Algorithm
每周至少做一个Leetcode算法题
第1道
【题目来源】
T2:实现Singleton模式,何海涛《剑指Offer》
【题目】
设计一个类,我们只能生成该类的一个实例。
【解答】
不好的解法一:只适用于单线程
/**
*
* 单例:线程不安全
*/
public class Singleton1 {
private static Singleton1 instance = null;
private Singleton1() {}
public static Singleton1 getInstance() {
if ( instance == null ) {
return new Singleton1();
}
return instance;
}
}
不好的解法二:适用于多线程,但效率不高
/**
* 单例:对getInstance()方法加锁,效率不高(instance!=null时,没必要加锁)
*
*/
public class Singleton2 {
private static volatile Singleton2 instance = null;
private Singleton2() {}
public static synchronized Singleton2 getInstance() {
if (instance == null ) {
return new Singleton2();
}
return instance;
}
}
推荐的解法一: 懒汉式-加锁前后两次判断实例是否已存在
/**
* 懒汉式:对类加锁 + 双重检查
*/
public class Singleton4 {
// volatile作用:禁止指令重排
private static volatile Singleton4 instance = null;
private Singleton4() {}
public static Singleton4 getInstance() {
if (instance == null ) {
synchronized (Singleton4.class) {
// A、B两个线程同时满足第一个if检查,A线程先获得锁,创建实例后,若没有二次if检查,B线程可能再次创建实例,单例目标失败
if ( instance == null ) {
return new Singleton4();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
推荐的解法二: 饿汉式
public class Singleton5 {
// JVM加载Singleton5类时,就创建了唯一的Singleton5对象
// 线程安全
private static Singleton5 instance = new Singleton5();
private Singleton5() {}
public static Singleton5 getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
推荐的解法三: 静态内部类
/**
* 懒汉式:静态内部类实现
*/
public class Singleton6 {
private Singleton6() {}
private static class SingleHolder {
private static final Singleton6 instance = new Singleton6();
}
public static Singleton6 getInstance() {
return SingleHolder.instance;
}
}
第2道
【题目来源】
T3:二维数组中的查找,何海涛《剑指Offer》
【题目】
在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
【例子】
// 给定二维数组,输入10,返回true;输入5,返回false
1,2,8,9
2,4,9,12
4,7,10,13
6,8,11,15
【解答】
-
举例分析法
-
排除法:小删行,大删列
步骤
1)初始猜测值guess选取二维数组右上角9;
2)guess=9和目标值10比较,9小那么剔除9所在的行,同时下移一步,因为9左边和
上边的值都比9小,不可能找到103)guess=12和目标值10比较,12大那么剔除所在的列,同时左移一步,因为12右边和下标的值都比12大,不可能找到10
4)guess=9和目标值10比较,9小那么剔除9所在的行,同时下移一步
5)guess=10等于目标值10,返回true,结束
public class FindInSortedMatrix {
/**
*
* @param arr 二维数组
* @param search 查找目标值
* @return true:search存在;false:search不存在
*/
public boolean isExist(int[][] arr, int search) {
if (arr == null ) {
return false;
}
int row = arr.length;
int col = arr[0].length;
// 选右上角为遍历起点
int i = col -1;
int j = 0;
while (i >= 0 && j < row) {
if (arr[i][j] == search) {
return true;
} else if (arr[i][j] > search) {
i--;
} else {
j++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
【思考】
-
思考遍历起点放在其他三个顶点是否可行?
-
思考时间复杂度是多少?
