 AbstractChannel 都 定义好了channel的结构。
不过Channel 需要一个事务(Transaction)来保证数据的一致性,而且这个事务必须是线程安全的,并且高效。
这一章主要学习的地方就是Transaction 的设计。
Transaction
public interface Transaction {
enum TransactionState { Started, Committed, RolledBack, Closed }
void begin();
void commit();
void rollback();
void close();
}
BasicTransactionSemantics
抽象类 BasicTransactionSemantics 实现了 Transaction。并且为channel的每个行为构建了上下文环境。Transaction 有4种不同的状态,不同的行为会导致不同的状态。
protected static enum State {
NEW, OPEN, COMPLETED, CLOSED
}
- 当BasicTransactionSemantics初始化的时候,为NEW状态。
- 当BasicTransactionSemantics 运行begin后,为OPEN状态。
- 当commit 或者 rollback 后,状态为COMPLETED。
- 不再做任何事情了,状态就为 CLOSED。
BasicChannelSemantics
BasicChannelSemantics 继承了 AbstractChannel,来实现 channel 的两个基本动作,put 和take。
BasicChannelSemantics 使用了ThreadLocal 来保存BasicTransactionSemantics 对象,这样每个线程就有一个独立的 BasicTransactionSemantics 对象。
put和take函数没什么好说的,里面是调用BasicTransactionSemantics 的方法。
getTransaction 函数 比较像单例模式初始化对象。
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
//如果没有初始化
if (!initialized) {
//获取锁
synchronized (this) {
//再次判断是否初始化,因为在获取锁后,很可能其他在其他地方也调用了这个方法,并且,初始化了。
if (!initialized) {
initialize();
initialized = true;
}
}
}
//获取当前的transaction,transaction 不存在,或者transaction 已经处于CLOSED状态,就再创建一个。
BasicTransactionSemantics transaction = currentTransaction.get();
if (transaction == null || transaction.getState().equals(
BasicTransactionSemantics.State.CLOSED)) {
transaction = createTransaction();
currentTransaction.set(transaction);
}
return transaction;
}
}
因为我经常使用MemoryChannel ,所以这里记录下MemoryChannel 的实现。这里贴一张类图。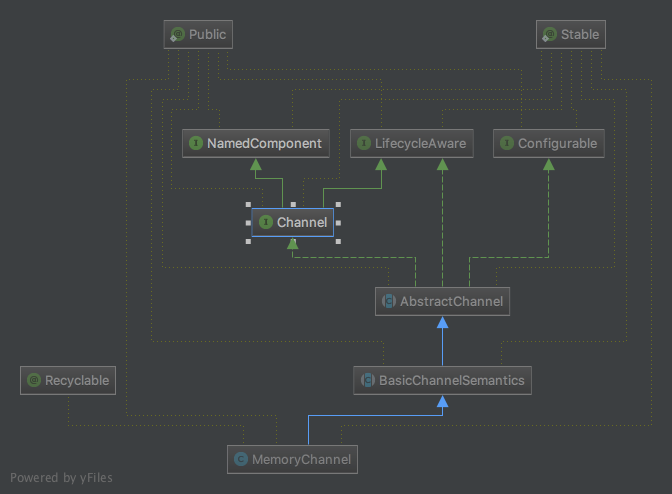
MemoryChannel
MemoryChannel 是将event放入内存中进行保存,并且能够同时按顺序进行写入和读取。要做这样一件事情,需要考虑到以下几点:
- 要合理的规划内存,不能够OOM。
- 要保证一个好的性能。
- 要保证线程安全。
根据上面的几点要求,我们可以想到:
- 在内存中保存,并且可以按顺序进行读写,那就选择队列了。
- 要合理的规划内存就必须要对内存进行管理,MemoryChannel 使用了 slot进行管理,而不是直接对bytes进行操作,为什么呢,我也不是很明白,如果非要加一个理由,就是管理方便吧。(我想起redis也是用slot来管理,后面可以找找资料学习下)
- 要在多线程的情况中要保证性能好,就不能够来个event处理一个,最好是批量操作,批量操作并且保证数据只被处理一次,那就用事务来保证。
- 要保证线程安全,第一要保证同一时刻对队列进行写操作,这就需要锁。同时要对线程进行同步,例如只有队列中有东西了, 才能够进行take操作。
实现:
- MemoryChannel使用了一个LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> queue 来保存event数据,对于BlockQueue,可以看这里。
- MemoryChannel使用了Semaphore bytesRemaining 进行内存管理。Semaphore bytesRemaining里面保存了整个channel中剩余的容量,里面保存的并不是byte大小,而是slot个数。在往队列queue 中插入添加events 的时候,需要从bytesRemaining中申请资源。在从queue中取出events后,需要bytesRemaining释放占的这部分资源。
- 要保证性能,就需要进行批操作,同时保证数据一致性,就考虑用事务。MemoryChannel使用了putList和takeList来保存需要添加到queue和从queue中取出的数据,并通过事务的commit来进行批操作。在内部定义了一个MemoryTransaction类,它继承BasicTransactionSemantics,并实现put,take,commit,rollback。
- 保证线程安全,MemoryChannel 使用 queueLock 进行互斥操作。
- 同时为了进行线程同步,设置两个 Semaphore.
