1、问题描述:
在N*N棋盘上,任意一个位置放置一个棋子马,要能选择一套合适的移动路线,按象棋中“马走日”的移动规则不重复地遍历棋盘上每一个位置点。
2、基本要求:
用图形化的界面显示结果。
3、设计思路:
(1) 首先要考虑,落下马的位置,马可能走到的位置,即最初定义两个数组分别储存马在二维空间中可能跳跃的八个位置。
(2) 其次是要用到递归的方法解决马不断跳跃的问题,所以要学会递归的基本思想,递归思想就是多次调用自身,也就是用解决一次马跳跃的问题就意味着可以多次解决马跳跃的问题。
(3) 最后要考虑到回溯,马的跳跃不可能是一帆风顺的,当碰到阻碍时,马需要跳回原来的位置重新选择路线。
(4) 最后设计到一些界面设计问题,比如调节窗口大小、字体大小和颜色、标题等等。
4、源代码:
(1)无蹩脚
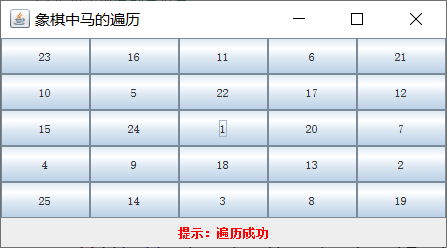
5×5
package cn.test.termtest.uglynumber; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; public class TestChess extends JFrame implements ActionListener { static JButton button[][]; //棋盘的按钮 static int boardSize; //棋盘大小(行数/列数) static int count; //落子的顺序 JLabel promptLabel =new JLabel(); //提示信息标签 //马走日子的偏坐标 static int dx[] = {1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1}; static int dy[] = {2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1,1,2}; public static void main(String[] args) { boardSize =5; TestChess testChess =new TestChess(); } public TestChess() { count =1; //定义font为微软雅黑,普通,12号 Font font =new Font("宋体",Font.PLAIN,12); this.setTitle("象棋中马的遍历"); JPanel p1 =new JPanel(); //正式面板 p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(boardSize,boardSize)); //GridLayout为网格布局 button =new JButton[boardSize+1][boardSize+1]; int n=1; for(int i=1;i<=boardSize;i++) for(int j=1;j<=boardSize;j++) { button[i][j]=new JButton(); button[i][j].setActionCommand(String.valueOf(n++));//动作命令,并非按钮上面的字,区别是哪个按钮 button[i][j].setFont(font); button[i][j].addActionListener(this);//添加监听 p1.add(button[i][j]); } add(p1,BorderLayout.CENTER);//面板添加到窗口当中 JPanel p2 =new JPanel(); promptLabel =new JLabel(); promptLabel.setForeground(Color.RED); promptLabel.setText("提示:单击某一个按钮,作为马的起始位置"); p2.add(promptLabel); add(p2,BorderLayout.SOUTH); setSize(300,200); this.setLocationRelativeTo(null); setVisible(true); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String buttonKey =e.getActionCommand(); int intKey = Integer.parseInt(buttonKey); int row =intKey /boardSize +1; int col= intKey%boardSize; button[row][col].setText("1"); if(DFS(row,col)) promptLabel.setText("提示:遍历成功"); else promptLabel.setText("提示:遍历失败"); } static boolean DFS(int x,int y) { //经过了所有的空位置 if(count == boardSize*boardSize) return true; //遍历从当前点走日字能够到达的8个点 for(int dir =0;dir<8;dir++) { //走日字到达下一个点 int next_x =x+dx[dir]; int next_y =y+dy[dir]; //超出边界 if(next_x<1 || next_x > boardSize || next_y<1 || next_y>boardSize) continue; if(!button[next_x][next_y].getText().equals("")) continue; //访问过的点计数 count++; button[next_x][next_y].setText(String.valueOf(count)); if(DFS(next_x,next_y)) return true; //从日字的一个对角线出发不能到达所有的位置 count--;//后退一步 button[next_x][next_y].setText(""); } return false; } }
(2)无蹩脚
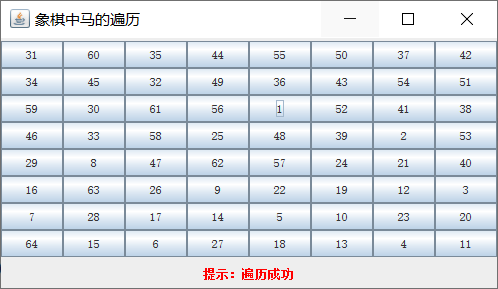
8×8
package cn.test.termtest.uglynumber; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; public class TestChess extends JFrame implements ActionListener { static JButton button[][]; //棋盘的按钮 static int boardSize; //棋盘大小(行数/列数) static int count; //落子的顺序 JLabel promptLabel =new JLabel(); //提示信息标签 //马走日子的偏坐标 static int dx[] = {1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1}; static int dy[] = {2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1,1,2}; public static void main(String[] args) { boardSize =8; TestChess testChess =new TestChess(); } public TestChess() { count =1; //定义font为微软雅黑,普通,12号 Font font =new Font("宋体",Font.PLAIN,12); this.setTitle("象棋中马的遍历"); JPanel p1 =new JPanel(); //正式面板 p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(boardSize,boardSize)); //GridLayout为网格布局 button =new JButton[boardSize+1][boardSize+1]; int n=1; for(int i=1;i<=boardSize;i++) for(int j=1;j<=boardSize;j++) { button[i][j]=new