为什么要封装?
我们看电视,只要按一下开关和换台就行了。有必要了解电视的内部结构吗?有必要了解显像管吗?
封装是为了隐藏对象内部的复杂性,只对外公开简单的接口。便于外界调用,从而提高系统的可扩展性,可维护性。
我们设计程序要追求:“高内聚,低耦合”。
高内聚:就是类的颞部数据的操作细节自己完成,不允许外部干涉;
低耦合:仅仅暴露少量的方法给外部使用
哪些应该封装,哪些不应该封装?
类无非就是属性和方法。对他们进行约束行了。
使用访问控制符,现实封装!
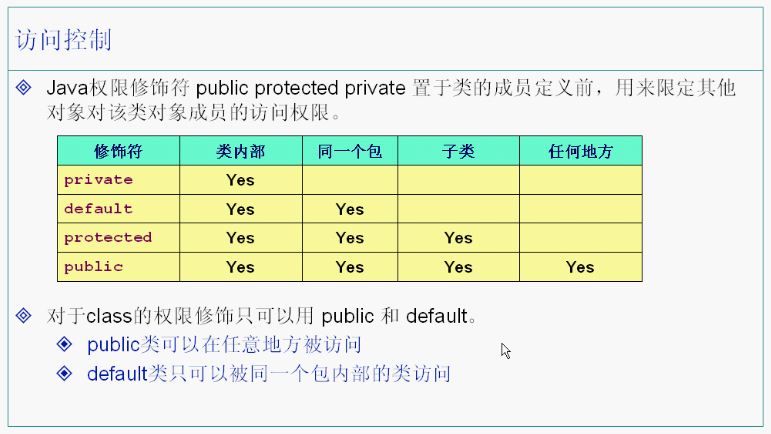
首先 private
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 3 public class Test01 { 4 private String str; 5 private void print(){ 6 System.out.println("Test01.print()"); 7 } 8 }
在同一个包的另外一个类,调用test01();
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 3 public class Test02 { 4 5 /** 6 * @param args 7 */ 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Test01 t = new Test01(); 10 t.print();//报错 The method print() from the type Test01 is not visible 11 } 12 13 }
换成default 默认(不用写)
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 3 public class Test01 { 4 private String str; 5 /*private*/ void print(){ 6 System.out.println("Test01.print()"); 7 } 8 }
同一个包
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 3 public class Test02 { 4 5 /** 6 * @param args 7 */ 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Test01 t = new Test01(); 10 t.print();//可以用! 11 } 12 13 }
private和default 看看不同包 可以调用吗?
private 同一个包的肯定不行 上面已经试了
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 3 public class Test01 { 4 private String str; 5 private void print(){ 6 System.out.println("Test01.print()"); 7 } 8 }
不同包
