0.目录
1.冒泡排序
2.希尔排序
3.小结
1.冒泡排序
冒泡排序的基本思想:

第 i 次冒泡排序示例:
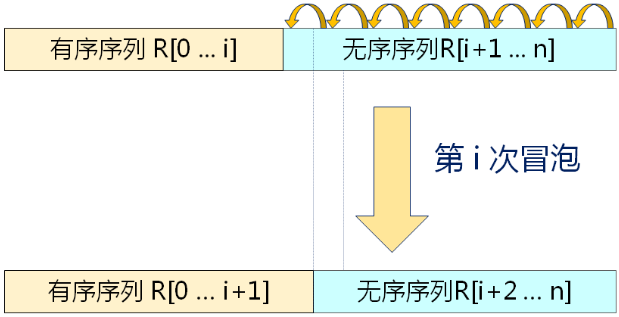
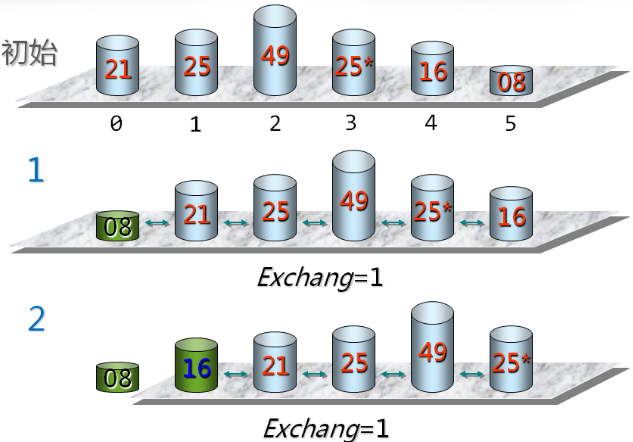
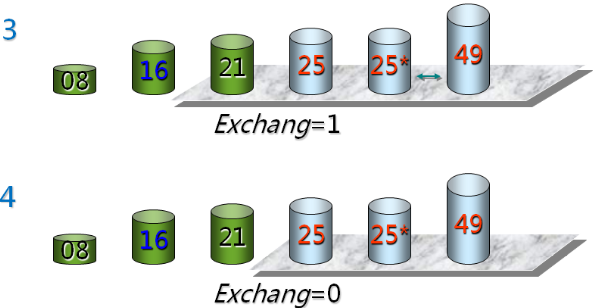
实现冒泡排序(在Sort.h中):
public:
template <typename T>
static void Bubble(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true)
{
bool exchange = true;
for(int i=0; (i<len) && exchange; i++)
{
exchange = false;
for(int j=len-1; j>i; j--)
{
if( min2max ? (array[j] < array[j-1]) : (array[j] > array[j-1]) )
{
Swap(array[j], array[j-1]);
exchange = true;
}
}
}
}
mian.cpp测试
#include <iostream>
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
int array[] = {3, 1, 2, 5, 4};
Sort::Bubble(array, 5);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
cout << "~~~" << endl;
Sort::Bubble(array, 5, false);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
~~~
5
4
3
2
1
2.希尔排序
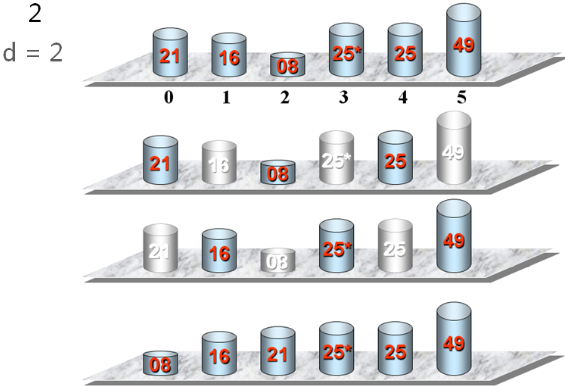
希尔排序的基本思想:
- 将待排序列划分为若干组,在每一组内进行插入排序,以使整个序列基本有序,然后再对整个序列进行插入排序。
希尔排序示例:

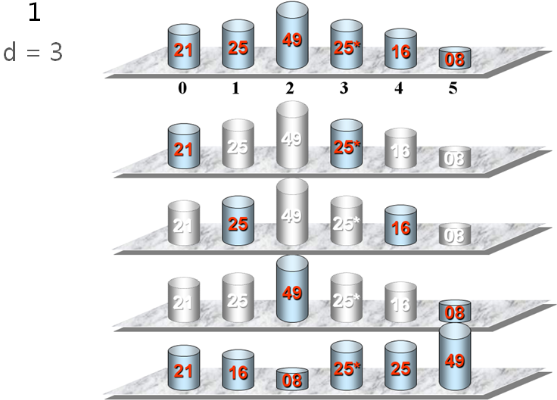

实现希尔排序(在Sort.h中):
public:
template <typename T>
static void Shell(T array[], int len, bool min2max = true)
{
int d = len;
do
{
d = d / 3 + 1; // d--
// 采用插入排序
for(int i=d; i<len; i+=d)
{
int k = i;
T e = array[i];
for(int j=i-d; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j]>e) : (array[j]<e)); j-=d)
{
array[j+d] = array[j];
k = j;
}
if( k != i )
{
array[k] = e;
}
}
} while( d > 1 );
}
mian.cpp测试
#include <iostream>
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
int main()
{
int array[] = {3, 1, 2, 5, 4};
Sort::Shell(array, 5);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
cout << "~~~" << endl;
Sort::Shell(array, 5, false);
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << array[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
1
2
3
4
5
~~~
5
4
3
2
1
3.小结
- 冒泡排序每次从后向前将较小的元素交互到位
- 冒泡排序是一种稳定的排序法,其复杂度为 O(n²)
- 希尔排序通过分组的方式进行多次插入排序
- 希尔排序是一种不稳定的排序法,其复杂度为 O(n³/²)