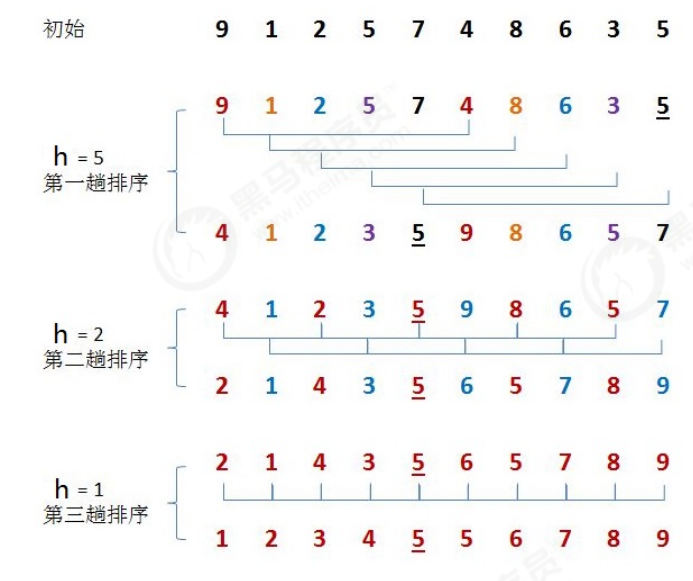
排序原理:
1.选定一个增长量h,按照增长量h作为数据分组的依据,对数据进行分组;
2.对分好组的每一组数据完成插入排序;
3.减小增长量,最小减为1,重复第二步操作。
排序过程:
例:{9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5}
package com.sort;
/*--------------
* Author:Real_Q
* Date:2021-01-06
* Time:18:43
* Description:
* {9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5}
* {1,2,3,4,5,5,6,7,8,9}
---------------*/
public class ShellSort {
//排序
public static void shellSort(Comparable[] comparables) {
//求增长量h
int h = 1;
int length = comparables.length;
while (h < length / 2) {
h = (h * 2 + 1);
}
//算法实体,当h大于等于一时,循环算法
while (h >= 1) {
//希尔排序规律,每次从h开始
for (int i = h; i < length; i++) {
//从i开始,倒叙遍历,比较后满足条件交换,条件不满足时,退出循环,进入下一次的循环
for (int j = i; j >= h; j -= h) {
if (Comparable(comparables[j - h], comparables[j])) {
exchange(comparables, j - h, j);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
//减小增长量
h /= 2;
}
}
//比较两个元素的大小
public static boolean Comparable(Comparable comparable1, Comparable comparable2) {
return comparable1.compareTo(comparable2) > 0;
}
//交换元素
public static void exchange(Comparable[] comparable, int leftIndex, int rightIndex) {
Comparable temp;
temp = comparable[leftIndex];
comparable[leftIndex] = comparable[rightIndex];
comparable[rightIndex] = temp;
}
}
测试类:
package com.testsort;
/*--------------
* Author:Real_Q
* Date:2021-01-06
* Time:19:05
* Description:
* {9,1,2,5,7,4,8,6,3,5}
* {1,2,3,4,5,5,6,7,8,9}
---------------*/
import java.util.Arrays;
import static com.sort.ShellSort.shellSort;
public class TestShell {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] array = {4,6,8,7,9,2,10,1};
shellSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
