一个学期即将过去,我们也迎来了2018年。这个学期,首次接触了web网站开发建设,不仅是这门课程,还有另外一门用idea的gradle框架来制作网页。
很显然,用python语言的flask框架更加简单易懂。Python不需要像Java语言一样设置类的类型,也没有gradle框架那么多的各层依赖,所以说Python更加容易上手。
初次接触网页开发,对我来说就像是打开了新世界的大门,无论是前端还是后端都有它有意思的地方,每次你写的网页成功实现你想要的效果的时候,都会有一种成就感。这种成就感也许也是做这一行的人继续坐下去的动力之一吧。
下面是我的Python+Flask+MysqL的web建设技术过程。
Python+Flask+MysqL的web建设技术过程
1 建立flask框架项目
首先是flask安装(这里默认已经安装好python了),这里我们学习的项目只是简单的用pip install flask的语句安装了flask库,如果你碰到多个项目并且有不同的python版本或外部依赖库,可以参考:http://docs.jinkan.org/docs/flask/installation.html
开发工具上使用了pycharm作为工具,建立项目首先新建项目,选择flask框架进行构建。
2 导航及CSS
在网页前端开发的过程中,我引用了bootstrap的前端架构(其实只用了一些组件)。具体的bootstrap学习可以参考菜鸟教程:http://www.runoob.com/bootstrap/bootstrap-tutorial.html
首先先建立前端html页面,页面导航通过标签<nav>进行编写。
<!-- 顶部导航 --> <nav class="navbar navbar-default" role="navigation"> <div class="navsize"> <ul class="nav nav-tabs"> <li class="active"><a href="#">首页</a></li> <li><a href="#">论坛</a></li> <li><a href="#">客户端</a></li> <li><a href="#">投稿</a></li> <ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right"><li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> 注册</a></li> <li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> 登录</a></li></ul> <form class="navbar-form navbar-right" role="search" action="{{ url_for("search") }}" method="get"> <div class="form-group"> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="q" placeholder="Search"> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default"> 搜索 </button> </form> </ul> </div> </nav>
.navsize{ width: 80%; margin:0 auto; }
效果:

3 图片导航CSS实例
首先要学会使用div等块级元素标签来放置我们的网页元素,并会使用CSS选择器进行网页的开发。
这里先了解一下CSS的盒子模型:
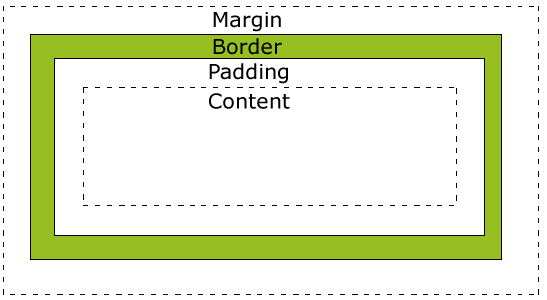
margin:盒子的最外层,一般用于设置与其他元素的间隔距离
border:盒子的边框层,可以根据自己的需要设置是否可见及大小、颜色等
padding:盒子放置的内容与边框的中间层,可用于设置隔开内容及边框
content:盒子放置的内容层
图片导航实例:
<div> <div class="img"> <a href="http://www.gzcc.cn"><img src="http://old.bz55.com/uploads/allimg/150316/140-150316134616.jpg"></a> <div class="desc"><a href="http://www.gzcc.cn">第一张图片</a></div> </div> </div> <div class="clearfloat"> <img src="http://old.bz55.com/uploads/allimg/150316/140-150316134616.jpg"> <img src="http://www.pp3.cn/uploads/201701/2017011709.jpg"> <img src="http://old.bz55.com/uploads/allimg/150316/140-150316134610.jpg"> <img src="http://old.bz55.com/uploads/allimg/150316/140-150316134613.jpg"> </div>
div.img{ width: 180px; border:1px solid #eeeeee; float: left; margin:5px; } div.img img{ width: 100%; height: auto; } div.desc{ text-align: center; padding: 5px; } div.clearfloat{ clear: both; } div.img:hover{ border: 1px solid blue; }
上面CSS语句中:
float:left是设置块级元素不换行并且向左边浮动,会根据浏览器大小进行浮动
clear:both是用于清除该块级元素与同一级上一个块级元素之间的浮动
hover:鼠标在该元素上时的样式,用于与鼠标不在元素上时的样式作为对比,形成一种动态效果
效果:

4 使用JS对登录、注册操作进行表单验证
JavaScript是现在各种网站十分常用的网页技术,动态的加载及相应请求等。
这里以登录及注册为例,可以用JavaScript来要求页面上登录账号及注册账号的输入,对数据的使用及存入数据库进行初步规范。
下面是登录功能的js代码:
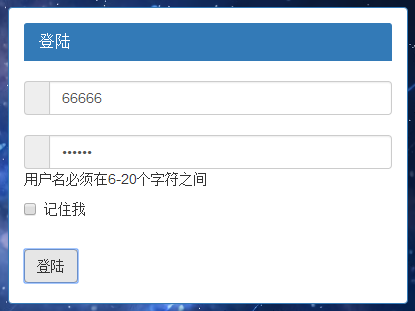
function Login(){ var un=document.getElementById("id"); var us=document.getElementById("password"); var er=document.getElementById("error_box"); er.innerHTML = "<br>"; if(un.value.length<6||un.value.length>20){ er.innerHTML="用户名必须在6-20个字符之间"; return false; }else if((un.value.charCodeAt(0))>=48 && un.value.charCodeAt(0)<=57){ er.innerHTML = "首字母不能为数字" return false; }else for(var i=0;i<un.value.length;i++){ if((un.value.charCodeAt(i)<48)||(un.value.charCodeAt(i)>57)&&(un.value.charCodeAt(i)<97)&&(un.value.charCodeAt(i)>122)){ er.innerHTML="用户名只能为数字和字母" return false; } } if(us.value.length<6||us.value.length>20){ er.innerHTML="密码必须在6-20个字符之间"; return false; } return true; }
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-default" onclick="return Login()" value="登陆"></input>
在登录按钮中引用js函数进行应用,这里注意一个问题,需要在函数名前面增加return,否则即使输入的数据有误,js文件虽然会执行,但并不会拦截在登录页面,而是依旧会跳转到登录后的界面,注册功能甚至会直接把数据存进数据库中。这个问题我在idea中并没有碰到,而在这个项目中却会出现,原因我现在也不是很清楚,初步判断应该是后面添加的一些功能与其起了冲突,或者flask框架的一些不同。
效果图:
5 父模板制作
我们在编写多个页面的时候,会发现有许多地方是会用到一样的设计的,比如导航就是每页都有并且是一样的。
