文件的字符集在Windows下有两种,一种是ANSI,一种Unicode。
对于Unicode,Windows支持了它的三种编码方式,一种是小尾编码(Unicode),一种是大尾编码(BigEndianUnicode),一种是UTF-8编码。
我们可以从文件的头部来区分一个文件是属于哪种编码。当头部开始的两个字节为 FF FE时,是Unicode的小尾编码;当头部的两个字节为FE FF时,是Unicode的大尾编码;当头部两个字节为EF BB时,是Unicode的UTF-8编码;当它不为这些时,则是ANSI编码。
按照如上所说,我们可以通过读取文件头的两个字节来判断文件的编码格式,代码如下(C#代码):
程序中System.Text.Encoding.Default是指操作系统的当前 ANSI 代码页的编码。
public System.Text.Encoding GetFileEncodeType(string filename) { using (System.IO.FileStream fs = new System.IO.FileStream(filename, System.IO.FileMode.Open, System.IO.FileAccess.Read)) { System.IO.BinaryReader br = new System.IO.BinaryReader(fs); byte[] buffer = br.ReadBytes(2); if (buffer[0] >= 0xEF) { if (buffer[0] == 0xEF && buffer[1] == 0xBB) { return System.Text.Encoding.UTF8; } else if (buffer[0] == 0xFE && buffer[1] == 0xFF) { return System.Text.Encoding.BigEndianUnicode; } else if (buffer[0] == 0xFF && buffer[1] == 0xFE) { return System.Text.Encoding.Unicode; } else { return System.Text.Encoding.Default; } } else { return System.Text.Encoding.Default; } } }
用StreamWriter和FileStream往文本文件中写入数据有什么不同
可能有些同学不知道,实际上用StreamWriter和FileStream往一个文本文件写入字符数据,其效果是不一样的。
我们新建一个.NET Core控制台项目,然后在其中Program类的Main方法中,使用UTF-8编码将一段html文本text转换为字节数组writeData,再用StreamWriter将html文本text写入文件C:DemoFolderDemo.html,然后接着我们用FileStream再将文件C:DemoFolderDemo.html读取为字节数组readData,我们来看看两个字节数组writeData和readData有什么不同,代码如下:
using System; using System.IO; using System.Text; namespace EncodingTesting { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string text = "<html><head></head><body>大家好!</body></html>"; Console.WriteLine($"字符串text的长度为:{text.Length}");//text长度为43 byte[] writeData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(text); Console.WriteLine($"字节数组writeData的长度为:{writeData.Length}");//writeData有51个字节 using (var sw = new StreamWriter(@"C:DemoFolderDemo.html", false, Encoding.UTF8)) { sw.Write(text); } byte[] readData; using (var fsr = new FileStream(@"C:DemoFolderDemo.html", FileMode.Open)) { readData = new byte[fsr.Length]; fsr.Read(readData, 0, readData.Length); } Console.WriteLine($"字节数组readData的长度为:{readData.Length}");//readData有54个字节 string readText = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(readData); Console.WriteLine($"字符串readText的长度为:{readText.Length}");//readText长度为44 Console.WriteLine(readText);//输出结果:?<html><head></head><body>大家好!</body></html> Console.WriteLine("Press any key to end..."); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
输出结果如下:

我们可以看到使用StreamWriter将html文本text写入文件C:DemoFolderDemo.html后,用FileStream读取回来的字节数组readData比writeData多了3个字节,这就是因为StreamWriter用UTF-8编码写入文本文件时会自动在文件的头部加上三个字节(在WIN10中实际测试下来是多了三个字节,而不是本文前面说的两个字节)的数据EF BB BF,由于多了这三个字节的数据,我们可以看到最后字符串readText前面有一个乱码字符"?",所以这样读写文本文件实际上是不对的。