JButton(); button[i][j].setActionCommand(String.valueOf(n++));//动作命令,并非按钮上面的字,区别是哪个按钮 button[i][j].setFont(font); button[i][j].addActionListener(this);//添加监听 p1.add(button[i][j]); } add(p1,BorderLayout.CENTER);//面板添加到窗口当中 JPanel p2 =new JPanel(); promptLabel =new JLabel(); promptLabel.setForeground(Color.RED); promptLabel.setText("提示:单击某一个按钮,作为马的起始位置"); p2.add(promptLabel); add(p2,BorderLayout.SOUTH); setSize(300,200); this.setLocationRelativeTo(null); setVisible(true); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String buttonKey =e.getActionCommand(); int intKey = Integer.parseInt(buttonKey); int row =intKey /boardSize +1; int col= intKey%boardSize; button[row][col].setText("1"); if(DFS(row,col)) promptLabel.setText("提示:遍历成功"); else promptLabel.setText("提示:遍历失败"); } static boolean DFS(int x,int y) { //经过了所有的空位置 if(count == boardSize*boardSize) return true; //遍历从当前点走日字能够到达的8个点 for(int dir =0;dir<8;dir++) { //走日字到达下一个点 int next_x =x+dx[dir]; int next_y =y+dy[dir]; //超出边界 if(next_x<1 || next_x > boardSize || next_y<1 || next_y>boardSize) continue; if(!button[next_x][next_y].getText().equals("")) continue; //访问过的点计数 count++; button[next_x][next_y].setText(String.valueOf(count)); if(DFS(next_x,next_y)) return true; //从日字的一个对角线出发不能到达所有的位置 count--;//后退一步 button[next_x][next_y].setText(""); } return false; } }
(3)有蹩脚
5×5
package cn.test.termtest.uglynumber; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; public class TestChess extends JFrame implements ActionListener { static JButton button[][]; //棋盘的按钮 static int boardSize; //棋盘大小(行数/列数) static int count; //落子的顺序 static int obstacleNum; JLabel promptLabel =new JLabel(); //提示信息标签 //马走日子的偏坐标 static int dx[] = {1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1}; static int dy[] = {2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1,1,2}; public static void main(String[] args) { boardSize =5; TestChess testChess =new TestChess(); } public TestChess() { count =1; //定义font为微软雅黑,普通,12号 Font font =new Font("宋体",Font.PLAIN,12); this.setTitle("象棋中马的遍历"); JPanel p1 =new JPanel(); //正式面板 p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(boardSize,boardSize)); //GridLayout为网格布局 button =new JButton[boardSize+1][boardSize+1]; int n=1; for(int i=1;i<=boardSize;i++) for(int j=1;j<=boardSize;j++) { button[i][j]=new JButton(); button[i][j].setActionCommand(String.valueOf(n++));//动作命令,并非按钮上面的字,区别是哪个按钮 button[i][j].setFont(font); button[i][j].addActionListener(this);//添加监听 p1.add(button[i][j]); } button[1][1].setText("卒"); button[5][1].setText("卒"); obstacleNum=2; add(p1,BorderLayout.CENTER);//面板添加到窗口当中 JPanel p2 =new JPanel(); promptLabel =new JLabel(); promptLabel.setForeground(Color.RED); promptLabel.setText("提示:单击某一个按钮,作为马的起始位置"); p2.add(promptLabel); add(p2,BorderLayout.SOUTH); setSize(300,200); this.setLocationRelativeTo(null); setVisible(true); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String buttonKey =e.getActionCommand(); int intKey = Integer.parseInt(buttonKey); int row =intKey /boardSize +1; int col= intKey%boardSize; button[row][col].setText("1"); if(DFS(row,col)) promptLabel.setText("提示:遍历成功"); else promptLabel.setText("提示:遍历失败"); } static boolean DFS(int x,int y) { //经过了所有的空位置 if(count == boardSize*boardSize-obstacleNum) return true; //遍历从当前点走日字能够到达的8个点 for(int dir =0;dir<8;dir++) { //走日字到达下一个点 int next_x =x+dx[dir]; int next_y =y+dy[dir]; //超出边界 if(next_x<1 || next_x > boardSize || next_y<1 || next_y>boardSize) continue; if(!button[next_x][next_y].getText().equals("")) continue; //访问过的点计数 count++; button[next_x][next_y].setText(String.valueOf(count)); if(DFS(next_x,next_y)) return true; //从日字的一个对角线出发不能到达所有的位置 count--;//后退一步 button[next_x][next_y].setText(""); } return false; } }
5、运行结果:
(1)
(2)
(3)