我们可以将其中相同的地方抽取出来,做一个父模板,然后让子页面继承父模板,就不需要多写许多相同的代码,减少了工作量,也使得代码更加简洁。
下面是我的父模板:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>{% block title %}{% endblock %}</title> <!-- 引入 Bootstrap --> <link href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"> <link href="{{ url_for("static",filename="CSS/bass.css") }}" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" charset="UTF-8"> {% block head %}{% endblock %} </head> <body class="bgimg"> <!-- 顶部导航 --> <nav class="navbar navbar-default" role="navigation"> <div class="navsize"> <ul class="nav nav-tabs"> <li class="active"><a href={{ url_for("index") }}>首页</a></li> <li><a href="#">论坛</a></li> <li><a href="#">客户端</a></li> <li><a href={{ url_for("tougao") }}>投稿</a></li> <ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right"> {% if username %} <li><a href="{{ url_for('author',user_id=useraction.id,tag=1) }}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> {{ username }}</a></li> <li><a href={{ url_for("logout") }}><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-out"></span> 注销</a></li> {% else %} <li><a href={{ url_for("register") }}><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> 注册</a></li> <li><a href={{ url_for("login") }}><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> 登录</a></li> {% endif %} </ul> <form class="navbar-form navbar-right" role="search" action="{{ url_for("search") }}" method="get"> <div class="form-group"> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="q" placeholder="Search"> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default"> 搜索 </button> </form> </ul> </div> </div> </div> </nav> <div class="body"> {% block main %}{% endblock %} </div> <!-- 底部导航 --> <nav class="navbar navbar-default navbar-fixed-bottom" role="navigation"> <div class="navsize"> <ul class="nav navbar-nav"> <li class="active"><a href="#">友情链接</a></li> <li><a href="#">联系我们</a></li> <li><a href="#">加入我们</a></li> <li><a href="#">关于我们</a></li> </ul> <ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right"> <li><a href="#"> 帮助中心</a></li> <li><a href={{ url_for('fankui') }}> 反馈中心</a></li> </ul> </div> </nav> </body> </html>
子页面:
{% extends 'base.html' %} {% block title %} 反馈中心 {% endblock %} {% block main %} <div class="divtouming"> <div class="panel panel-default" style=" 800px"> <div class="panel-body"> <form class="form-horizontal" role="form"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="fankuititle" class="col-sm-2 control-label">反馈原因</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="text" class="form-control" id="fankuititle"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="fankuitext" class="col-sm-2 control-label">详情</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <textarea id="fankuitext" rows="5" cols="87"></textarea> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">提交</button> </div> </div> </form> </div> </div></div> {% endblock %}
在父模板中,通过添加 {% block title %}{% endblock %} 标签来连接父模板与子页面的关系,父模板中的 {% block title %}{% endblock %} 标签位置就是子页面的继承父模板后的代码插入位置。父模板的继承用 {% extends 'base.html' %} 这样的标签来继承。
并且也可以看到将后端的数据渲染到模板中则是使用 {{name}} 这样的形式,里面是变量名,用两个花括号包着。
6 flask项目开始
下面是一个简单的开始项目(后端):
from flask import Flask,render_template
url_for('static',filename='js/login.js')
app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/') def index(): return render_template("base.html") @app.route('/login') def login(): return render_template("login.html") @app.route('/regis') def register(): return render_template("Zhuce.html") if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True)
app = Flask(__name__) 即初始化一个flask实例对象。
app.run(debug=True) 将debug模式打开,是程序员测试时用的模式,真正使用项目的时候需要把这个模式关掉。
@app.route("/") 在运行实体上绑定URL路由
render_template("Zhuce.html") 返回一个模板文件
url_for('static',filename='js/login.js') 获取“static”文件夹下的静态资源
7 连接mysql数据库,创建用户模型
首先,需要安装好python+flask、MySQL。然后需要根据python的版本下载好MySQL和python的中间件。