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation02; 2 3 import com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01.Test01; 4 5 public class test03 { 6 7 /** 8 * @param args 9 */ 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 12 Test01 t = new Test01(); 13 t.print();//报错The method print() from the type Test01 is not visible 14 } 15 16 }
试试 default 同包的肯定可以 上面试了
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 3 public class Test01 { 4 private String str; 5 /*private*/ void print(){ 6 System.out.println("Test01.print()"); 7 } 8 }
不同包
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation02; 2 3 import com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01.Test01; 4 5 public class test03 { 6 7 /** 8 * @param args 9 */ 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 12 Test01 t = new Test01(); 13 t.print();//报错The method print() from the type Test01 is not visible 14 } 15 16 }
不可以 报错
public 就不用试了 都可以
那么
protected
首先在同一个包下创建一个子类,然后在别的包再创建一个子类
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 3 public class Test01 { 4 private String str; 5 /*private*//*public*/protected void print(){ 6 System.out.println("Test01.print()"); 7 } 8 } 9 class Test001 extends Test01{ 10 public void pp(){ 11 super.print(); 12 } 13 }
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation02; 2 3 import com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01.Test01; 4 5 public class Test0001 extends Test01{ 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 Test0001 t = new Test0001(); 8 t.print(); 9 } 10 }
