基于双向链表实现的链接表
双向链表结点定义

package com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common;
//双向链表结点
public class DLNode implements Node {
private Object element;
private DLNode pre;
private DLNode next;
public DLNode() {
}
public DLNode(Object element, DLNode pre, DLNode next) {
super();
this.element = element;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
public DLNode getPre() {
return pre;
}
public void setPre(DLNode pre) {
this.pre = pre;
}
public DLNode getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(DLNode next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public Object getData() {
return element;
}
@Override
public void setData(Object obj) {
element = obj;
}
}
双向链表是通过上述定义的结点使用 pre 以及 next 域依次串联在一起而形成的。一个双向链表的结构如下图:

链接表接口定义
package com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.exception.InvalidNodeException;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.exception.OutOfBoundaryException;
//链接表接口
public interface LinkedList {
/**
* 查询链接表当前的规模
*
* @return
*/
public int getSize();
/**
* 判断列表是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 返回第一个结点
*
* @return
* @throws OutOfBoundaryException
*/
public Node first() throws OutOfBoundaryException;
/**
* 返回最后一个结点
*
* @return
* @throws OutOfBoundaryException
*/
public Node last() throws OutOfBoundaryException;
/**
* 返回p之后的结点
*
* @param p
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
* @throws OutOfBoundaryException
*/
public Node getNext(Node p) throws InvalidNodeException, OutOfBoundaryException;
/**
* 返回p之前的结点
*
* @param p
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
* @throws OutOfBoundaryException
*/
public Node getPre(Node p) throws InvalidNodeException, OutOfBoundaryException;
/**
* 将 e 作为第一个元素插入链接表,并返回 e 所在结点
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
public Node insertFirst(Object e);
/**
* 将 e 作为后一个元素插入列表,并返回 e 所在结点
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
public Node insertLast(Object e);
/**
* 将 e 插入至 p 之后的位置,并返回 e 所在结点
*
* @param p
* @param e
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
*/
public Node insertAfter(Node p, Object e) throws InvalidNodeException;
/**
* 将 e 插入至 p 之前的位置,并返回 e 所在结点
*
* @param p
* @param e
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
*/
public Node inserBefore(Node p, Object e) throws InvalidNodeException;
/**
* 删除给定位置处的元素,并返回之
*
* @param p
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
*/
public Object remove(Node p) throws InvalidNodeException;
/**
* 删除首元素,并返回之
*
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
*/
public Object removeFirst() throws InvalidNodeException;
/**
* 删除首元素,并返回之
*
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
*/
public Object removeLast() throws InvalidNodeException;
/**
* 将处于给定位置的元素替换为新元素,并返回被替换的元素
*
* @param p
* @param e
* @return
* @throws InvalidNodeException
*/
public Object replace(Node p, Object e) throws InvalidNodeException;
/**
* 元素迭代器
*
* @return
*/
public Iterator elements();
}
迭代器接口定义
- 迭代器(Iterator)是程序设计的一种模式,它属于设计模式中的行为模式,它的功能是 提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚集对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
- 多个对象聚在一起形成的总体称之为聚集(Aggregate),聚集对象是能够包容一组对象 的容器对象。聚集依赖于聚集结构的抽象化,具有复杂性和多样性。例如数组就是一种基本的聚集。
- 聚集对象需要提供一种方法,允许用户按照一定的顺序访问其中的所有元素。而迭代器 提供了一个访问聚集对象中各个元素的统一接口,简单的说迭代器就是对遍历操作的抽象。
package com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.exception.OutOfBoundaryException;
//迭代器接口
public interface Iterator {
/**
* 移动到第一个元素
*/
public void first();
/**
* 移动到下一个元素
*/
public void next() throws OutOfBoundaryException;
/**
* 检查迭代器中是否还有剩余的元素
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isDone();
/**
* 返回当前元素
*
* @return
*/
public Object currentItem();
}
链接表的实现
- 在在结点 p 之前插入 s
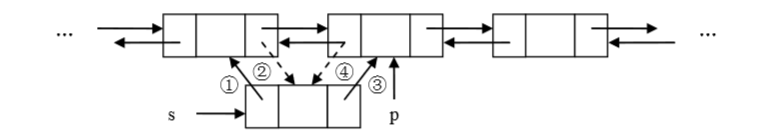
主要操作:
s.setPre (p.getPre());
p.getPre().setNext(s);
s.setNext(p);
p.setPre(s);
- 删除结点 p