因此最好的方法是用StreamWriter来写入文本文件,用StreamReader来读入文本文件,这样C#会自动帮我们处理UTF-8编码多出来的三个字节数据,不会出现乱码,代码如下:
using System; using System.IO; using System.Text; namespace EncodingTesting { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string text = "<html><head></head><body>大家好!</body></html>"; Console.WriteLine($"字符串text的长度为:{text.Length}");//text长度为43 using (var sw = new StreamWriter(@"C:DemoFolderDemo.html", false, Encoding.UTF8)) { sw.Write(text); } string readText; using (var sr = new StreamReader(@"C:DemoFolderDemo.html", Encoding.UTF8)) { readText = sr.ReadToEnd(); } Console.WriteLine($"字符串readText的长度为:{readText.Length}");//readText长度为43 Console.WriteLine(readText);//输出结果:<html><head></head><body>大家好!</body></html> Console.WriteLine("Press any key to end..."); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
输出结果如下:
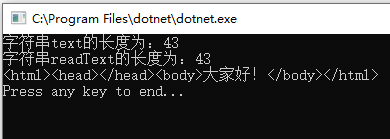
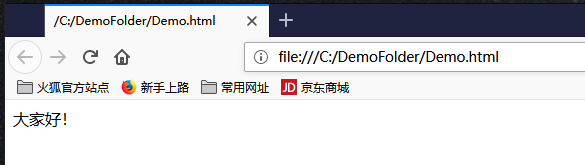
值得注意的是虽然我们用StreamWriter向文本文件C:DemoFolderDemo.html写入html文本时,由于UTF-8编码文件头会多写三个字节的数据,但是我们使用常用的Web浏览器(例如IE、Edge、Firefox等)打开C:DemoFolderDemo.html时,其内容是可以正常显示的:
但是如果我们使用FileStream来写入html文本到文本文件C:DemoFolderDemo.html,也就是不写入UTF-8编码文件头的三个字节数据,使用常用的Web浏览器(例如IE、Edge、Firefox等)打开C:DemoFolderDemo.html,反而是乱码,代码如下:
using System; using System.IO; using System.Text; namespace EncodingTesting { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string text = "<html><head></head><body>大家好!</body></html>"; Console.WriteLine($"字符串text的长度为:{text.Length}");//text长度为43 byte[] writeData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(text); Console.WriteLine($"字节数组writeData的长度为:{writeData.Length}");//writeData有51个字节 using (var fsw = new FileStream(@"C:DemoFolderDemo.html", FileMode.Create)) { fsw.Write(writeData, 0, writeData.Length); } byte[] readData; using (var fsr = new FileStream(@"C:DemoFolderDemo.html", FileMode.Open)) { readData = new byte[fsr.Length]; fsr.Read(readData, 0, readData.Length); } Console.WriteLine($"字节数组readData的长度为:{readData.Length}");//readData有51个字节 string readText = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(readData); Console.WriteLine($"字符串readText的长度为:{readText.Length}");//readText长度为43 Console.WriteLine(readText);//输出结果:<html><head></head><body>大家好!</body></html> Console.WriteLine("Press any key to end..."); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
输出结果如下:
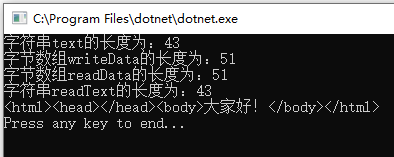
由于此时文件中没有UTF-8编码文件头的三个字节数据,所以用常用的Web浏览器(例如IE、Edge、Firefox等)打开C:DemoFolderDemo.html后为乱码:
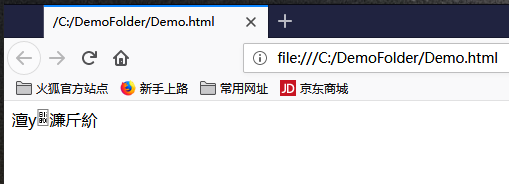
所以由此可见,正常情况下采用UTF-8编码的文本文件,都要有三个字节的文件头,其内容才能够被正确地读取出来。