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation02; 2 3 import com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01.Test01; 4 5 public class Test03 { 6 7 /** 8 * @param args 9 */ 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 12 Test01 t = new Test01(); 13 t.print();//报错The method print() from the type Test01 is not visible 14 } 15 16 }
发现 他的子类是可以的
不是子类的就不行了
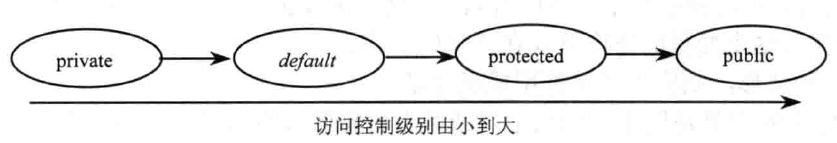
总之,记住上面的图,或者下面的话就行。
封装要点:
1.类的属性的处理
一般(成员变量)使用private 常量或者static变量的话用public (除非本属性确定会被子类继承)
提供相应get/set方法(public) 从而对属性进行操作 (boolean类型的get方法变成了is)
2.类的方法的处理
一些只用于本类的辅助方法可以用 private
希望其他类调用的方法用public
下面是一般建类时 属性和方法的设置
1 package com.bjsxt.oop.encapsulation01; 2 /** 3 * 一般这么定义类的访问权限 4 * 5 * @author Administrator 6 * 7 */ 8 public class Man { 9 //成员变量私有 10 private String name; 11 private int id; 12 //静态变量公开 13 public static int cc; 14 //常量可以公开 也可以不公开 看需求 15 public static final int MAX_SPEED =120; 16 public boolean man; 17 18 19 20 //设置set、get方法 直接 Source里的set get方法创建就可以 21 public String getName() { 22 return name; 23 } 24 public void setName(String name) { 25 this.name = name; 26 } 27 public int getId() { 28 return id; 29 } 30 public void setId(int id) { 31 this.id = id; 32 } 33 public boolean isMan() { 34 return man; 35 } 36 public void setMan(boolean man) { 37 this.man = man; 38 } 39 40 }
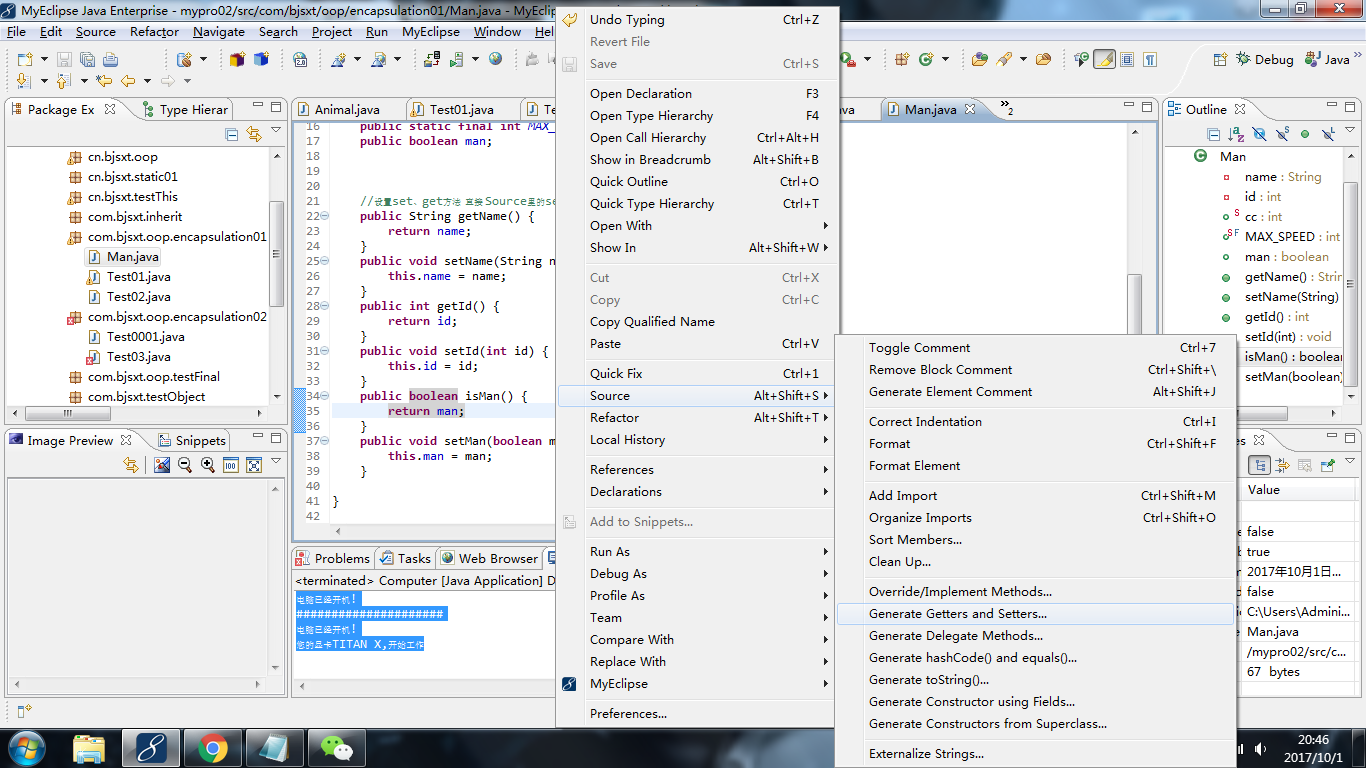
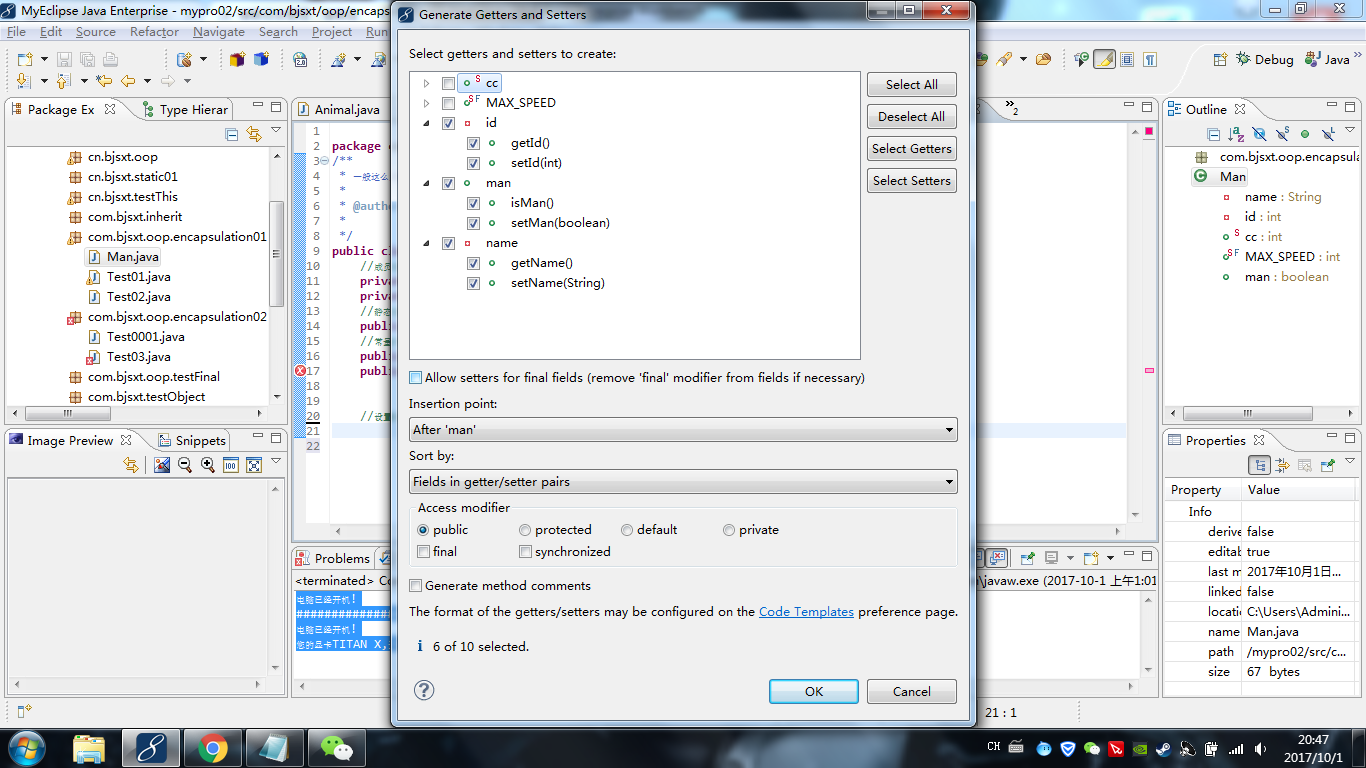
注意设置set/get方法时,没必要手写,可以右键source 找到 Generate Getters and Setters...
注意设置boolean布尔类型变量的set/get 变成了is/get 自己写可能会忘,用source里面的Generate Getters and Setters...创建自动添加,选上即可