- queueRemaining 这个是记录队列的剩余容量的信号量,这个信号量的计算方式为queue.remaining - takeList.size(),这样子,channel就有足够的容量进行rollback。
- queueStored 保存了queue中event的个数,take的时候,会试着去tryAcquire。
public class MemoryChannel extends BasicChannelSemantics {
private static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MemoryChannel.class);
private static final Integer defaultCapacity = 100;
private static final Integer defaultTransCapacity = 100;
private static final double byteCapacitySlotSize = 100;
private static final Long defaultByteCapacity = (long)(Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() * .80);
private static final Integer defaultByteCapacityBufferPercentage = 20;
private static final Integer defaultKeepAlive = 3;
private class MemoryTransaction extends BasicTransactionSemantics {
private LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> takeList;
private LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> putList;
//用来做监控
private final ChannelCounter channelCounter;
private int putByteCounter = 0;
private int takeByteCounter = 0;
public MemoryTransaction(int transCapacity, ChannelCounter counter) {
//
putList = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(transCapacity);
takeList = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(transCapacity);
channelCounter = counter;
}
/**
* 将 event 添加到putList
* **/
@Override
protected void doPut(Event event) throws InterruptedException {
channelCounter.incrementEventPutAttemptCount();
int eventByteSize = (int) Math.ceil(estimateEventSize(event) / byteCapacitySlotSize);
//如果添加失败了,就抛出异常
if (!putList.offer(event)) {
throw new ChannelException(
"Put queue for MemoryTransaction of capacity " +
putList.size() + " full, consider committing more frequently, " +
"increasing capacity or increasing thread count");
}
putByteCounter += eventByteSize;
}
/*
* 从queue 里面获取一个event放到takeList里面
* */
@Override
protected Event doTake() throws InterruptedException {
channelCounter.incrementEventTakeAttemptCount();
//检查容量
if (takeList.remainingCapacity() == 0) {
throw new ChannelException("Take list for MemoryTransaction, capacity " +
takeList.size() + " full, consider committing more frequently, " +
"increasing capacity, or increasing thread count");
}
//获取信号量,queueStored这个信号量是在commit中被release 的
if (!queueStored.tryAcquire(keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
return null;
}
Event event;
//从队列中点获取event
synchronized (queueLock) {
//注意这里使用了poll,如果去不到,它会返回NULL,所以后面会有一个checkNotNull
event = queue.poll();
}
Preconditions.checkNotNull(event, "Queue.poll returned NULL despite semaphore " +
"signalling existence of entry");
//放到takeList,注意这里用的是put,如果空间不足,会一直阻塞
takeList.put(event);
//记录takeList 的容量大小
int eventByteSize = (int) Math.ceil(estimateEventSize(event) / byteCapacitySlotSize);
takeByteCounter += eventByteSize;
return event;
}
/**
*
* bytesRemaining 保存了整个channel中剩余的容量,里面保存的并不是byte大小,而是slot大小
* 如果takeList.size() 小于 putList.size()
* */
@Override
protected void doCommit() throws InterruptedException {
int remainingChange = takeList.size() - putList.size();
//如果takeList 的容量 小于putList 的容量
if (remainingChange < 0) {
//这里应该是根据putList的大小,从bytesRemaining中申请空间
//如果申请不到就说明分配给的容量已经用完了
if (!bytesRemaining.tryAcquire(putByteCounter, keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
throw new ChannelException("Cannot commit transaction. Byte capacity " +
"allocated to store event body " + byteCapacity * byteCapacitySlotSize +
"reached. Please increase heap space/byte capacity allocated to " +
"the channel as the sinks may not be keeping up with the sources");
}
//我理解这里申请这个容量是保证,takeList能够有足够的空间保存putList的内容
