1. BeanPostProcessor简介
BeanPostProcessor是Spring IOC容器给我们提供的一个扩展接口。接口声明如下:
public interface BeanPostProcessor { //bean初始化方法调用前被调用 Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; //bean初始化方法调用后被调用 Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
运行顺序
===Spring IOC容器实例化Bean===
===调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法===
===调用bean实例的初始化方法===
===调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法===
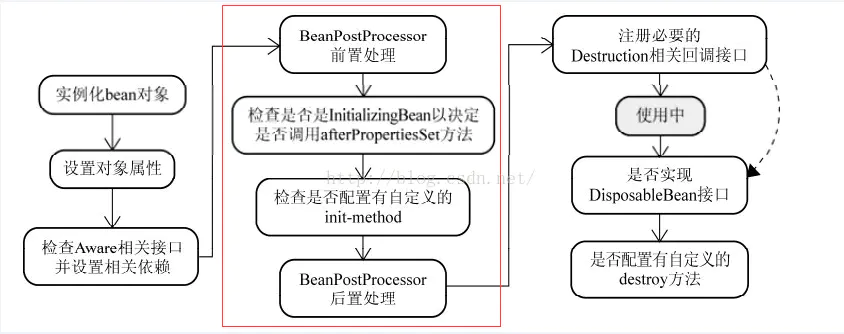
不要将BeanPostProcessor标记为延迟初始化。因为如果这样做,Spring容器将不会注册它们,自定义逻辑也就无法得到应用。假如你在<beans />元素的定义中使用了'default-lazy-init'属性,请确信你的各个BeanPostProcessor标记为'lazy-init="false"'。BeanFactory和ApplicationContext对待bean后置处理器稍有不同。ApplicationContext会自动检测在配置文件中实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的所有bean,并把它们注册为后置处理器,然后在容器创建bean的适当时候调用它,因此部署一个后置处理器同部署其他的bean并没有什么区别。而使用BeanFactory实现的时候,bean 后置处理器必须通过代码显式地去注册,在IoC容器继承体系中的ConfigurableBeanFactory接口中定义了注册方法
2. BeanPostProcessor实例
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization..." + beanName + "=>" + bean); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean); return bean; } }
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的子接口,可以在Bean生命周期的另外两个时期提供扩展的回调接口,即实例化Bean之前(调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法)和实例化Bean之后(调用postProcessAfterInstantiation方法),该接口定义如下:
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException;
boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
}
其使用方法与上面介绍的BeanPostProcessor接口类似,只时回调时机不同。
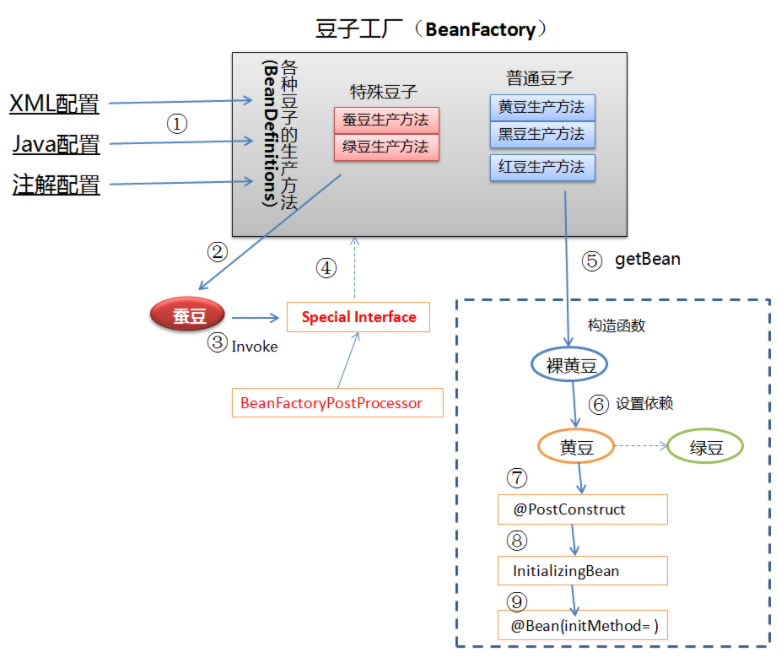
3. BeanFactoryPostProcessor简介
bean工厂的bean属性处理容器,说通俗一些就是可以管理我们的bean工厂内所有的beandefinition(未实例化)数据,可以随心所欲的修改属性。
4. BeanFactoryPostProcessor实例
@Component public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor...postProcessBeanFactory..."); int count = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionCount(); String[] names = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames(); System.out.println("当前BeanFactory中有"+count+" 个Bean"); System.out.println(Arrays.asList(names)); } }
区别:
注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实例,需要重载
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
通过beanFactory可以获取bean的示例或定义等。同时可以修改bean的属性,这是和BeanPostProcessor最大的区别。