这篇博客,本蒟蒻会详解各种lca求法,朴素和倍增会后续增加上去

欧拉序列+RMQ 【O(n+m+nlogn+q)】
这种求法对于询问次数特别的多的情况比较好用,有一些出题人可能会特意卡这个,让你必须要用欧拉序列
原理:
把每个点搜索到的顺序记录下来,形成一个序列(就是欧拉序列),然后rmq深度,最后O(1)输出
看这个例子

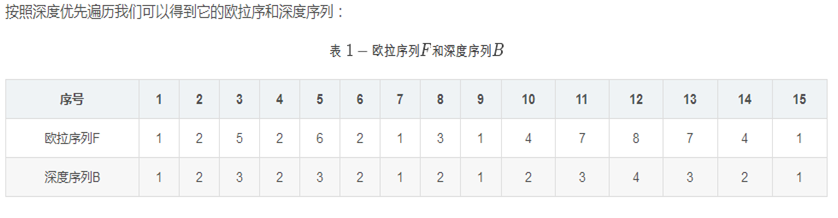
很明显记录序号+rmq深度就好
它的核心在这里
1 void dfs(int now,int fa,int deep){ 2 dfn[now]=++tt;dep[now]=deep; 3 rmq[tt][0]=now;//这里记录了一次 4 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt){ 5 int to=edge[i].to; 6 if(to==fa)continue; 7 dfs(to,now,deep+1); 8 rmq[++tt][0]=now;//这里又记录了一次 9 } 10 }
会发现记录了两次,这样rmq数组就能把整个搜索顺序都记录下来
rmq就很简单了,就是用dep来rmq
1 for(int j=1;j<=19;j++) 2 { 3 for(int i=1;i+(1<<j)-1<=tt;i++) 4 { 5 rmq[i][j]=dep[rmq[i][j-1]]<dep[rmq[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]]?rmq[i][j-1]:rmq[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]; 6 } 7 }
最后输出就好
但是有一点玄学的地方,就是rmq数组不能开太大,本人就是开大了之后就T了,用多大开多大就好

1 //欧拉序列 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #define N 500111 6 #define clear(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a)) 7 using namespace std; 8 struct star{int to,nxt;}edge[N*2]; 9 int n,m,u,v,s,cnt=1,tt; 10 int head[N],dep[N],rmq[2*N][20],dfn[N],lg2[2*N]; 11 inline void add(int u,int v){ 12 edge[cnt].nxt=head[u]; 13 edge[cnt].to=v; 14 head[u]=cnt++; 15 } 16 void dfs(int now,int fa,int deep){ 17 dfn[now]=++tt;dep[now]=deep; 18 rmq[tt][0]=now; 19 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt){ 20 int to=edge[i].to; 21 if(to==fa)continue; 22 dfs(to,now,deep+1); 23 rmq[++tt][0]=now; 24 } 25 } 26 int main() 27 { 28 clear(head,-1); 29 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s); 30 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 31 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); 32 add(u,v),add(v,u); 33 }dep[s]=1,dfs(s,-1,1); 34 for(int i=2;i<=tt;i++) 35 { 36 lg2[i]=lg2[i>>1]+1; 37 } 38 for(int j=1;j<=19;j++) 39 { 40 for(int i=1;i+(1<<j)-1<=tt;i++) 41 { 42 rmq[i][j]=dep[rmq[i][j-1]]<dep[rmq[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]]?rmq[i][j-1]:rmq[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]; 43 } 44 } 45 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 46 { 47 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); 48 int l=dfn[u],r=dfn[v]; 49 if(l>r)swap(l,r); 50 int lg=lg2[r-l+1]; 51 printf("%d ",dep[rmq[l][lg]]<dep[rmq[r-(1<<lg)+1][lg]]?rmq[l][lg]:rmq[r-(1<<lg)+1][lg]); 52 } 53 return 0; 54 }
Trajan【离线O(n+m+q)】
这是一个很神的算法,但是有些题可能会卡离线
它的思路就是对询问进行用链式前向星离散化(双向边),然后在做的过程中用并查集维护父亲,然后如果发现搜到x时,有询问(x,y),而且y已经搜过了(也就是更新过父亲了),这组询问的答案就是find(y)

核心
1 void tarjan(int now,int fa) 2 { 3 f[now]=now; 4 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) 5 { 6 int to=edge[i].to; 7 if(to==fa)continue; 8 if(!vis[to])tarjan(to,now),f[to]=now; 9 } 10 vis[now]=1; 11 for(int i=hd[now];i!=-1;i=ee[i].nxt) 12 { 13 int to=ee[i].to; 14 if(vis[to])ans[ee[i].num]=find(to); 15 } 16 }
有一个注意的地方,就是f要放在循环里进行更新这个是我右桌大佬亲身实WA的,放在外面如果更新它和它儿子的答案就会错(yy一下就知道)
离散化的时候加一个问题编号,处理起来非常方便