//这样子就不会出现保存到队列中却取不出来的问题了
if (!queueRemaining.tryAcquire(-remainingChange, keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
bytesRemaining.release(putByteCounter);
throw new ChannelFullException("Space for commit to queue couldn't be acquired." +
" Sinks are likely not keeping up with sources, or the buffer size is too tight");
}
}
int puts = putList.size();
int takes = takeList.size();
//将putList放入队列中
synchronized (queueLock) {
if (puts > 0) {
while (!putList.isEmpty()) {
if (!queue.offer(putList.removeFirst())) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue add failed, this shouldn't be able to happen");
}
}
}
//将putList清空
putList.clear();
//清空takeList,里面的event已经被sink用掉了,不需要了
//后面需要看下sink是怎么去取event
takeList.clear();
}
//释放takeList 占用的内存
bytesRemaining.release(takeByteCounter);
takeByteCounter = 0;
putByteCounter = 0;
//释放信号量
queueStored.release(puts);
if (remainingChange > 0) {
queueRemaining.release(remainingChange);
}
if (puts > 0) {
channelCounter.addToEventPutSuccessCount(puts);
}
if (takes > 0) {
channelCounter.addToEventTakeSuccessCount(takes);
}
channelCounter.setChannelSize(queue.size());
}
@Override
//rollback就是将takeList 的内容放回queue中
//清空了putList
protected void doRollback() {
int takes = takeList.size();
synchronized (queueLock) {
Preconditions.checkState(queue.remainingCapacity() >= takeList.size(),
"Not enough space in memory channel " +
"queue to rollback takes. This should never happen, please report");
while (!takeList.isEmpty()) {
queue.addFirst(takeList.removeLast());
}
//不明白这里为什么会清空putList
putList.clear();
}
bytesRemaining.release(putByteCounter);
putByteCounter = 0;
takeByteCounter = 0;
queueStored.release(takes);
channelCounter.setChannelSize(queue.size());
}
}
// lock to guard queue, mainly needed to keep it locked down during resizes
// it should never be held through a blocking operation
private Object queueLock = new Object();
@GuardedBy(value = "queueLock")
private LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> queue;
// invariant that tracks the amount of space remaining in the queue(with all uncommitted takeLists deducted)
// we maintain the remaining permits = queue.remaining - takeList.size()
// this allows local threads waiting for space in the queue to commit without denying access to the
// shared lock to threads that would make more space on the queue
//这个是记录队列的剩余容量的信号量,这个信号量的计算方式为queue.remaining - takeList.size(),
//这样子,channel就有足够的容量进行rollback
private Semaphore queueRemaining;
// used to make "reservations" to grab data from the queue.
// by using this we can block for a while to get data without locking all other threads out
// like we would if we tried to use a blocking call on queue
private Semaphore queueStored;
// maximum items in a transaction queue
private volatile Integer transCapacity;
private volatile int keepAlive;
private volatile int byteCapacity;
private volatile int lastByteCapacity;
private volatile int byteCapacityBufferPercentage;
//里面保存了整个channel中剩余的容量,里面保存的并不是byte大小,而是slot大小
private Semaphore bytesRemaining;
private ChannelCounter channelCounter;
public MemoryChannel() {
super();
}
/**
* Read parameters from context
* <li>capacity = type long that defines the total number of events allowed at one time in the queue.
* <li>transactionCapacity = type long that defines the total number of events allowed in one transaction.
* <li>byteCapacity = type long that defines the max number of bytes used for events in the queue.
* <li>byteCapacityBufferPercentage = type int that defines the percent of buffer between byteCapacity and the estimated event size.
