C++STL1--set
一、说明
set的用法:单一元素,自动排序
set的方法:用编译器的提示功能即可,不需要自己记
二、简单测试
1 /* 2 安迪的第一个字典 3 set的用法:单一元素,自动排序 4 set的方法:用编译器的提示功能即可,不需要自己记 5 */ 6 7 #include <iostream> 8 #include <set> 9 using namespace std; 10 set<int> setTest; 11 12 int main(){ 13 int a[]={8,3,2,5,1,3,8,9,17,3}; 14 //将数组a里面的元素存入集合 15 for(int i=0;i<10;i++) 16 { 17 setTest.insert(a[i]);//添加数据 18 } 19 //遍历输出,使用迭代器iterator 20 //无序方式输入,输出时已经从小到大排好序了,并且重复元素没有输出 21 for(set<int>::iterator it=setTest.begin();it!=setTest.end();++it) 22 { 23 cout<<*it<<" "; 24 } 25 cout<<endl; 26 return 0; 27 }
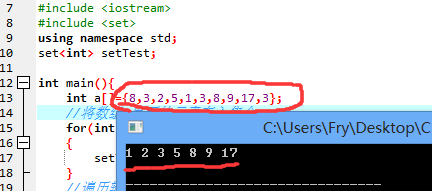
结果说明:重复元素只存储一次,像3和8
并且会默认从小到大排序
三、实例
安迪的第一个字典
题目:
输入一个文本,找出所有不同的单词(连续的最序列),按字典序从小到大输出,单词不区分大小写。
样例输入:
Today was my friend’s birthday, and I was invited to her birthday party.
The party was so great and the theme was red color. I saw many pictures of Hello Kitty.
They were so lovely. We sang the song to her and played a lot of funny games.
At last, we sent our best wishes to her. We had a great time.
The sign read:"Disneyland Left."
样例输出:(前五个)
a
and
at
best
birthday
1 /* 2 安迪的第一个字典 3 题目: 4 输入一个文本,找出所有不同的单词(连续的最序列),按字典序从小到大输出,单词不区分大小写。 5 样例输入: 6 Today was my friend’s birthday, and I was invited to her birthday party. 7 The party was so great and the theme was red color. I saw many pictures of Hello Kitty. 8 They were so lovely. We sang the song to her and played a lot of funny games. 9 At last, we sent our best wishes to her. We had a great time. 10 The sign read:"Disneyland Left." 11 样例输出:(前五个) 12 a 13 and 14 at 15 best 16 birthday 17 18 */ 19 /* 20 set的用法:单一元素,自动排序 21 set的方法:用编译器的提示功能即可,不需要自己记 22 */ 23 /* 24 分析: 25 1、大写变小写,其它符号变空格 26 2、存入set 27 */ 28 #include <iostream> 29 #include <set> 30 #include <string> 31 #include <sstream> 32 using namespace std; 33 set<string> dict;//string集合 34 35 int main(){ 36 freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 37 string s,buf;//s用于读入单词,buf做缓存,解决read:"Disneyland是一个单词的问题 38 while(cin>>s){ 39 for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ 40 if(isalpha(s[i])) //判断是否是字符 41 s[i]=tolower(s[i]);//是字符就变成小写 42 else //不是字符就变成空格 43 s[i]=' '; 44 } 45 stringstream ss(s);//字符串流,作用和inputstream很相似 46 //引入stringstream是为了防止把read:"Disneyland 这样的形式看出一个单词 47 while(ss>>buf) dict.insert(buf);//插入到dict集合中 48 } 49 //迭代器遍历,注意迭代器是指针 50 for(set<string>::iterator it=dict.begin();it!=dict.end();it++) 51 { 52 cout<<*it<<endl; 53 } 54 55 return 0; 56 }
四、常用用法
set集合容器:实现了红黑树的平衡二叉检索树的数据结构,插入元素时,它会自动调整二叉树的排列,把元素放到适当的位置,以保证每个子树根节点键值大于左子树所有节点的键值,小于右子树所有节点的键值;另外,还得保证根节点左子树的高度与右子树高度相等。
平衡二叉检索树使用中序遍历算法,检索效率高于vector、deque和list等容器,另外使用中序遍历可将键值按照从小到大遍历出来。
构造set集合主要目的是为了快速检索,不可直接去修改键值。
常用操作:
1.元素插入:insert()
2.中序遍历:类似vector遍历(用迭代器)
3.反向遍历:利用反向迭代器reverse_iterator。
例:
set<int> s;
......
set<int>::reverse_iterator rit;
for(rit=s.rbegin();rit!=s.rend();rit++)
4.元素删除:与插入一样,可以高效的删除,并自动调整使红黑树平衡。
set<int> s;
s.erase(2); //删除键值为2的元素
s.clear();
5.元素检索:find(),若找到,返回该键值迭代器的位置,否则,返回最后一个元素后面一个位置。
set<int> s;
set<int>::iterator it;
it=s.find(5); //查找键值为5的元素
if(it!=s.end()) //找到
cout<<*it<<endl;
else //未找到
cout<<"未找到";
6.自定义比较函数
(1)元素不是结构体:
例:
//自定义比较函数myComp,重载“()”操作符
struct myComp
{
bool operator()(const your_type &a,const your_type &b)
[
return a.data-b.data>0;
}
}
set<int,myComp>s;
......
set<int,myComp>::iterator it;
(2)如果元素是结构体,可以直接将比较函数写在结构体内。
例:
struct Info
{
string name;
float score;
//重载“<”操作符,自定义排序规则
bool operator < (const Info &a) const
{
//按score从大到小排列
return a.score<score;
}
}
set<Info> s;
......
set<Info>::iterator it;