下载中间件后用 pip install filename的方法将文件安装到python的Script文件夹中,然后创建一个数据库。
另外写一个config.py的配置文件,写入下面两行代码:
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI = 'mysql+pymysql://root:数据库密码@数据库地址:3306/数据库名称?charset=utf8' SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS = False
然后在主py文件中导入config文件并初始化对象:
import config from flask import Flask,render_template from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config) db=SQLAlchemy(app)
开始创建用户模型,即在数据库中创建表格:
class User(db.Model): __tablename__='user' id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) username=db.Column(db.String(20),nullable=False) password=db.Column(db.String(20),nullable=False) db.create_all()
db.create_all()用来执行db的建表操作
8 通过用户模型对数据库进行增删该查
class User(db.Model): __tablename__='user' id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) username=db.Column(db.String(20),nullable=False) password=db.Column(db.String(20),nullable=False) #创建表格 db.create_all() #数据查询方法 User.query.filter(User.username == 'mis1114').first() #数据添加方法 user=User(username='mis777789',password='g6666') db.session.add(user) db.session.commit() # 数据的修改方法 user = User.query.filter(User.username=='mis777789').first user.password='0.0.0.0' db.session.commit() # 数据的删除方法 user = User.query.filter(User.username=='mis777789').first() db.session.delete(user) db.session.commit()
9 完成注册及登陆功能
- js文件: onclick函数return True时才提交表单,return False时不提交表单。
- html文件:
- <form>中设置 action和method="post"
- <input> 中设置 name
- 主py文件中:
- from flask import request, redirect, url_for
- @app.route('/regist/', methods=['GET', 'POST’])
注册:
@app.route('/regis',methods=['GET','POST']) def register(): if request.method=='GET': return render_template('Zhuce.html') else: username=request.form.get('zcid')#与html页面名字相同 password=request.form.get('zcpassword') user=User.query.filter(User.username==username).first() if user: return 'exit' else: user=User(username=username,password=password) db.session.add(user) db.session.commit() return redirect(url_for('login'))
登陆:
从flask中导入session,在config配置中加入SECRET_KEY=os.urandom(24),将登陆的用户存入session对象中。
@app.route('/login',methods=['GET','POST']) def login(): if request.method == 'GET': return render_template('login.html') else: username = request.form.get('id') # 与html页面名字相同 password = request.form.get('password') user = User.query.filter(User.username == username,User.password==password).first() if user: sessions['username']=username sessions.permanent=True return redirect(url_for('index')) else: return '用户不存在'
登陆与注册的HTML页面:
<form class="bs-example bs-example-form" role="form" action="{{ url_for('login') }}" method="post">
10 登陆之后更新导航
在父模板中使用IF函数判断是否有登陆对象:
<ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right"> {% if username %} <li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> {{ username }}</a></li> <li><a href={{ url_for("logout") }}><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> 注销</a></li> {% else %} <li><a href={{ url_for("register") }}><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> 注册</a></li> <li><a href={{ url_for("login") }}><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> 登录</a></li> {% endif %} </ul>
主py文件中,通过使用上下文处理器,将获取的session中的值以字典的形式返回页面:
@app.context_processor def mycontext(): username=session.get('user') if username: return {'username':username} else: return {}
11 发布功能
登陆装饰器:
def log(func):#参数类型为函数 @wraps(func) def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): if session.get('user'): return func(*args,**kwargs) else: return redirect(url_for('login')) return wrapper
装饰器应用:
应用装饰器,要求在发布前进行登录,登录后可发布。
@app.route('/tougao',methods=['GET','POST']) @log def tougao():
完成发布功能:
@app.route('/tougao',methods=['GET','POST']) @log def tougao(): if request.method=='GET': return render_template('tougao.html') else: title=request.form.get('tougaotitle') content=request.form.get('tougaotext') id=User.query.filter(User.username==session.get('user')).first().id tougao=Tougao(title=title,content=content,userid=id) db.session.add(tougao) db.session.commit() return redirect(url_for('index'))
