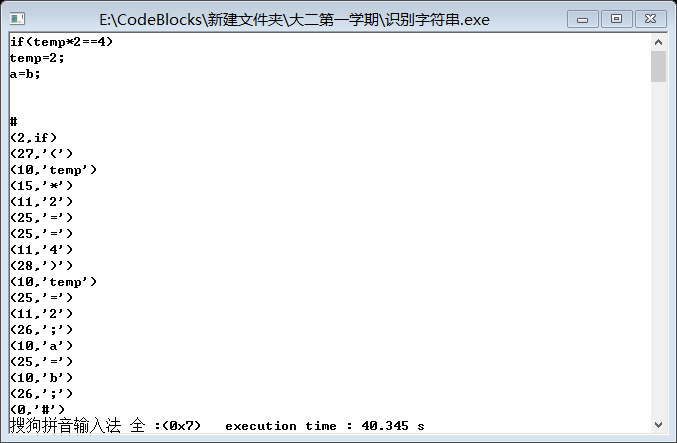
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char tempc[100];
char tempf[100];
char tempn[100];
char ch[100];
char r1[] = {"begin"};
char r2[] = {"if"};
char r3[] = {"then"};
char r4[] = {"while"};
char r5[] = {"do"};
char r6[] = {"end"};
int c=0;
void scanner();
void Swit(int num);
void recignition();
void main()
{
int i=-1;
printf("请输入字符串(end of '#'):");
do{
i++;
scanf("%c",&ch[i]);
}while(ch[i]!='#');
scanner();
printf("(0,'#')");
}
void scanner()
{ int i=0,j=0,k=0,t,l=0,f=0,n=0,m=0,q=0;
char cf[100]="";
while(ch[i]!='#')
{
while (ch[i]!='#' && ch[i]!=' ' && ch[i]!='
' && ch[i]!=' ')//在用户输入的字符串中找到分界符,用i记录界符前元素个数
i++;
for(;j<i;j++)//把字符串数组中的元素分类,字母,数字,符号
{
if((ch[j]>='a'&&ch[j]<='z') || (ch[j]>='A'&&ch[j]<='Z'))//判断字母
{
tempc[c]=ch[j];
c++;
if(!((ch[j+1]>='a'&&ch[j+1]<='z') || (ch[j+1]>='A'&&ch[j+1]<='Z')))
recignition();
}
else if(ch[j]>='0'&& ch[j]<='9')//判断数字并输出
{
tempn[n]=ch[j];
n++;
for(;q<n;q++)
printf("(11,'%d')",tempn[q]-48);
if(!(ch[j+1]>='0' && ch[j+1]<='9'))
printf("
");
}
else//判断符号
{
tempf[f]=ch[j];
f++;
for(;l<f;l++)
{
switch(tempf[l])
{
case '+': m=13;break;
case '-': m=14;break;
case '*': m=15;break;
case '/': m=16;break;
case ':':
if(tempf[l+1]=='=')
{
m=18;
l++;
}
else m=17;
break;
case '<':
if(tempf[l+1]=='=')
{
m=21;
l++;
}
else if (tempf[l+1]=='>')
{
m=22;
l++;
}
else m=20;
break;
case '>':
if(tempf[l+1]=='=')
{
m=24;
l++;
}
else m=23;
break;
case '=': m=25;break;
case ';': m=26;break;
case '(': m=27;break;
case ')': m=28;break;
default :printf("%c
",tempf[l]);
break;
}
if(m>0)
Swit(m);
m=0;
}
}
}
l++;
if(ch[i]!='#')
i++;
}
}
/*函数名:Swit
形参:num
函数功能:引用形参num,与字符串中对应的种别码进行配对,
输出种别码和字符本身。
返回值:无*/
void Swit(int num)
{
switch(num)
{
case 1:printf("(1,begin)
");break;
case 2:printf("(2,if)
");break;
case 3:printf("(3,then)
");break;
case 4:printf("(4,while)
");break;
case 5:printf("(5,do)
");break;
case 6:printf("(6,end)
");break;
case 13:printf("(13,'+')
");break;
case 14:printf("(14,'-')
");break;
case 15:printf("(15,'*')
");break;
case 16:printf("(16,'/')
");break;
case 17:printf("(17,':')
");break;
case 18:printf("(18,':=')
");break;
case 20:printf("(20,'<')
");break;
case 21:printf("(21,'<=')
");break;
case 22:printf("(22,'<>')
");break;
case 23:printf("(23,'>')
");break;
case 24:printf("(24,'>=')
");break;
case 25:printf("(25,'=')
");break;
case 26:printf("(26,';')
");break;
case 27:printf("(27,'(')
");break;
case 28:printf("(28,')')
");break;
}
}
/*函数名:recignition
形参:无
函数功能:存放字母的数组tempc[]与关键字进行对比,
输出字符数组中的关键字
返回值:无*/
void recignition()
{
int t=0;
int i=0;
char cc[100]="";
if(strcmp(tempc,r1)==0)
t=1;
else if(strcmp(tempc,r2)==0)
t=2;
else if(strcmp(tempc,r3)==0)
t=3;
else if(strcmp(tempc,r4)==0)
t=4;
else if(strcmp(tempc,r5)==0)
t=5;
else if(strcmp(tempc,r6)==0)
t=6;
if(t>0)
Swit(t);
else
printf("(10,'%s')
",tempc);
for(;c>0;c--)
tempc[c]=cc[0];
t=0;
}