Review
阅读并点评至少1篇英文技术文章
【原文】:Java Exception Handling: A Tutorial on How to Catch Errors and Improve Performance
【译文】:
【点评】:
作者:Rafal Kuć
Exception Class Hierarchy(异常的类层级结构)
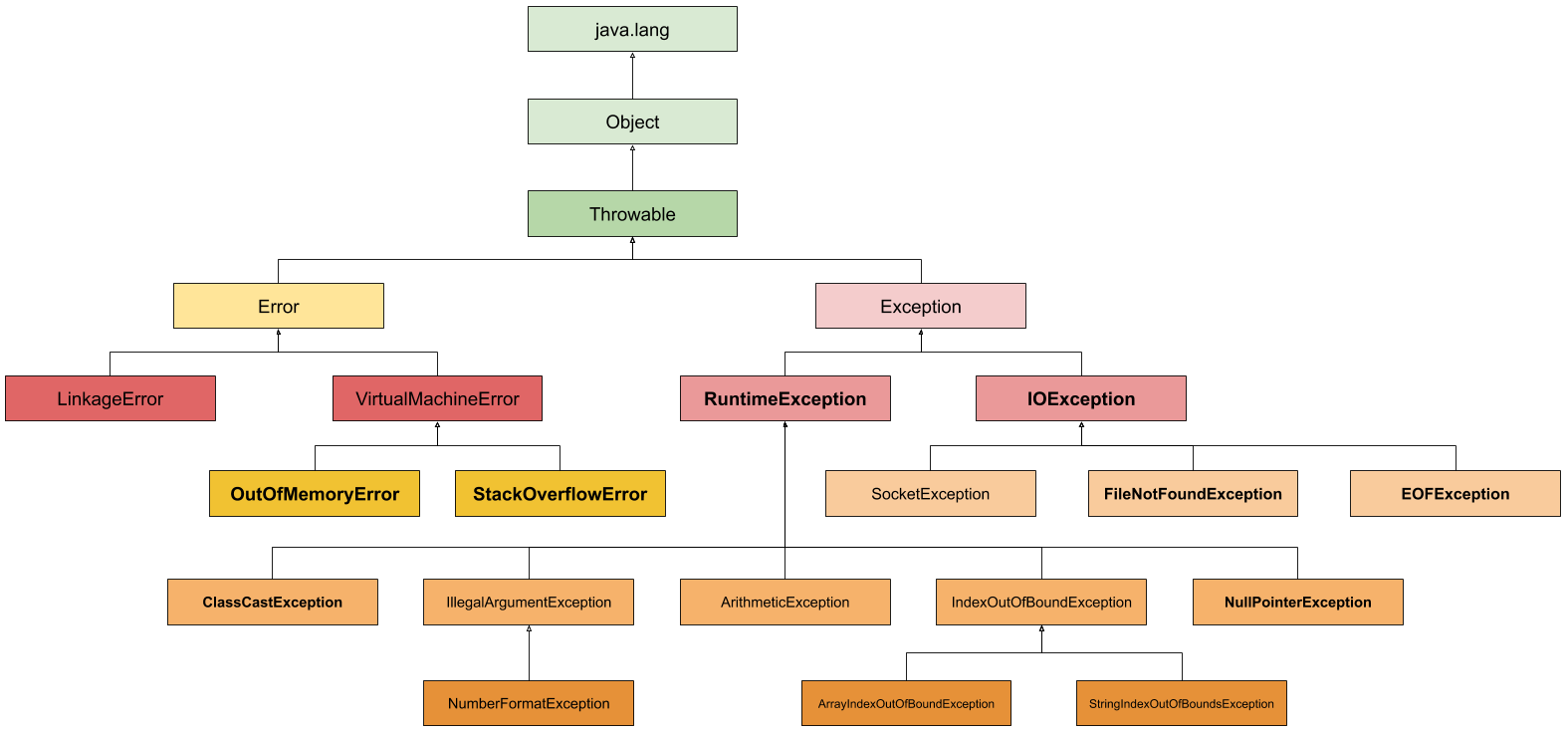
如何抛异常
// create exception
throw new IOException();
// declare exception
throws IOException
throw
package com.pengluo.arts;
import java.io.*;
public class week5_exception {
public File openFile(String path) throws IOException {
File file = new File(path);
if (!file.exists()) {
throw new IOException();
}
return file;
}
}
re-throw
package com.pengluo.arts;
import java.io.IOException;
public class RethrowException {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RethrowException exec = new RethrowException();
exec.run();
}
public void run() throws IOException {
try {
methodThrowingIOE();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw ioe; // re-throw 捕获到的ioe
}
}
public void methodThrowingIOE() throws IOException {
throw new IOException();
}
}
如何处理异常
要么Handle:try-catch,要么Declare:throws,二者必须选其一
try-catch 块
注意catch块的执行顺序,粒度更细的异常类(specialized)要放在粒度更粗(general)前面,否则specialized捕捉不到
finally 块
一定执行的代码块,且最后执行,为了避免因return 、break、continue造成需要清除的资源未清除设计,finally中用来关闭资源,文件流...。此外,try代码块中禁止return
try-with-resources
使用try-with-sources的class需要实现java.lang.AutoCloseable接口,然后上面在finally代码块的关闭资源功能就交给JVM处理。
Tip
学习至少一个技术技巧
Git的学习,教程参考廖雪峰的Git教程,本周的技术技巧分享有点偷懒了!
Share
分享一篇有观点和思考的技术文章
米罗说
-
不要浪费太多的时间在模仿”马云人“,成功不可以复制
-
阅读-思考-写作的训练人人都需要掌握
