lock锁的是地址
而.net有内部机制使得相同的字符串内存地址是相同的(new string)除外
下面上实验代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
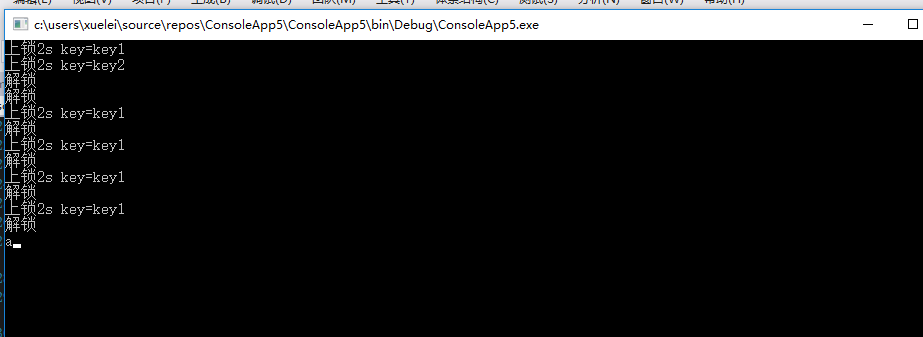
List<string> keyList = new List<string> { "key1","key2", "key1", "key1", "key1", "key1", };
keyList.ForEach(u =>
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(s =>
{
test.lockTestByString(u);
});
});
Console.Read();
}
}
public class test {
public static void lockTestByString(string key)
{
lock (key)
{
Console.WriteLine("上锁2s key="+key);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("解锁");
}
}
}
}
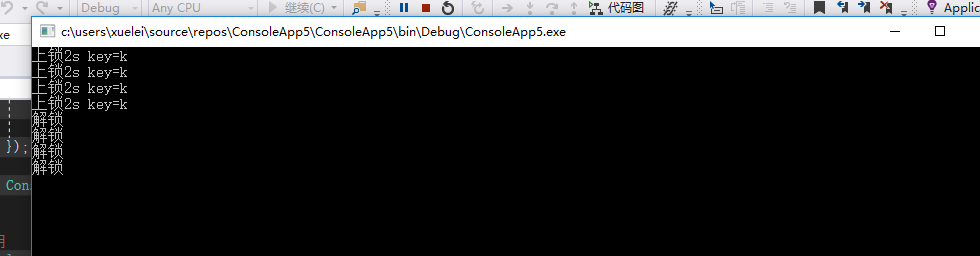
运行
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<string> keyList = new List<string> {new string('k',1), new string('k', 1), new string('k', 1), new string('k', 1) };
keyList.ForEach(u =>
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(s =>
{
test.lockTestByString(u);
});
});
Console.Read();
}
}
public class test {
public static void lockTestByString(string key)
{
lock (key)
{
Console.WriteLine("上锁2s key="+key);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("解锁");
}
}
}
}
通过new字符串得出的运行结果