1 //tarjan 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #define N 500111 6 #define clear(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a)) 7 using namespace std; 8 struct star{int to,nxt;}edge[N*2]; 9 struct moon{int to,nxt,num;}ee[N*2]; 10 int n,m,u,v,s,cnt=1,ct=1; 11 int head[N],hd[N],f[N],ans[N]; 12 bool vis[N]; 13 int find(int x){return x==f[x]?f[x]:f[x]=find(f[x]);} 14 inline void add(int u,int v){ 15 edge[cnt].nxt=head[u]; 16 edge[cnt].to=v; 17 head[u]=cnt++; 18 } 19 inline void ad(int u,int v,int num){ 20 ee[ct].nxt=hd[u]; 21 ee[ct].to=v; 22 ee[ct].num=num; 23 hd[u]=ct++; 24 } 25 void tarjan(int now,int fa) 26 { 27 f[now]=now; 28 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) 29 { 30 int to=edge[i].to; 31 if(to==fa)continue; 32 if(!vis[to])tarjan(to,now),f[to]=now; 33 } 34 vis[now]=1; 35 for(int i=hd[now];i!=-1;i=ee[i].nxt) 36 { 37 int to=ee[i].to; 38 if(vis[to])ans[ee[i].num]=find(to); 39 } 40 } 41 int main() 42 { 43 clear(head,-1),clear(hd,-1); 44 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s); 45 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) 46 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v),add(u,v),add(v,u); 47 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 48 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v),ad(u,v,i),ad(v,u,i); 49 tarjan(s,-1); 50 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 51 printf("%d ",ans[i]); 52 return 0; 53 }
树链剖分【O(n+m+qlogn)】
这个算法是非常快的,也是最常用的!!而且还好写,所以一定要记住
它的原理呢
关于重儿子轻儿子重链轻链的知识可以百度

首先这个预处理
1 int init(int now,int fa) 2 { 3 size[now]=1; 4 int maxson=-1; 5 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) 6 { 7 int to=edge[i].to; 8 if(to==fa)continue; 9 dep[to]=dep[now]+1,f[to]=now; 10 size[now]+=init(to,now); 11 if(size[to]>maxson)maxson=size[to],son[now]=to; 12 } 13 return size[now]; 14 }
这里的son存的就是每个节点的重儿子,然后size的维护之前博客有写过,f的记录是必要的,因为查询的时候会用到,
然后第二个重标记过程
1 void remark(int now,int topf,int fa) 2 { 3 id[now]=++tt; 4 top[now]=topf; 5 if(!son[now])return; 6 remark(son[now],topf,now); 7 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) 8 { 9 int to=edge[i].to; 10 if(!id[to] && to!=fa)remark(to,to,now); 11 } 12 }
这个比较好理解,先搜重儿子(这样会使重链编号是连续的),topf维护的是重链的起点,fa用来防止双向边死循环
然后代码

1 //树链剖分 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #define N 500111 6 #define clear(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a)) 7 using namespace std; 8 struct star{int to,nxt;}edge[N*2]; 9 int n,m,u,v,s,cnt=1,tt; 10 int head[N],dep[N],size[N],f[N],son[N],id[N],top[N]; 11 inline void add(int u,int v){ 12 edge[cnt].nxt=head[u]; 13 edge[cnt].to=v; 14 head[u]=cnt++; 15 } 16 int init(int now,int fa) 17 { 18 size[now]=1; 19 int maxson=-1; 20 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) 21 { 22 int to=edge[i].to; 23 if(to==fa)continue; 24 dep[to]=dep[now]+1,f[to]=now; 25 size[now]+=init(to,now); 26 if(size[to]>maxson)maxson=size[to],son[now]=to; 27 } 28 return size[now]; 29 } 30 void remark(int now,int topf,int fa) 31 { 32 id[now]=++tt; 33 top[now]=topf; 34 if(!son[now])return; 35 remark(son[now],topf,now); 36 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) 37 { 38 int to=edge[i].to; 39 if(!id[to] && to!=fa)remark(to,to,now); 40 } 41 } 42 int ask(int u,int v) 43 { 44 while(top[u]!=top[v]) 45 { 46 if(dep[top[u]]<dep[top[v]])swap(u,v); 47 u=f[top[u]]; 48 } 49 if(dep[u]>dep[v])swap(u,v); 50 return u; 51 } 52 int main() 53 { 54 clear(head,-1); 55 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s); 56 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) 57 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v),add(u,v),add(v,u); 58 dep[s]=1,top[s]=1,init(s,-1),remark(s,s,-1); 59 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 60 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v),printf("%d ",ask(u,v)); 61 return 0; 62 }

