概述:
Trie是个简单但实用的数据结构,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种,相邻节点间的边代表一个字符,这样树的每条分支代表一则子串,而树的叶节点则代表完整的字符串。和普通树不同的地方是,相同的字符串前缀共享同一条分支。
例如:pool,prize,preview,prepare,produce,progress这些关键词的Tire树
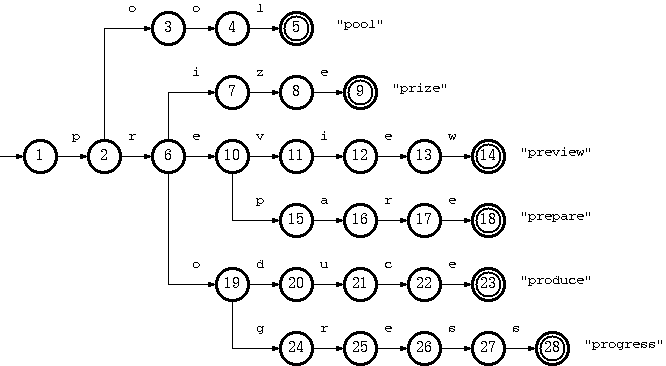
典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。
它的优点是:利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希树高。
基本性质:
- 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符;
- 从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串;
- 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。
应用场景:
字典数查找效率很高,时间复杂度是O(m),m是要查找的单词中包含的字母的个数,但是会浪费大量存放空指针的存储空间,属于以空间换时间的算法。
1、串快速检索
给出N个单词组成的熟词表,以及一篇全用小写英文书写的文章,请你按最早出现的顺序写出所有不在熟词表中的生词。
2、单词自动完成
编辑代码时,输入字符,自动提示可能的关键字、变量或函数等信息。
3、最长公共前缀
对所有串建立字典树,对于两个串的最长公共前缀的长度即他们所在的结点的公共祖先个数,于是,问题就转化为最近公共祖先问题。
4、串排序方面的应用
给定N个互不相同的仅由一个单词构成的英文名,让你将他们按字典序从小到大输出用字典树进行排序,采用数组的方式创建字典树,这棵树的每个结点的所有儿子很显然地按照其字母大小排序。对这棵树进行先序遍历即可。
程序代码:
#include <gtest/gtest.h> #include <list> using namespace std; class TrieTree { public: const static int MAX_CHILD_KEY_COUNT = 30; const static char STRING_END_TAG = 'xFF'; struct TrieNode { char nodeValue; int nodeFreq; list<TrieNode*> childNodes[MAX_CHILD_KEY_COUNT]; //为了避免这里数组太大,采用数组+链表方式 TrieNode() { nodeValue = 0; nodeFreq = 0; } }; TrieTree(); ~TrieTree(); public: void Insert(const string& strVal); void Delete(const string& strVal); int Search(const string& strVal); int CommonPrefix(const string& strVal); private: void Clean(TrieNode* rootNode); bool DeleteNode(TrieNode* rootNode, const string& strVal, int nOffset); TrieNode m_RootNode; }; TrieTree::TrieTree() { }; TrieTree::~TrieTree() { Clean(&m_RootNode); }; void TrieTree::Insert(const string& strVal) { if (strVal.empty()) { return; } // 在字符串末尾添加一个特殊字符,以区分是前缀还是完整字符串 string strValue(strVal); strValue += STRING_END_TAG; TrieNode* pCurrentNode = &m_RootNode; unsigned int nIndex = 0; unsigned int nLength = strValue.length(); do { bool bExistVal = false; char cValue = strValue[nIndex]; list<TrieNode*>& refListNode = pCurrentNode->childNodes[(unsigned char)cValue % MAX_CHILD_KEY_COUNT]; if (refListNode.size()) { list<TrieNode*>::iterator it = refListNode.begin(); list<TrieNode*>::iterator itEnd = refListNode.end(); for (; it != itEnd; ++it) { if (cValue == (*it)->nodeValue) { (*it)->nodeFreq++; bExistVal = true; pCurrentNode = *it; break; } } } // 当前不存在对应的字符,则新建一个 if (!bExistVal) { TrieNode* pNewNode = new TrieNode(); pNewNode->nodeFreq = 1; pNewNode->nodeValue = cValue; refListNode.push_back(pNewNode); pCurrentNode = pNewNode; } ++nIndex; } while(nIndex < nLength); } void TrieTree::Delete(const string& strVal) { if (strVal.empty()) { return; } string strValue(strVal); strValue += STRING_END_TAG; DeleteNode(&m_RootNode, strValue, 0); } int TrieTree::Search(const string& strVal) { if (strVal.empty()) { return 0; } string strValue(strVal); strValue += STRING_END_TAG; return CommonPrefix(strValue); } int TrieTree::CommonPrefix(const string& strVal) { if (strVal.empty()) { return 0; } TrieNode* pCurrentNode = &m_RootNode; unsigned int nIndex = 0; unsigned int nLength = strVal.length(); int nFreq = 0; do { bool bExistVal = false; char cValue = strVal[nIndex]; list<TrieNode*>& refListNode = pCurrentNode->childNodes[(unsigned char)cValue % MAX_CHILD_KEY_COUNT]; if (refListNode.size()) { list<TrieNode*>::iterator it = refListNode.begin(); list<TrieNode*>::iterator itEnd = refListNode.end(); for (; it != itEnd; ++it) { if (cValue == (*it)->nodeValue) { nFreq = (*it)->nodeFreq; bExistVal = true; pCurrentNode = *it; break; } } } // 当前不存在对应的字符,则没有找到 if (!bExistVal) { nFreq = 0; break; } ++nIndex; } while(nIndex < nLength); return nFreq; } void TrieTree::Clean(TrieNode* rootNode) { if (!rootNode) { return; } for (int i=0; i<MAX_CHILD_KEY_COUNT; ++i) { list<TrieNode*>& refListNode = rootNode->childNodes[i]; if (refListNode.size()) { list<TrieNode*>::iterator it = refListNode.begin(); list<TrieNode*>::iterator itEnd = refListNode.end(); for (; it != itEnd; ++it) { Clean(*it); delete *it; } refListNode.clear(); } } } bool TrieTree::DeleteNode(TrieNode* rootNode, const string& strVal, int nOffset) { if (!rootNode) { return false; } bool bDelChild = false; char cValue = strVal[nOffset]; list<TrieNode*>& refListNode = rootNode->childNodes[(unsigned char)cValue % MAX_CHILD_KEY_COUNT]; if (refListNode.size()) { list<TrieNode*>::iterator it = refListNode.begin(); list<TrieNode*>::iterator itEnd = refListNode.end(); for (; it != itEnd; ++it) { if ((*it)->nodeValue == cValue) { bDelChild = true; // 字符串没有结束,删除下一个节点 if (++nOffset < (int)strVal.length()) { bDelChild = DeleteNode(*it, strVal, nOffset); } // 该节点次数为0,说明已经没有子节点了,移除该节点 if (bDelChild && (0 == (--(*it)->nodeFreq))) { delete *it; refListNode.erase(it); } break; } } } return bDelChild; } TEST(Structure, tTireTree) { // "abc","ab","bd","dda" TrieTree tree; tree.Insert("abc"); tree.Insert("ab"); tree.Insert("bd"); tree.Insert("dda"); ASSERT_EQ(tree.Search("ab"), 1); ASSERT_EQ(tree.CommonPrefix("ab"), 2); tree.Delete("ab"); ASSERT_EQ(tree.Search("ab"), 0); ASSERT_EQ(tree.CommonPrefix("ab"), 1); tree.Delete("abcd"); ASSERT_EQ(tree.Search("ab"), 0); ASSERT_EQ(tree.Search("d"), 0); ASSERT_EQ(tree.CommonPrefix("d"), 1); ASSERT_EQ(tree.Search("fg"), 0); tree.Delete("fg"); }
参考引用:
百度百科“字典树”
http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2012/11/25/2788268.html
看书、学习、写代码