12 首页列表显示全部问答
首页HTML代码:
<div class="container"> <div class="row clearfix"> <div class="col-md-2 column"> </div> <div class="col-md-6 column"> <ul> {% for item in touGao %} <a href="" class="list-group-item list-group-item-light"> <li> <div class="page-header"> <h3>{{ item.title }}</h3> <p><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user">{{ item.author.username }}</span> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-time">{{ item.time }}</span></p> </div> <p>{{ item.content}}</p> </li> </a> {% endfor %} </ul> </div> <div class="col-md-4 column"> </div> </div> </div>
主py文件:
@app.route('/') def index(): context={ 'touGao':Tougao.query.order_by('-time').all() } return render_template("index.html",**context)
13从首页投稿到文章详情页
主PY文件写视图函数,带id参数。
@app.route('/pinglun/<question_id>') def detial(question_id): quest=Question.query.filter(Question.id==question_id).first() return render_template('commentdetail.html',que=quest)
首页标题的标签做带参数的链接。
<a href="{{ url_for('commentdetail',question_id=foo.id) }}">{{ foo.title}}</a>
在详情页将数据的显示在恰当的位置。
{% for foo in question %} <li class="list-group-item"> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-leaf" aria-hidden="true"></span> <a href="{{ url_for('commentdetail',question_id=foo.id) }}">{{ foo.title}}</a> <p style="...">{{ foo.detail}}</p> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-leaf" aria-hidden="true"></span> <span class="badge">{{ foo.creat_time}}</span> </li> {% endfor %}
建立评论的对象关系映射:
class Question(db.Model): __tablename__ = 'comment' id =db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) author_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('uesr.id')) question_id=db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('question.id')) creat_time=db.Column(db.DateTime,default=datetime.now) detail=db.Column(db.Text,nullable=False) question =db.relationship('Question',backref=db.backref('comments')) author=db.relationship('User',backref=db.backref('comments'))
14 完成评论功能
定义评论的视图函数,读取前端页面数据,保存到数据库中。
@app.route('/pinglun',methods=['POST']) @log def pinglun(): pl=request.form.get('pingluntext') tougao_id=request.form.get('tougaoid') user_id=User.query.filter(User.username==session.get('user')).first().id pinglun=Pinglun(userid=user_id,tougaoid=tougao_id,content=pl) db.session.add(pinglun) db.session.commit() context={ 'pingLun':Pinglun.query.order_by('-time').all() } return render_template(url_for('digital',tougao_id=tougao_id),**context)
显示所有评论:
{% extends "base.html" %} {% block title %}标题{% endblock %} {% block main %} <div class="container"> <div class="row clearfix"> <div class="col-md-12 column divcolor" > <div class="page-header"> <h1> {{ quest.title }} </h1> <small><a href="{{ url_for('author',user_id=quest.author.id) }}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user">{{ quest.author.username }}</span></a> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-time">{{ quest.time }}</span></small> </div> <p> {{ quest.content }} </p> <hr> <form class="form-horizontal" role="form" action="{{ url_for('pinglun') }}" method="post"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="toutaotext" class="col-sm-2 control-label">评论</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <textarea id="pingluntext" rows="5" cols="100" name="pingluntext"></textarea> <input name="tougaoid" type="hidden" value="{{ quest.id }}" id="tougaoid"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-success">评论</button> </div> </div> </form> <h4>评论({{ quest.pinglun|length }}):</h4> <ul> {% for pl in quest.pinglun %} <li class="list-group-item"> <p><a href="{{ url_for('author',user_id=pl.author.id) }}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span>{{ pl.author.username }}</a></p> <p class="text-right"><span class="label label-default">{{ pl.time }}</span></p> <h4>{{ pl.content }}</h4> </li> {% endfor %} </ul> </div> </div> </div> {% endblock %}