1 //欧拉序列 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #define N 500111 6 #define clear(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a)) 7 using namespace std; 8 struct star{int to,nxt;}edge[N*2]; 9 int n,m,u,v,s,cnt=1,tt; 10 int head[N],dep[N],rmq[2*N][20],dfn[N],lg2[2*N]; 11 inline void add(int u,int v){ 12 edge[cnt].nxt=head[u]; 13 edge[cnt].to=v; 14 head[u]=cnt++; 15 } 16 void dfs(int now,int fa,int deep){ 17 dfn[now]=++tt;dep[now]=deep; 18 rmq[tt][0]=now; 19 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt){ 20 int to=edge[i].to; 21 if(to==fa)continue; 22 dfs(to,now,deep+1); 23 rmq[++tt][0]=now; 24 } 25 } 26 int main() 27 { 28 clear(head,-1); 29 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s); 30 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 31 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); 32 add(u,v),add(v,u); 33 }dep[s]=1,dfs(s,-1,1); 34 for(int i=2;i<=tt;i++) 35 { 36 lg2[i]=lg2[i>>1]+1; 37 } 38 for(int j=1;j<=19;j++) 39 { 40 for(int i=1;i+(1<<j)-1<=tt;i++) 41 { 42 rmq[i][j]=dep[rmq[i][j-1]]<dep[rmq[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]]?rmq[i][j-1]:rmq[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]; 43 } 44 } 45 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 46 { 47 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v); 48 int l=dfn[u],r=dfn[v]; 49 if(l>r)swap(l,r); 50 int lg=lg2[r-l+1]; 51 printf("%d ",dep[rmq[l][lg]]<dep[rmq[r-(1<<lg)+1][lg]]?rmq[l][lg]:rmq[r-(1<<lg)+1][lg]); 52 } 53 return 0; 54 }

1 //tarjan 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #define N 500111 6 #define clear(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a)) 7 using namespace std; 8 struct star{int to,nxt;}edge[N*2]; 9 struct moon{int to,nxt,num;}ee[N*2]; 10 int n,m,u,v,s,cnt=1,ct=1; 11 int head[N],hd[N],f[N],ans[N]; 12 bool vis[N]; 13 int find(int x){return x==f[x]?f[x]:f[x]=find(f[x]);} 14 inline void add(int u,int v){ 15 edge[cnt].nxt=head[u]; 16 edge[cnt].to=v; 17 head[u]=cnt++; 18 } 19 inline void ad(int u,int v,int num){ 20 ee[ct].nxt=hd[u]; 21 ee[ct].to=v; 22 ee[ct].num=num; 23 hd[u]=ct++; 24 } 25 void tarjan(int now,int fa) 26 { 27 f[now]=now; 28 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].nxt) 29 { 30 int to=edge[i].to; 31 if(to==fa)continue; 32 if(!vis[to])tarjan(to,now),f[to]=now; 33 } 34 vis[now]=1; 35 for(int i=hd[now];i!=-1;i=ee[i].nxt) 36 { 37 int to=ee[i].to; 38 if(vis[to])ans[ee[i].num]=find(to); 39 } 40 } 41 int main() 42 { 43 clear(head,-1),clear(hd,-1); 44 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s); 45 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) 46 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v),add(u,v),add(v,u); 47 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 48 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v),ad(u,v,i),ad(v,u,i); 49 tarjan(s,-1); 50 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 51 printf("%d ",ans[i]); 52 return 0; 53 }

1 //N<=500000,M<=500000 2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 3 #define clear(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a)); 4 #define N 500010 5 #define M 500010 6 using namespace std; 7 struct star{ 8 int to,next; 9 }edge[N*2]; 10 int cnt=1,head[N],f[N][20],deep[N]; 11 void add(int u,int v) 12 { 13 edge[cnt].next=head[u]; 14 edge[cnt].to=v; 15 head[u]=cnt++; 16 } 17 void dfs(int now,int fa,int dep) 18 { 19 deep[now]=dep;f[now][0]=fa; 20 for(int i=head[now];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next) 21 { 22 int to=edge[i].to; 23 if(to!=fa)dfs(to,now,dep+1); 24 } 25 } 26 int lca(int x,int y) 27 { 28 if(deep[x]<deep[y])swap(x,y); 29 for(int i=16;i>=0;i--) 30 { 31 if(deep[f[x][i]]>=deep[y])x=f[x][i]; 32 } 33 if(x==y)return x; 34 for(int i=16;i>=0;i--) 35 { 36 if(f[x][i]!=f[y][i])x=f[x][i],y=f[y][i]; 37 } 38 return f[x][0]; 39 } 40 int main() 41 { 42 clear(head,-1); 43 int n,m,root; 44 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&root); 45 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) 46 { 47 int x,y; 48 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 49 add(x,y);add(y,x); 50 }deep[root]=1; 51 dfs(root,0,1); 52 for(int j=1;j<=16;j++) 53 { 54 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 55 { 56 f[i][j]=f[f[i][j-1]][j-1]; 57 } 58 } 59 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 60 { 61 int a,b; 62 scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); 63 printf("%d ",lca(a,b)); 64 } 65 return 0; 66 }