* <li>keep-alive = type int that defines the number of second to wait for a queue permit
*/
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
Integer capacity = null;
try {
capacity = context.getInteger("capacity", defaultCapacity);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
capacity = defaultCapacity;
LOGGER.warn("Invalid capacity specified, initializing channel to "
+ "default capacity of {}", defaultCapacity);
}
if (capacity <= 0) {
capacity = defaultCapacity;
LOGGER.warn("Invalid capacity specified, initializing channel to "
+ "default capacity of {}", defaultCapacity);
}
try {
transCapacity = context.getInteger("transactionCapacity", defaultTransCapacity);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
transCapacity = defaultTransCapacity;
LOGGER.warn("Invalid transation capacity specified, initializing channel"
+ " to default capacity of {}", defaultTransCapacity);
}
if (transCapacity <= 0) {
transCapacity = defaultTransCapacity;
LOGGER.warn("Invalid transation capacity specified, initializing channel"
+ " to default capacity of {}", defaultTransCapacity);
}
Preconditions.checkState(transCapacity <= capacity,
"Transaction Capacity of Memory Channel cannot be higher than " +
"the capacity.");
try {
byteCapacityBufferPercentage = context.getInteger("byteCapacityBufferPercentage",
defaultByteCapacityBufferPercentage);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
byteCapacityBufferPercentage = defaultByteCapacityBufferPercentage;
}
try {
//内存容量的大小 * 容量比例 / byteCapacitySlotSize
byteCapacity = (int) ((context.getLong("byteCapacity", defaultByteCapacity).longValue() *
(1 - byteCapacityBufferPercentage * .01)) / byteCapacitySlotSize);
if (byteCapacity < 1) {
byteCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
byteCapacity = (int) ((defaultByteCapacity * (1 - byteCapacityBufferPercentage * .01)) /
byteCapacitySlotSize);
}
try {
keepAlive = context.getInteger("keep-alive", defaultKeepAlive);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
keepAlive = defaultKeepAlive;
}
//这个在什么情况下会出现呢,不明白,因为修改参数后,所有的组件都会停止然后重新启动
//并且这里没有更新queueRemaining
if (queue != null) {
try {
resizeQueue(capacity);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
} else {
synchronized (queueLock) {
queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(capacity);
//注意,这个queueRemaining 只会在这里初始化一次,后面就不会改变了
queueRemaining = new Semaphore(capacity);
queueStored = new Semaphore(0);
}
}
//如果bytesRemaining 为空,也就是队列第一次初始化
if (bytesRemaining == null) {
bytesRemaining = new Semaphore(byteCapacity);
lastByteCapacity = byteCapacity;
} else {
if (byteCapacity > lastByteCapacity) {
bytesRemaining.release(byteCapacity - lastByteCapacity);
lastByteCapacity = byteCapacity;
} else {
try {
if (!bytesRemaining.tryAcquire(lastByteCapacity - byteCapacity, keepAlive,
TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
LOGGER.warn("Couldn't acquire permits to downsize the byte capacity, resizing has been aborted");
} else {
lastByteCapacity = byteCapacity;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
if (channelCounter == null) {
channelCounter = new ChannelCounter(getName());
}
}
//重新分配队列的大小
private void resizeQueue(int capacity) throws InterruptedException {
int oldCapacity;
synchronized (queueLock) {
//获取旧的队列的容量,话说这个不就是queue.capacity 么
oldCapacity = queue.size() + queue.remainingCapacity() ;
}
//如果旧的队列容量 等于 新的队列容量,就不做任何操作
if (oldCapacity == capacity) {
return;
//如果旧的队列容量 大于 新的队列容量,就试图获取足够的容量,并将东西付给新队列
} else if (oldCapacity > capacity) {
if (!queueRemaining.tryAcquire(oldCapacity - capacity, keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
LOGGER.warn("Couldn't acquire permits to downsize the queue, resizing has been aborted");
} else {
synchronized (queueLock) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> newQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(capacity);
newQueue.addAll(queue);
queue = newQueue;
}
}
} else {
synchronized (queueLock) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> newQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(capacity);
newQueue.addAll(queue);
queue = newQueue;
}
//queueRemaining 释放掉不需要的资源
queueRemaining.release(capacity - oldCapacity);
}
}
ChannelProcessor
ChannelProcessor 是所有channel的入口,Source会通过这个类将event转移到channel中。
在ChannelProcessor 中 最主要是processEventBatch函数。它首先会使用已经指定好的interceptor来对event进行一遍操作。然后再将event 放入对应的channel中。