15 个人中心页标签导航
新页面authorbase.html,用<ul ><li role="presentation"> 实现标签页导航。
<ul class="nav nav-tabs">
<li role="presentation"><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li role="presentation"><a href="#">Profile</a></li>
<li role="presentation"><a href="#">Messages</a></li>
</ul>
authorbase.html继承base.html。重写title,head,main块.将上述<ul>放在main块中.定义新的块user。
让上次作业完成的个人中心页面,继承user.html,原个人中心就自动有了标签页导航。
制作个人中心的三个子页面,重写authorbase.html中定义的user块。
authorbase:
{% extends "base.html" %} {% block head %}{% endblock %} {% block main %} <div class="container"> <div class="row clearfix divcolor"> <div class="col-md-8 column"> <h2>{{ user.username }}</h2> <p>投稿总数:{{ tougao|length }} 评论数量:{{ pinglun|length }}</p> <hr> <ul class="nav nav-pills" role="tablist"> <li class="active"><a href="#">全部投稿</a></li> <li><a href="#">全部评论</a></li> <li><a href="#">用户信息</a></li> </ul> <br> {% block author %}{% endblock %} </div> <div class="col-md-4 column"> </div> </div> </div> {% endblock %}
author1:
{% extends "authorbase.html" %} {% block title %}个人中心{% endblock %} {% block head %}{% endblock %} {% block author %} <div> <ul> {% for tg in tougao %} <a href="{{ url_for('digital',tougao_id=tg.id) }}" class="list-group-item list-group-item-light"> <li> <div class="page-header"> <h3>{{ tg.title }}</h3> <p><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user">{{ tg.author.username }}</span> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-time">{{ tg.time }}</span></p> </div> </li> </a> {% endfor %} </ul> </div> {% endblock %}
像上面这个继承authorbase编写三个不同的子网页,然后写一个视图函数带标签页面参数tag,从而达到点击点击不同按钮有不同的页面的效果。
@app.route('/author/<user_id>/<tag>') def author(user_id,tag): user=User.query.filter(User.id==user_id).first() context={ 'user':user, 'tougao':user.tougao, 'pinglun':user.pinglun } if tag=='1': return render_template('author1.html', **context) elif tag=='2': return render_template('author2.html', **context) else: return render_template('author3.html', **context)
导航标签链接增加tag参数:
<small><a href="{{ url_for('author',user_id=quest.author.id,tag=1) }}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user">{{ quest.author.username }}</span></a> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-time">{{ quest.time }}</span></small>
有链接到个人中心页面的url增加tag参数:
<a href="{{ url_for('usercenter',user_id = session.get('userid'), tag=1) }}">{{ session.get('user') }}</a>
16 实现搜索功能
准备视图函数search():
from sqlalchemy import or_ @app.route("/search") def search(): q=request.args.get("q") tg=Tougao.query.filter( or_( Tougao.title.contains(q), Tougao.content.contains(q) ) ).order_by("-time") return render_template("index.html",touGao=tg)
修改base.html 中搜索输入框所在的:
<form class="navbar-form navbar-right" role="search" action="{{ url_for("search") }}" method="get"> <div class="form-group"> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="q" placeholder="Search"> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default"> 搜索 </button> </form>
17 密码保护
1.更新User对象,设置对内的_password
class User(db.Model): __tablename__='user' id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) username=db.Column(db.String(20),nullable=False) _password=db.Column(db.String(200),nullable=False)
2.编写对外的password
from werkzeug.security import generate_password_hash, check_password_hash @property def password(self): #外部使用,取值 return self._password @password.setter def password(self, row_password):#外部使用,赋值 self._password = generate_password_hash(row_password)
3.密码验证方法:
def check_password(self, row_password): #密码验证 result = check_password_hash(self._password,row_password) return result
4.登录验证:
password1 = request.form.get('password') user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first() if user: if user.check_password(password1):