主要操作:
p.getPre().setNext(p.getNext()); p.getNext().setPre(p.getPre());
package com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.listslinkimpl;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common.DLNode;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common.Iterator;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common.LinkedList;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common.Node;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.exception.InvalidNodeException;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.exception.OutOfBoundaryException;
//基于双向链表实现的链接表
public class LinkedListDLNode implements LinkedList {
private int size; // 规模
private DLNode head; // 头结点
private DLNode tail; // 尾结点
// 构建只有头尾结点的链表
public LinkedListDLNode() {
this.size = 0;
this.head = new DLNode();
this.tail = new DLNode();
this.head.setNext(tail);
tail.setPre(this.head);
}
// 辅助方法,判断结点 p 是否合法,如合法转换为 DLNode
protected DLNode checkPosition(Node p) throws InvalidNodeException {
if (p == null) {
throw new InvalidNodeException("错误:p 为空。");
}
if (p == head) {
throw new InvalidNodeException("错误:p 指向头节点,非法.");
}
if (p == tail) {
throw new InvalidNodeException("错误:p 指向尾结点,非法.");
}
DLNode node = (DLNode) p;
return node;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public Node first() throws OutOfBoundaryException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new OutOfBoundaryException("错误,链接表为空");
}
return head.getNext();
}
@Override
public Node last() throws OutOfBoundaryException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new OutOfBoundaryException("错误:链接表为空");
}
return tail.getPre();
}
@Override
public Node getNext(Node p) throws InvalidNodeException, OutOfBoundaryException {
DLNode node = checkPosition(p);
node = node.getNext();
if (node == tail)
throw new OutOfBoundaryException("错误: 已经是链接表尾端");
return node;
}
@Override
public Node getPre(Node p) throws InvalidNodeException, OutOfBoundaryException {
DLNode node = checkPosition(p);
node = node.getPre();
if (node == head)
throw new OutOfBoundaryException("错误:已经是链接表前段");
return null;
}
@Override
public Node insertFirst(Object e) {
DLNode node = new DLNode(e, head, head.getNext());
head.getNext().setPre(node);
head.setNext(node);
size++;
return node;
}
@Override
public Node insertLast(Object e) {
DLNode node = new DLNode(e, tail.getPre(), tail);
tail.getPre().setNext(node);
tail.setPre(node);
size++;
return node;
}
@Override
public Node insertAfter(Node p, Object e) throws InvalidNodeException {
DLNode node = checkPosition(p);
DLNode newNode = new DLNode(e, node, node.getNext());
node.getNext().setPre(newNode);
node.setNext(newNode);
size++;
return newNode;
}
@Override
public Node inserBefore(Node p, Object e) throws InvalidNodeException {
DLNode node = checkPosition(p);
DLNode newNode = new DLNode(e, node.getPre(), node);
node.getPre().setNext(newNode);
node.setPre(newNode);
size++;
return newNode;
}
@Override
public Object remove(Node p) throws InvalidNodeException {
DLNode node = checkPosition(p);
Object obj = node.getData();
node.getPre().setNext(node.getNext());
node.getNext().setPre(node.getPre());
size--;
return obj;
}
@Override
public Object removeFirst() throws InvalidNodeException {
return remove(head.getNext());
}
@Override
public Object removeLast() throws InvalidNodeException {
return remove(tail.getPre());
}
@Override
public Object replace(Node p, Object e) throws InvalidNodeException {
DLNode node = checkPosition(p);
Object obj = node.getData();
node.setData(e);
return obj;
}
@Override
public Iterator elements() {
return new LinkedListIterator(this);
}
}
基于 LinkedList 聚集对象的迭代器实现
package com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.listslinkimpl;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common.Iterator;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common.LinkedList;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.common.Node;
import com.wjy.Data_Structure.linearlist.exception.OutOfBoundaryException;
public class LinkedListIterator implements Iterator {
private LinkedList list;// 链接表
private Node current;// 当前结点
public LinkedListIterator(LinkedList list) {
this.list = list;
if (list.isEmpty())
current = null;
else
current = list.first();// 从第一个元素开始
}
@Override
public void first() {
if (list.isEmpty())
current = null;
else
current = list.first();// 从第一个元素开始
}
@Override
public void next() throws OutOfBoundaryException {
if (isDone())
throw new OutOfBoundaryException("错误:已经没有元素");
if (current == list.last())
current = null;// 当前元素后面没有更多元素
else
current = list.getNext(current);
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
return current == null;
}
@Override
public Object currentItem() {
if (isDone())
throw new OutOfBoundaryException("错误:已经没有元素");
return current.getData();
}
}