目录
思路分析
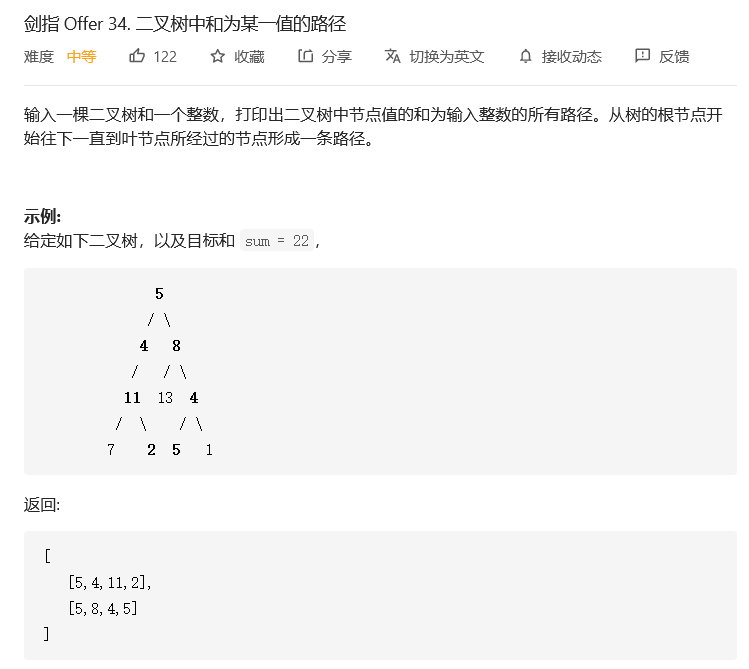
就是DFS,然后到达叶子结点的时候就判断是否满足条件,如果满足的话就是一个答案.
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int sum){
if(!root)return;
sum -= root->val;
path.push_back(root->val);
if(!root->left && !root->right && !sum)ans.push_back(path);
dfs(root->left,sum);
dfs(root->right,sum);
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
dfs(root,sum);
return ans;
}
};
python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = []
path = []
def dfs(root,sum):
if not root:return
sum -= root.val
path.append(root.val)
if not root.left and not root.right and not sum:
ans.append(list(path))
dfs(root.left,sum)
dfs(root.right,sum)
path.pop()
dfs(root,sum)
return ans